In a chainsaw, all elements are equally important. Only in case of high-quality execution is comfortable productive work possible, the result of which can satisfy the user. The good cutting capabilities of the tool can be negated by an unadjusted carburetor or an incorrectly prepared gasoline-oil mixture. However, there is a unit without which even a motor running like a clock will not allow you to make a correct, smooth and fast cut. This is a chainsaw chain.
With an incorrectly selected or heavily worn chain, even small amounts of work becomes a pain. Well, professionals generally need to keep the saw set in perfect condition - after all, the speed of work mainly depends on it.
Chain size
This parameter always depends on the size of the tire installed on the unit.
If you accidentally purchased a chain that is smaller than your tire, you will not be able to fit it. If this element is larger than the tire size, you will not be able to tension it. Both options prevent the use of inappropriate chain sizes. They are usually indicated in inches and have the following values: 10″, 12″, 13″, 14″, 15″, 16″, 18″ and above. The length of the chain is determined by the number of links. Links refer to the connecting links that fit into the groove of the bar, rather than the cutting teeth. When purchasing, you can indicate to the seller either the length of the part in inches or the number of links included in its composition. Some manufacturers, instead of length, indicate the number of links in the saw element. As a rule, this number does not depend in any way on the thickness of the tail, the pitch and the height of the profile. For example, a low-profile chain with a drive link thickness of 1.3 mm may consist of 72 links, 56 links, or some other number.
Some important points when choosing chains or chainsaws
There are other indicators that influence the performance of the tool and the specifics of the work.
Values that are recommended to be taken into account:
- geometry of the cutting tooth (profile);
- number of cutting links;
- type of sharpening of the cutting edge of the link.
Saw chain structure.
There are two types of cutting profile: chisel and chipper. The first option has a straight working surface and is more productive. The second type has a sickle shape and reduced productivity. A chipper chain is easier to maintain because it is easier to sharpen and strict adherence to sharpening angles is not required. Chisel options are most often used in 3/8 and 0.404” pitches.
The number of cutting teeth is always determined by their ratio to the number of guides included in the saw bar. That is, the link with the cutting part has two guide links. If such a combination is not observed, this means that the chain is of questionable manufacture.
The type of sharpening of cutting profiles is regulated by the type of future work. Typically, a classic chainsaw is used for cross cuts of wood and extremely rarely for longitudinal cuts. In rare cases, you come across chains with cutting links oriented for longitudinal cuts.
How to choose
The selection issue is relevant for inexperienced users. Professionals know almost everything about the headset and know how to choose what they need. For this reason, our advice will be aimed specifically at amateurs, and not at pros. So let's get started.
In order to choose correctly you need:
- Know the characteristics of the chainsaw, namely the pitch and length of the bar. When choosing, you should not rely on the name and model of the chainsaw, because... One chainsaw can be equipped with tires of different lengths and seat widths.
- Decide in advance on the volume and type of work for which you plan to use it. If you cut across, we choose chisel ones; if we cut along, we choose chipper ones.
Important! You will have to sharpen it for a longitudinal cut (10 0) yourself or at a service center. A headset sharpened for longitudinal cutting is rarely found on sale.
Separately, it is necessary to mention the choice of the Shtil headset. If you are planning to buy a chain from this manufacturer (they are considered the highest quality today), then to make your choice it is better to use a special search form, which can be found on the company’s website.
By entering the chainsaw data into the search form, the program will automatically select and offer you suitable options. The service is convenient, but has one big drawback: selection is carried out only according to Shtil chainsaw models. In order to select a chain for saws of other brands, you will have to arm yourself with a catalog.
Chain design
Since there are specific terms used when discussing saw blades, it is important to understand what is meant. It is better to place the removed chain in front of you on the table and workbench and look at it carefully.
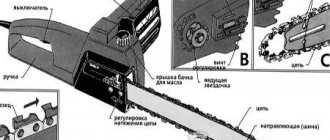
This element contains three types of links:
- Cutting - it is thanks to them that the saws bite into the wood. They are equipped with a cutting edge. There are right and left.
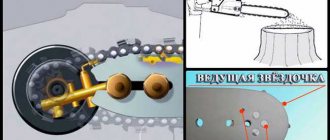
- Drivers - they engage with the teeth of the guide and drive sprockets, due to which the chain moves along the tire. The tooth on the inside of the link is called the shank.
- Connecting - with their help, all elements of the chain form one whole. They have no protruding parts, but only holes for rivets.
Causes of uneven cuts
In amateur chainsaw practice, many questions arise related to the cutting going in one direction or another. This malfunction creates significant inconvenience when using a chainsaw in wood construction technologies.
The reason for this phenomenon is the deformation of the tire, which is hardly noticeable to the eye, improper sharpening or uneven wear of the cutting links of the chain. If professional adjustment of the chain does not give a positive result, the problem is eliminated by replacing the entire set.
How many links should there be in a bicycle chain?
I would like to dwell on one point. You can often hear the question: “How many links should there be in a bicycle chain?”
It is impossible to answer this unequivocally. There should be as many of them as needed for normal driving.
First of all, you need to clearly define what is meant by the term chain link.
As a reminder, all bicycle chains have the same full link size of one inch (25.4 mm) and therefore one half link of 1/2″ or 12.7 mm. And there are also Halflink chains (in English Half-link, where half is half, link is a link), in which the link length is 1/2″ (12.7 mm). This is discussed in the article on the design of a bicycle chain.
Therefore, the length of the chain depends on the type of bicycle frame, the size of the stays, etc. Typically road or hybrid bikes have 114 to 116 half links or slightly less. Mountain bikes have smaller frames and typically have 106 to 108 half-link chains or slightly larger. Well, how to correctly determine the chain length for your specific bicycle was described above.
If you need to know exactly how many links there are in the chain of your bicycle, there are two ways: simply count them or measure the length of the chain with a tape measure (centimeter) and divide this number expressed in mm by 25.4 - the length of one link (or 12.7 for a Halflink chain).
Sequence of links
The length of a chain refers to the number of links it consists of. The parameters of your circuit must be indicated in the documents attached to the construction equipment.
The main part of the load falls on this element of the chainsaw. To measure the thickness of the connecting elements of the chain included in the tire, use a caliper.
Let's list the standard indicators:
- 1.1-1.3 mm - more often found in products for infrequent home use and gentle operation. This tail thickness is suitable for light loads.
- 1.5mm is the most common option found in household saws, but is not suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- 1.6-2.0 mm is an option for complex work. This width of tails is found in professional saws, the elements of which are made of special steel.
Chain cutting elements are divided into two types: chisel and chipper. Chisel links are similar in shape to the number 7. These links provide fast and high-quality work.
However, they also have negative sides: firstly, the links are sensitive to dust, dirt and other small debris, secondly, they are not so easy to sharpen, and thirdly, working with such a saw requires great precision.
- Standard - 2 driving links, 1 cutting link;
- With semi-pass - 2 links 1 connecting;
- With a pass - one additional link is installed between each cutting blade.
The length of the chain depends entirely on the characteristics of the chainsaw itself: dimensions, sprocket sizes and power. With a standardized tension, the length for a particular chainsaw is determined and indicated in the passport.
Another question is the number of links, i.e. number of cutting teeth at this length. This parameter depends entirely on the pitch of the links. Thus, the problem of how to select a chain taking into account the length is solved in complex, taking into account the pitch of the links. Chainsaw chains how to measure length ask a professional to help determine the length. In general, increasing the length requires an increase in the power of the chainsaw, but increases productivity.
In any standard high-quality chain, all cutting links have two tails. Typically, cutting teeth are made from durable materials and determine the overall price in almost everything. Despite the higher price, it is better to choose a chain based on its properties. At the same time, you should consider options that reduce the cost of the tool, especially if the chainsaw is used occasionally.
Additionally: Which chain is best for a chainsaw: review, tips for choosing. Chainsaw chain with pobedit tips
In order to reduce the cost of chains, they can be made with omission or semi-omission of cutting links. When semi-missing, additional connecting links are installed in every 2nd pair of cutting teeth. When skipping, additional links are installed after each cutting tooth. In a standard chain, the number of cutting teeth is 50% of all tails, in a half-skip - 40% and in a skip - 37.5%. Naturally, the load on the cutting teeth increases, and they fail much more quickly.
Therefore, when purchasing a new copy, you should only visually check the quality of production of the cutting parts and their sharpening. But to use the tool when processing particularly hard, frozen or very dirty materials, it becomes necessary to harden the teeth. For such purposes, options are offered on the teeth of which special carbide brazing is made. They have increased wear resistance. The presence of soldering marks is marked on the surface of each cutting tooth.
Shank parameters
Another important parameter for choosing a chain is the thickness of the tail section. The most commonly used thicknesses are from 1.1 to 2.6 mm.
Thin chains and corresponding bars are popular in low-power household chainsaw models. They provide good cutting accuracy and surface quality. For many short-grain woods, the surface does not even need finishing.
More powerful machines are designed for 1.3-2 mm shanks. They provide a reasonable balance between performance and accuracy. Such tools usually have a large resource.
The width of 2.6 mm is more typical for professional models with high cutting speeds. Chainsaws used in logging and cutting trunks in a logging area have a width of up to 4 mm.
Preparing a fuel mixture for a chain saw.
Since the majority of chain saws available to consumers are equipped with two-stroke engines that do not provide separate lubrication of rubbing parts, it is very important to prepare the correct fuel mixture during break-in. It is prepared from gasoline and two-stroke engine oil in a certain proportion recommended by the chainsaw manufacturer
What gasoline should I use for the fuel mixture?
The basis is gasoline with an octane rating of at least 90. For Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan and other CIS countries, the optimal fuel option is AI-92. Avoid using questionable fuels, as well as using any additives that increase the octane number. Over time, additives lose their properties, and gasoline becomes of low quality.
Using fuel with a low octane number when running in and operating a chainsaw causes uneven engine operation and knocking. At the same time, there is an increase in engine temperature and an increase in the load on the main bearings. Imaginary savings most often lead to failure of the cylinder-piston group, requiring significant funds to restore it.
New chainsaw owners often have a question about what kind of gasoline to pour into the tool tank: leaded or unleaded? Leaded fuel is used to start an engine without a catalyst. If your saw has a catalyst (green gas tank cap), then use unleaded fuel.
What oil should I use in the fuel mixture, and in what proportions?
Two-stroke engine oil is used both for break-in and for continuous operation of the chainsaw. If you don’t want to take risks and experiment, then purchase the lubricant recommended by the tool manufacturers. As a rule, large companies produce fuel and lubricants for them to order. This allows the manufacturer of chain saws and other gas-powered tools to guarantee proper starting and trouble-free operation of their products.
Since branded oils for chainsaws Husqvarna, Stihl, Partner, Oregon, Jonsered are bottled from the same barrel, you can break in the tool with any of the following
In this case, it is very important to take into account the recommendations both in the instructions for oils and the recommendations of chain saw manufacturers. When using branded fuels and lubricants, when preparing the fuel mixture, follow the operating instructions for the gas-powered tool
| Recommended proportions of fuels and lubricants when preparing fuel | |||
| Break-in chainsaw | Proportion | Gasoline, (liters) | Oil, (liters) |
| Husqvarna up to 1.5 kW | 1:40 | 1 | 0,025 |
| Husqvarna over 1.5 kW | 1:50 | 1 | 0,020 |
| Stihl up to 1.5 kW | 1:40 | 1 | 0,025 |
| Stihl over 1.5 kW | 1:50 | 1 | 0,020 |
| Partner | 1:40 | 1 | 0,025 |
| Partner | 1:33 | 1 | 0,030 |
If branded oils are not available, you can break in a new chainsaw using third-party lubricants of the JASOFB or ISOEGB class. According to the instructions, the ratio of components is taken at the rate of 1:33. At the same time, the tool manufacturer does not recommend using four-stroke motor oils or two-stroke motor oils for water-cooled outboard engines, labeled as TCW.
The fuel mixture for a chainsaw to be run in should be prepared in a clean container intended for storing fuel and lubricants.
- Pour half the required gasoline into the container;
- Add required amount of oil;
- Gently mix the ingredients;
- Pour in the remaining gasoline and stir.
Design of traditional bicycle chains
The two inner plates in a traditional bicycle chain are connected to each other by a glass (bushing) - it is similar to a hollow axle. If you disassemble a link of such a chain, you can see the flared edge of the glass outside the inner plates.
When assembled, the outer plates cover the glass - its outer part is also not visible, it is covered by a roller. The rivets that connect the chain plates pass inside the glasses, the rollers are outside. In this case, the inner and outer sides of the glass are subject to wear.
Chains without glasses
In such bicycle chains, the internal plates are not flat. Instead of the usual hole for pressing the glass, each hole in the inner plate has an annular protrusion half the internal width of the chain. The edge of this protrusion is chamfered, allowing the chain to move more smoothly when misaligned than a traditional bicycle chain. Perhaps because of this, switching is also easier. Due to the fact that the “glass” in a chain without a glass consists of two halves that are not directly connected to each other, such a chain bends better in the transverse direction - there is a small gap between the halves of the “glass”.
Lubrication points
I believe that the main reason for the increased life of chains without cups is better lubrication of the chain in its vulnerable areas.
There are three points where the lubricant should be. The first and most important point is where the rivets rub against the inner plates as the chain links rotate relative to each other. The second is the inner surface of the roller; lubricant in this place ensures free rotation of the roller when it hits the teeth and when it comes off them.
When the roller does not rotate, it slides along the teeth and causes increased wear on the sprockets. The third point is where the outer and inner plates meet, although the point of contact is much less loaded than other places.
In traditional bicycle chains, in order for the oil to get to the rivet, it needs to pass inside the glass between the inner and outer plates. If you use a spray, the oil penetrates into the link from both sides at the same time. Air remaining inside the glass can clog the inlet for further lubrication. In addition, road dust gets into the open space between the inner and outer plates and heavily contaminates the chain. Therefore, if oil does get inside the glass, it will already be contaminated.
In chains without cups, lubricant gets in differently. When oil hits the roller, it seeps in from both sides and displaces air through the gap between the two halves of the glass. Having dripped oil on such a chain only onto the roller, it gets onto the inner surface of the roller and onto the rivet, and along it to the gaps between the plates. Since the side plates are lubricated from the inside, the flow of lubricant washes dirt out. The chain rollers clean themselves when they come into contact with the sprocket teeth.
Sheldon Brown
More reading on this topic:
Bicycle chain links sticking. It happens that when riding a bicycle, you regularly feel that the pedals are skipping or jerking every three or four revolutions. This suggests that...
Bicycle chain slipping. Chain slippage causes one of two unrelated phenomena - direct slippage and spontaneous gear shifting. The main thing to solve the problem is to determine what exactly happens from the two cases...
Bicycle chain wear. We take a section of a chain with the number of links in it - 20. Multiplying the number of links by the length of a standard link of 12.7 mm, we obtain the size of a section of a new chain of 20 links equal to 254 mm. We take a ruler and measure...
Bicycle block chain. In the late 70s, blockchains finally disappeared from sale. These were replaced by modern 1/2" pitch, 3/32" wide chains that were used with derailleurs. But track cyclists still preferred to use wider chains...
Recommendations for extending service life
The approximate service life of a branded tire is equal to the total service life of 3 high-quality saw chains; the drive sprocket varies depending on its condition. Experts recommend using a set of several circuits.
This method allows you to reduce the loss of working time, which is spent on periodic sharpening of chains, as well as optimize the wear of the saw mechanism as a whole. Accelerated tire wear is a consequence of unqualified maintenance of the chainsaw and its illiterate operation.
The main factors for early tire failure:
- excessive chain tension or discrepancy between its pitch and the characteristics of the drive sprocket crown, which initiates the rapid development of the groove and shanks;
- applying significant force when sawing hard or frozen wood;
- the tire heats up and wears out intensively due to lack of lubricant supply, due to a malfunction or incorrect adjustment of the standard oil pump;
- saving money on the use of low-quality chain oil or oil surrogates such as waste.
Forced consumption of the saw set resource occurs when soil or sand gets into it, or when a new chain operates on a worn drive sprocket.
Main characteristics
Like all tools and garden equipment associated with direct contact of the cutting element with the material, the chainsaw chain requires constant sharpening, lubrication and replacement
When purchasing a new consumable part, you should pay attention to compatibility. In order not to miscalculate or mislead the buyer, manufacturers of global brands use universally established norms for marking the technical parameters of chainsaw chains. The main parameters include:
The main parameters include:
- angles of sharpening the tooth of the cutting element of the chain;
- shape (geometry) of cutting teeth;
- height of the teeth relative to the cut stop (profile).
In addition to the parameters of the cutting teeth, chains have different sizes, thickness and length. They differ in:
- distance between cutting elements (chain pitch);
- total chain length (number of links);
- the thickness of the guide tails relative to the chainsaw bar.
Next, we will consider in detail all the parameters on which the choice of circuit depends.
Popular models
The most popular foreign manufacturers of chainsaws and their components are Husqvarna and Shtil. The Russian chainsaw market is represented by the most popular Ural model.
Husqvarna chainsaw bars come in many varieties, allowing them to be used on a variety of saw models. There are many positive reviews for the company's products. Particularly noted is the durability of the tires, the smooth running of the chain and the ease of oil supply.
The best alternative when purchasing are Oregon or Husqvarna tires - they are made of higher quality materials and therefore last much longer than their cheap counterparts.
There are several types of chains
Chain for single-speed bicycles (Single-speed)
As the name implies, it is used on single-speed city bicycles without gear shifting, on children's and teenage bicycles, as well as on bicycles with a planetary hub. These bikes have a single sprocket on the rear wheel, and gear shifting occurs inside the rear hub.
With proper use, a single-speed chain practically does not wear out to the point of complete “death” and “lives” as long as the bicycle itself. This is because the chain on a single-speed bicycle is a straight line from the front to the rear sprocket and does not experience the lateral bending stresses of multi-speed bicycles.
They are made from thicker and, accordingly, stronger and stiffer plates, and are subjected to thermal and chemical treatment to increase wear resistance.
Please note that the teeth of single-speed sprockets grip the chain link to the full height of the roller and hold it more tightly. The load on the roller is uniform and constant. This is one of the reasons why they practically do not stretch, unlike multi-speed bicycle chains
This is one of the reasons why they have virtually no stretch, unlike multi-speed bicycle chains.
Single-speed chain width, measured as the distance between the inner link plates, is from 8.7 to 11.0 mm.
By the way, the efficiency of pedaling on a straight chain is higher than on a skewed multi-speed chain - there is no energy loss to overcome the friction that occurs when it bends.
Chain for multi-speed bicycles
Multi-speed bicycle chain is designed for bicycles with gear shifting. It differs from single-speed in the presence of a gap between the link plates. It allows the chain to bend sideways (see picture above). They are also usually smaller in width, since the thickness of the cassette chainrings on shift-shift bikes is smaller than on single-speed models.
Please note that the teeth of the cassette sprockets and front sprockets on multi-speed bicycles do not grip the chain link to the full height of the roller, but approximately half. Their teeth are lower, since the chain jumps from one sprocket to another when changing gears. Because of this, the load on the chain rollers is not as uniform as on single-speed models
Because of this, the load on the chain rollers is not as uniform as on single-speed models.
In the article “What are the gears (speeds) of a bicycle and how to change them”, recommended and not recommended options for switching gears have already been mentioned. They are caused by severe misalignment of the chain, which leads to rapid wear not only of the chain itself, but also of the rear (on the cassette) and front (in the system) sprockets. Let's look at these options again:
The chain of a multi-speed bicycle is almost always misaligned, which reduces pedaling efficiency and leads to wear on the transmission elements: chain, front and rear sprockets.
Just like the previous type, they consist of internal and external links.
Lightweight bicycle chains.
They have hollow pins and perforations in the plates.
They are often 20-25 percent lighter than their standard counterparts, but are also more expensive and less durable. Used by cyclists who fight for every gram of excess weight. These are mostly racers.
Due to their design features, such bicycle chains stretch more and are generally not as strong as the types discussed above.
4. Half-link bicycle chains
Chains with one repeating link are called Half-link chains (in English Half-link, where half is half, link is link).
The peculiarity here is that they do not have internal and external links, and all links are the same. The length of the link is 1/2″ (12.7 mm). They are easier to adjust to the desired length, because... You can shorten one link at a time. However, operating experience shows that due to the design features, they tear more often and stretch more strongly.
The dangers of buying cheap Chinese tires
The materials stated that the tire is one of the most important parts of the tool. If this part fails, then using the tool is extremely dangerous. At any moment, the chain can jump off the guide and cause serious consequences. It’s a different matter when a new tire has just been purchased and installed on the tool. Its disadvantage is that it was not purchased in a company store, but on the market under an unknown brand and at a very low price. Finding a cheap tire for a chainsaw today is not difficult, but is it worth buying such a headset? Of course not, and here's what it can lead to.
- First of all, non-original products wear out very quickly, which leads to the need for frequent replacement
- At the same time as the guide, the chain wears out and must also be replaced.
- During the operation of a fake guide, a phenomenon such as wear of one side part is often observed, which ultimately leads to the inability to make an even or straight cut.
- Violation of the integrity of a part is the most difficult and dangerous case, since breaking the tire will cause a break in the chain rotating at a speed of over 10,000 rpm
That is why manufacturers recommend not saving on the purchase of a saw set for a chainsaw, and buying only branded and high-quality tires and chains from trusted sellers. After all, a person’s life depends on the quality of these parts.
Preparatory work
In the package version of making a knife from a chain, the product is suitable for various mechanisms: a motorcycle, a car, a bicycle or a chainsaw. Having decided on the manufacturing method, you need to prepare the tools and materials:
- an anvil, two hammers - large and small;
- oven or forge;
- vices, angle grinders with discs for various purposes;
- tetraboric acid (borax);
- Hydraulic Press;
- grinding machine;
- welding machine, steel chain;
- high carbon steel plate;
- motor oil and a container of water;
- drill, wooden block, epoxy glue;
- masking tape, sandpaper of different grains;
- Handle impregnation made from natural oils.
Knife from a chain. Tools and materials are professional in nature. From the very beginning it was stated that this was a job for experienced craftsmen. Beginners should not try this material. You need to start experimenting with simple preparations.
Instructions for making a knife from a chain
A distinctive feature of the batch forging process is the work with several metal plates. Having everything you need, you need to start the initial forging of the blade:
- Using a cutting wheel on an angle grinder, cut the chain into several pieces of equal length. Having folded them into a single form, using welding, we “grab” them to obtain a solid workpiece.
- A rod is welded to the resulting rectangle for ease of holding. Having warmed up the oven, place the workpiece in it and heat it to 1100-1200 °C.
- Once the metal has reached a bright red hue, remove it and sprinkle it generously with borax. This will allow you to more reliably fasten the pieces of the chain together and get rid of voids in the links. Place in the oven for further heating.
- We take it out again, sprinkle it with borax and quickly move to the press. With its help, we gradually compress the workpiece from all sides. We monitor the temperature; when the part has cooled down, go back into the oven. The process performed by the press will help get rid of voids in the workpiece and forge weld it into a monolith.
- After making sure that the welding is sufficient, use a large hammer to flatten the workpiece into one plate. Cool the product in air, cut off the rod using an angle grinder. And with the same tool we halve the plate.
- Between the resulting halves we lay carbon steel, sprinkling the layers with brown. We carefully “grab” it with welding and return the rod to its place. Place in the oven and heat until bright red. Having taken out the plates, we forge them with a large hammer. The plates must be welded together using the forging method.
Knives from a chainsaw chain.
Tables of saw chain and chainsaw bar sizes by model
This is a defining parameter, and depending on its value, all existing chains are divided into five groups with pitches of 1/4'', 0.325'', 3/8'', 0.404'' and 3/4''. Step 1/4'' ' (6.35 mm) is typical for small chains installed on low-power one-handed saws.
0.325'' (8.25 mm) and 3/8'' (9.3 mm) pitch chains are the most common options. More than 80% of saws produced around the world are equipped with them.
0.404'' (10.26mm) and 3/4'' (19.05mm) pitches feature larger link chains for increased performance. For several decades, they were equipped with Russian-made saws, but now they are installed only on powerful felling saws and harvesting equipment.
The larger the chain pitch, the larger the links that make it up and the higher its performance, but the wider the cut. To overcome the increasing cutting resistance, a more powerful saw is required. Chains with a small pitch have other advantages - a larger number of teeth per unit length, smooth movement in the cut and, accordingly, reduced vibration, a cleaner cut.
Drive link thickness. During operation, the chain slides in the groove of the bar, and this sliding should be smooth, without snagging and at the same time without unnecessary “bumpiness”. The thickness of the shank and the thickness of the groove must strictly correspond to each other, which increases the reliability of the chain fit and eliminates the possibility of it “jumping off.” Everything is provided in five standard sizes:
- 1.1 mm (0.043'') for low power saws
- 1.3 mm (0.050'') household and semi-professional chains,
- 1.5 mm (0.058'') powerful and productive saws,
- 1.6 mm (0.063'') and 2.0 mm (0.080'') highly professional saws.
The purpose of use imposes its own requirements on the circuits used. For example, if you need to saw hard and contaminated wood or during demolition and construction of structures, it is better to use special carbide chains Picco Duro or Rapid Duro, which have carbide teeth or linings, giving them unsurpassed strength and durability. Some jobs simply cannot be completed without their help.
It is also known that for longitudinal sawing of wood (along the grain) it is advisable to use special chains. The main difference between longitudinal and transverse type chains is the angle of attack of the cutting links. For crosscut chains they are 25–35 degrees. Ripping chains (such as the Stihl Picco Micro X chain) have sharper angles - from 5 to 15 degrees.
The use of chains inappropriate for their purpose leads to either reduced performance or increased “aggressiveness”, strong vibration and additional load on the chainsaw engine.
Additional characteristics of the chain are the profile height and cutting depth.
Profile height.
Chains are available in high and low profile depending on the height of the cutting edge above the plane of the guide bar. High profile chains are usually used for professional purposes to achieve maximum sawing performance. Low-profile chains are installed on household and amateur chainsaws, because... Thanks to the increased support area of the cutting links and the reduced thickness of the cut chips, they are safer.
The depth of cut is the amount of clearance between the top edge of the tooth and the cut stop, which regulates the thickness of the chips. Most often, there are samples with gaps of 0.025 inches (or 0.635 mm) and 0.030 inches (or 0.762 mm), less often - with gaps up to 0.07 inches (or 1.778 mm), the latter are intended for machine felling units.
Cutting depth and profile height
What is the configuration of the cutting links on your chainsaw chain?
Chipper roomChisel room
If you look closely at the chainsaw chain, you will notice that the working part of the cutting links is raised above the general level to a certain height. This height can vary, depending on what distinguishes between high-profile and low-profile chains. The difference will be in the depth to which the cutter will plunge into the wood. A large blade height produces thick chips, the work goes faster, but the power of the saw must be sufficient. Low cutters have thinner chips and cut more slowly, but the cut is neat and even. Such work can be performed by a medium and low power motor. Absolutely all models of amateur and most semi-professional tools are equipped with low-profile chains. There is a choice in the professional tool segment.
In addition to the profile height, the cutting depth limiter affects the nature of the cut. During operation, it rests against the surface of the wood so that the cut layer enters the gap between the cutter and the stop. Sharpening plays an important role here. In good branded chains, the factory sharpening is done correctly, but with cheap Chinese chains you literally have to finish it yourself.
Saw chain lubrication system
The reliability and efficiency of the latter directly depends on the quality of lubrication of the chain and chain saw bar. In order to ensure normal operation of the tool, manufacturers supply it with an oil pump, which supplies oil to the cutting system through special holes. The chain itself is responsible for the uniform distribution of oil - its shanks, passing through the sprocket, capture the lubricant, which, as a result of the movement of the headset, spreads over it and the saw bar. Often, to increase the efficiency of lubrication, special channels are made in the drive links using a milling cutter or drill, and additional recesses are made in the connecting links.
The chain saw's lubrication system works to reduce the destructive effect of friction and, of course, heating. This significantly increases the service life of both the chain set and the tool as a whole. Therefore, the user must control the lubrication process. If, when the chain accelerates, there is no oil trace on the cutting line, this means that the saw is overheating, and the chain itself can quickly become dull, or even burst.
In order to increase the lubrication effect, global manufacturers produce saw oils on an organic basis. They cost a little more, but provide a quarter of the consumption, and when released into the environment, they self-decompose within a few hours.
Leaders in consumer demand
In the process of natural selection, the first lines of sales ratings were taken by the products of leading European and Asian manufacturers of chainsaw equipment. Maximum demand for components of the brands Shtil, Husqvarna, Makita, and a number of others.
In all respects, the Oregon tire has proven itself to be excellent, and in various modifications it is used to equip removable equipment for mid- and higher-priced saws.
→ MAKITA 3/8 TIRE AT THE BEST PRICE
Bicycle chain device
Any bicycle chain (except Half-Link) consists of several elements, namely:
- Outer link plate.
- Inner plate.
- Video clip.
- Bushing (glass).
- Pin.
- Complete chain link.
- Gap for side bending.
1 link consists of 2 half-links. They are connected to each other using a pin placed in the “glass”. A roller is put on it. The roller is necessary to hold the bicycle sprockets on the teeth (where the chain is put on). The length of one full link is 1 inch, which translates to 25.4 millimeters. The length of the entire chain is determined by how many links it contains.
For a 12-speed adult bicycle, a 126-link chain is typically used. There are many variations, the number of links varies from 110 to 126 pieces. Mountain bikes (MTB) use 106 or 108 chainstays.
If after purchase it turns out that the chain is too long, it can be shortened. This is done by disconnecting the lock (if there is one) and knocking out the pin. After that, everything is connected back together and installed on the bike. This way you can adjust a chain that is too long to fit your bike.
What it is
To improve the quality of the cut, as well as extend the period from one sharpening to another, carbide chains were invented. The use of hard alloys in wood sawing is not new. Composite bonding technology has long been successfully used in the production of circular saw blades.
The carbide chain is not homogeneous in its structure. It is a combination of two metals: ordinary tool steel and a special alloy of increased hardness. The first one is used to make driving, cutting and connecting links, as well as rivets. The alloy is applied to the cutting edge and the upper plane of the working link in the form of a thin plate. Fastening method: soldering. This means. that copper-nickel and copper-brass solders are used to connect the solid part and the steel base. The choice of these particular materials is not accidental: they have good fluidity, adhesion, and also have a melting point that is approximately 300 degrees different from the operating heating of the chain. That is why you should not overheat the saw set.
Pobedit is the popular name for alloys based on tungsten carbide, which makes up up to 90% of the total mass of the substance. The remaining 10% is cobalt, which is needed as a binder, and just a little carbon. In fact, tungsten carbide is a cermet material that is extremely hard and has excellent temperature resistance.
Types of teeth
- Chipper - with a large area of the working edge, cutting wood, the quality of sharpening does not play a special role, it gets dull quite rarely. Used for longitudinal and transverse cuts;
- Chisel - with a small working edge area, thin and sharp, but quickly dulls and sharpening requires precise angles. Used for cross cutting.