The modern world is unthinkable without steel. This is a metal alloy of iron, carbon, and other components. Their ratio determines the brand, characteristics of the final material, and its application. Steel is supplied to production in the form of rolled products—sheets of a given thickness, produced by hot or cold methods. Technology directly affects the characteristics of the resulting material.
It is impossible to say which sheet is better, hot-rolled or cold-rolled. The answer depends on the requirements of the specific area for which the rental with the required parameters is selected.
Properties of hot rolled steel
Hot rolled sheets have a rough surface. The finished sheet has rounded, imprecise corners. If they are trimmed, the material is marked with the index O; if it is supplied without trimming, it receives the index HO. The thickness of this type of steel is uneven and is characterized by a high percentage of scale content.
Assortment of hot-smoked sheets according to GOST
Accepted standards divide hot-rolled sheet metal into types according to thickness and area of use. Currently there are GOST standards with numbers:
- 14637-89, which describes the parameters of hot-rolled thick sheets with a thickness of 4-160 mm of normal quality, produced from carbon steels;
- 16523-97, which determines the properties of thin hot-rolled steel up to 3.9 mm;
- 5520-79, which normalizes the production of hot-rolled plate products with a thickness of 4-160 mm, the basis of which is carbon, low-alloy, alloy steel, used for the manufacture of boiler equipment and industrial vessels;
- 5521-93, describing sheets of normal and increased strength with a thickness of 4-60 mm, produced from steel with an increased proportion of manganese for use in shipbuilding;
- 6713-91, which specifies the parameters of rolled plates of low-alloy grades for the construction of bridges (conventional and northern);
- R 55374-2012, responsible for bridge structures made of alloy steels.
Hot rolled sheet dimensions
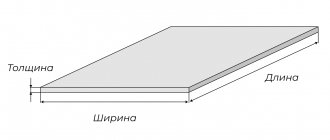
Hot rolled steel is cut into sheets according to dimensions regulated by GOST 19903-2015. This standard specifies a thickness of 0.4-160 mm. It takes ordinary unalloyed or low-alloy steel as a basis. If the metal is wrapped in rolls, its thickness should be 1.2-12 mm.
The edge may or may not be trimmed. Accuracy is described as improved or normal for thicknesses up to 12 mm. Flatness options: normal, improved, high, extra high.
Rolls are formed from a single piece of fabric or two welded pieces. Acceptable fragment lengths are no less than 1:5. Other parameters for the lengths and number of pieces are discussed with the customer.
Sheet width - 0.5-3.8 m, length - 7.1-12 m.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of the hot rolled method:
| Disadvantages of the hot rolled method:
|
Properties of cold rolled steel
The basis for the production of cold-rolled sheets is hot-rolled sheets. They undergo additional processing to improve their characteristics:
- make edges, dimensions, thickness clearer;
- get rid of impurities - scale;
- give the surface smoothness, uniform color, and a characteristic metallic sheen;
- add rigidity to the material.
Unlike hot-rolled steel sheet, cold-rolled metal is thinner: thickness varies from 0.35 mm to 5 mm.
This material requires additional anti-corrosion treatment. It is usually coated with zinc, chrome, aluminum or other elements to prevent accelerated rusting.
Assortment of cold-rolled sheets according to GOST
Cold-rolled sheets are standardized by GOST numbers:
- 9045-93 - rolled products for cold stamping or production of car bodies. Upon request, the surface receives an increased, high or especially high category.
- 16523-97 - standards for cold-rolled sheets made of black carbon steel. The standard describes three types of surface finishing.
- 19904-90 - production of rolled products with a thickness of 0.35-5 mm. The document specifies the width of the rolled products produced in the form of cards equal to 500-2350 mm, and the length - 1-6 m. The dimensions of the rolls are not limited, only the thickness is standardized - up to 3.5 mm.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of the cold rolled method:
| Disadvantages of the cold rolled method:
|
This leads to the fact that the choice between cold-rolled sheet and hot-rolled sheet is determined by the area of application of the metal products.
Brief information
Cold rolled sheet (C/C) is a flat metal product that looks like long strips. C/C products are usually made of steel alloys, but sheets of other metals (aluminum, copper, duralumin alloys, brass) are also found. Cold sheets are produced in metallurgical shops by pressing hot-rolled sheets. C/C sheets are used for the production of car frames, cans and boxes, metal utensils, and corrugated sheets.
Cold steel is produced in large, long rolls, and to obtain an individual rectangle, the sheet metal is cut into individual pieces using industrial shears. Most cold-rolled strips have a small thickness - from 0.35 to 2 millimeters. Although there are also thick products, the thickness of which can reach up to 5 millimeters. The width of cold steel sheets usually ranges from 1.5 to 5 meters, although wider products are also available. C/C products, if necessary, can undergo additional processing - heating, tempering, galvanizing, mechanical deformation, applying a protective layer, painting.
Differences in the properties of hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel sheets
The main difference between cold-rolled sheet and hot-rolled sheet is quality, thickness and price.
Theoretically, the minimum thickness of hot-rolled metal is 0.4 mm, but in practice it is rarely less than 1.2 mm. The maximum value reaches 20 cm. Low quality is due to the use of inexpensive steel grades, which is reflected in the price.
Unlike hot-rolled sheets, cold-rolled sheets can be rolled out to the thinnest foil. In construction and industry, materials from 0.35 mm are used. The upper limit here is 5 mm. This type of metal is stronger and stiffer, but it is more vulnerable to corrosion, so it is galvanized or protected in other ways. Since achieving these properties requires additional production steps, the price of cold rolled steel is higher.
| Options | Cold rolled sheet | Hot rolled sheet |
| GOST | 19903-2015 (19903-74) | 19904-90 |
| Production temperature | from 1150С - 1200С to 900С - 950С | 450С – 550С |
| Thickness (mm) | 0,35–5 | 0,4–160 |
| Number of thickness classes (mm) | 3 (+/- 0.02 to +/- 0.25) | 2 (+/- 0.05 to +3.1 and -4.2) |
| Width (mm) | 500 – 2 350 | 500 – 2 200 |
| Number of width classes (mm) | 3 (+2 to +10) | 1 (+6 to +75) |
| Length (mm) | 1 000 – 6 000 | 710 – 12 000 |
| Number of accuracy classes by length | 3 (+2 to +25) | 1 (+10 to +75) |
Features of the material
- High strength. Cold-rolled sheet metal undergoes a number of technological treatments that eliminate internal tension in the alloy and improve the strength of the material.
- Small thickness. The C/C product is produced by repeated pressing, which makes it possible to obtain a product of small thickness (less than 1 millimeter).
- Nice view. The surface of cold rolled products is clean (no scale, burning, or traces of thermal effects). Therefore, the material can be used for aesthetic finishing of surfaces or products.
- Low risk of rust formation. At the end of processing of C/C products, the material is usually heated for recrystallization, which minimizes the risk of corrosion during long-term use.
Please note that in addition to cold-rolled sheets, there are also hot-rolled sheets. These materials have much in common, and C/C products are produced from hot-rolled sheets using pressing.
The main differences between cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel
| Category | Cold rolled steel | Hot rolled steel |
| Production method | Rolling hot-rolled steel using industrial presses without heating | Heating steel blanks and then rolling them using a press |
| Strength | Very high | Medium or high |
| View | Nice look, has a metallic shine | Mediocre look, lack of shine |
| Complexity of production | High | Low or medium |
| Sheet thickness | From 0.35 to 5 millimeters | From 2 to 50 millimeters |
| Areas of application | Car frames, corrugated sheets, tableware, structural elements, finishing structures, pipe production | Flights of stairs, elements of suspended structures, production of underground pipes, construction |
Differences in steel sheet production
The production of hot-rolled and cold-rolled sheets follows similar technologies. The difference lies in the number of production processes. First, raw materials are sent to the furnace in the form of ingots or slabs (slab-shaped pieces), where they are melted at a temperature of 900-1200 degrees Celsius (heating depends on the chemical composition, dimensions of the slabs, and steel grade). Then the scale is loosened and the oxide is removed. The next steps are in order:
- the hot workpiece is crimped on all sides so that its dimensions meet the standards;
- the leveled ingot is sent to the roughing stand and then to the finishing stand, where it is compressed by rotating shafts, the distance between which determines the thickness of the rolled product;
- metal strips obtained after processing by rollers are rolled or cut;
- At the final stage, the workpieces undergo heat treatment in furnaces - they are hardened, fired, and cleaned.
At this stage, hot-rolled steel is ready for tempering, sale or use in further production.
The cold rolled sheet receives additional processing. It is made from hot-rolled steel, which is cleaned of remaining scale mechanically or chemically. Often both methods are combined.
Mechanical cleaning is carried out by grinding rolled metal with spherical metal particles supplied by an air stream. This removes various contaminants carried away with the air.
Chemical cleaning involves immersing rolled steel in a bath with a 25% solution of hydrochloric acid, which corrodes the smallest contaminants, giving the surface of the material smoothness and cleanliness.
After processing to obtain cold rolled steel, the material goes through the following processes:
- edge trimming;
- oiling before rolling;
- crimping with rollers to the required thickness;
- firing at temperatures up to 730 degrees Celsius to increase strength;
- cooling;
- compression on the temper mill to 3% to increase hardness;
- if necessary, final trimming of the edges.
Additionally, rolled products can be galvanized.
Main stages of cold rolling
The source material (roll) supplied to the cold rolling mill may have scale on the surface, which must be removed in the most convenient way:
- using shot blasting;
- dissolving oxides with acids - hydrochloric or sulfuric; hydrochloric acid is more effective;
- by combining the two methods mentioned above.
After pre-treatment, the hot-rolled product is supplied to the cold rolling mill, which includes:
- four or five stands in which compression is carried out to the specified parameters;
- winder;
- scissors;
- loop-forming mechanism and other devices.
After the cold rolling operation, a hardened layer is formed on the surface of the sheet, which has high strength and low ductility. To eliminate work hardening, heat treatment is used - annealing at a temperature of +700°C - which allows the plasticity characteristics to be restored. The equipment used is bell-type or broaching furnaces.
One of the final operations is training, which is a small compression that provides the following positive aspects:
- increasing the strength of steel;
- reduction of strip waviness;
- improvement of surface quality;
- slight decrease in yield strength;
- after training, shear lines do not appear, which necessarily appear during stamping.
Areas of use of hot-rolled and cold-rolled metal
| Hot-roll sheet | Cotton sheet |
Hot rolled steel sheets are used in:
This type of metal products is necessary where steel is needed, but there is no increased demand for aesthetics. For example, the construction of bridges, boilers, furnaces, structures with bolted or welded connections. | Cold rolled sheets are needed for:
|
Hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel serves as the basis for the profiles of metal frame structures, which we use for the installation of prefabricated tent hangars. Depending on the project and loads on the structure, we offer 3 options for metal frames. Read more about this at the link.
Practical use
Cold-rolled sheets, individual sheets and strips are widely used in various industries. Products of this type do not require special care and do not rust if stored properly. Another major advantage is a pleasant appearance (hot rolled products lack this advantage due to technological processing features). Producers of cold steel are the People's Republic of China, Russia, USA, Germany, France, Japan.
Areas of application
- Cold-rolled sheets with a low carbon content are used in mechanical engineering (therefore often called auto sheets). A metal car frame, as well as various parts (motor elements, tank, moving parts), are made from this material on robotic conveyor lines. For the needs of the automotive industry, they are usually smelted in strips that have an average thickness (from 1 to 2.5 millimeters).
- Cold rolled steel is also used to produce tin. For production, the original sheet is cold deformed using heavy-duty rolling presses, which help produce material less than 0.5 millimeters thick. For convenience, the resulting tin is cut with industrial scissors into small strips, the width of which is up to 1.5 meters. The resulting strips can be used for decorative purposes, as well as for the production of tin cans, metal fences, and partitions.
- Cold steel can also be used to produce a material called decapir, which is used to make homemade enamel cookware. To make decapir, tin is annealed in high-temperature furnaces to make the material more ductile. After annealing, the dishes are formed using presses. During annealing, metal scale and various debris are formed on the surface of the alloy. To remove harmful substances, decapir is cleaned with acids using the etching method in baths. After cooling, we receive high-quality metal utensils without scale, which can be used for cooking or storing any products.
- Cold-rolled steel sheets are also used for the production of corrugated sheets. This material is a thin metal sheet on which an additional zinc layer is applied. Corrugated sheets are used to create fences or fences, as well as for exterior decoration of houses (roofs, external walls, partitions, inclined surfaces). The zinc layer acts as a protective element that prevents contact of the material with the external environment. After all, the profiled sheet, due to the nature of its operation, will often come into contact with precipitation, and zinc will prevent the formation of rust and harmful compounds. If necessary, the corrugated sheet can be made with additional stiffening ribs, which will protect the material from mechanical damage.