Table of cutting thicknesses and gas consumption for NX type mouthpieces This results in a cut. Oxygen is supplied under high pressure, often reaching 12 atmospheres; such a jet, even without fire, can cut the skin.
The structure of the cutting apparatus is designed as follows:
- gas-burner;
- two cylinders;
- mixer;
- pressure regulator;
- hoses.
A gas burner consists of a head with several nozzles, usually three are enough. A flammable substance is supplied through two side ones, and oxygen is supplied through the third, which is located in the middle. The cylinders are designed directly for gas and oxygen; depending on the volume of intended work, cylinders of appropriate capacity are selected.
Gas-burner
To ensure one hour of continuous operation, an average of 0.7 m3 of acetylene (1 m3 of propane) and 10 m3 of oxygen will be consumed. In general, the required amount of feedstock will depend on the density of the metal and the required temperature to heat it. Propane consumption can be reduced by using special nozzle attachments that fix the gas supply in a certain direction; the closer the supply is to the oxygen stream, the higher the fuel consumption.
Hoses are necessary for supplying oxygen and flammable substances from cylinders to the mixer; they are also called hoses. The material from which the hoses are made is two-layer rubber, between the layers there is a frame made of cotton thread. Diameter – up to 12 mm, possibility of operation at air temperatures not lower than -35 °C.
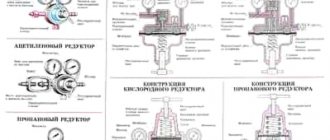
A pressure regulator is necessary to provide different cutting modes and speeds. By supplying less fuel, it is possible to ensure the low temperature required for thin steel or low-strength metal, and also reduce the consumption of raw materials.
Another important function of the reducer is to maintain a uniform pressure level. If the gas supply is interrupted during the cutting process, the metal will quickly cool and further processing will become impossible.
Metal cutting with propane and oxygen
Features of the technology
The choice of gas for cutting depends on the properties of the metal workpiece. In addition to technical oxygen, acetylene, coke oven and petroleum gas, methane, propane, butane and mixtures of them can be used.
Oxygen is used when cutting metal with gas if the material has certain characteristics:
- high thermal conductivity;
- melting point above the ignition temperature in oxygen;
- the melting point of refractory oxides is lower than the melting point of the metal;
- the formation of liquid slag during the cutting process;
- releasing a large amount of heat.
To cut a metal workpiece, it must first be heated. Then the material is burned, the combustion products are removed by a gas stream.
- superficial – formation of slots and channels;
- spear - the formation of holes or openings;
- separating – in the form of a through cut.
Different burners are selected for different jobs. There are several types that are designed to perform different jobs.
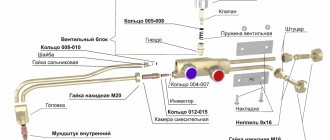
Any burner consists of:
- handles;
- valve;
- valve (not on all models);
- tip (extension tube);
- mouthpiece (nozzle).
Mixing of gas with air can occur in the tip or mouthpiece. In models with a valve, gas and oxygen are mixed in the head, which increases the level of safety. The use of models without a valve allows the use of gas with different pressures. Gas cutters for cutting thick metal are equipped with several mouthpieces.
The technology consists of four steps:
- heating the workpiece;
- introducing a gas mixture into the processing area;
- ignition of the material;
- combustion process.
The stream must be uniform so that the flame does not go out. During the combustion process, oxides are formed, which are removed by a gas jet.
Propane cutter, device, operating principle, types
A propane cutter is a simple piece of equipment for manually cutting metal using propane as a flammable fuel. The cutting process consists of the combustion of metal with supplied oxygen, but before this, with a well-heated metal surface to the required ignition temperature of oxygen on the metal surface. This is followed by the removal of oxides from the cutting zone using a jet of flame.
Nowadays, a universal-purpose propane cutter is more often used. They can cut steel with a thickness of 3 to 300 mm, in any direction, have good resistance to kickbacks, and are mobile in handling. The oxygen-propane cutter consists of a main barrel and a tip. The barrel is attached to a handle that has two nipples, one for oxygen and the other for flammable gas. A little higher, the barrel has control valves for oxygen and gas, mixing chambers for oxygen and gas, tubes, a cutter head with an internal and external mouthpiece, and a cutting oxygen supply tube.
An oxygen-propane cutter will perform a high-quality cut if you select the appropriate nozzle size correctly, as well as select the appropriate ratio of gas supply pressure to metal thickness. A lack of oxygen supply results in incomplete oxidation of the metal and poor removal of oxides, while an excess of oxygen leads to unnecessary cooling and heat removal from the cutting zone. The purer the oxygen, the cleaner the quality of the cut edges and the less slag that is difficult to separate later. The cutting speed must be optimal, otherwise the edges will melt or incomplete cutting at low speeds.
The propane cutter RZP can also operate on acetylene or propane-butane. It cuts metal up to 300 mm thick quite efficiently, has a low weight of 0.8 kg, a cutter length of 520 mm, has 100% resistance to backfire, high-quality durable components, thanks to a special lubricant that is not dangerous to oxygen. Propane cutter RZP (2.3), Izhevsk, is designed for manual cutting of carbon steel, as well as low-alloy steels. Produces high-quality cutting of metals with a thickness of 3-300 mm. and cutting up to 450 mm. It has a mass of 0.91 kg, models of these cutters operate on propane-butane, acetylene and can also use natural gas. Conditional diameter of hoses, mm-dy9, if by special order dy6. Such cutters have a different set of mouthpieces, which allows high-quality cutting of different thicknesses of steel.
The propane cutter RZP type “MAYAK” is also capable of cutting thick steel up to 300 mm. The weight of the cutter is 0.75 kg, there are four internal nozzle numbers and one external one. Universal nipple d6/9. This type of cutter is designed for cutting long and low-carbon steel sheet metal. Slotted nozzle, valve gas supply, high resistance to blowback.
The propane cutter RZP-03M type KRASS operates on propane-butane and successfully cuts sheet and long metal made of low-carbon steel. Cutter weight 0.75 kg, length 475 mm. Capable of cutting steel from 8 to 300 mm thick. Propane cutter of the listed types of cutters do not have significant differences in the quality of cutting and the ability to cut metals, but they have different lengths, weights, the number of attached mouthpieces, and sometimes the thickness of the metal being cut
Leave your comment Cancel reply
Cutting metal, especially on an industrial scale, is labor-intensive and...
Metal cutting instructions
It is important to connect and prepare the torch correctly. Tubes with valves at the ends are connected to the cylinders. Next, the gas supply is checked (if it is oxygen-propane metal cutting) - the valve closes, the valve on the cylinder opens. Then, watching the pressure gauge, the valve is slowly opened. The pressure should be 0.35–0.55 atmospheres. Then you need to blow out the hose - open the valve. Gas begins to escape with a characteristic sound. If the pressure gauge shows stable pressure, the valve closes.
The next step is to check the oxygen supply and adjust the pressure. First, the valve on the cylinder opens, then the regulator (flow pressure 1.7-2.7 atmospheres). To purge the hose, open the oxygen valves on the cutter. There are two of them: for feeding into the nozzle and forming a mixture. First you need to open the first one, then the second one (for 3-5 seconds).
Attention! Before igniting the valve, make sure that there are no leaks in the connections, that children are not playing nearby and that animals are not walking around.
The gas supply valve is opened first to allow oxygen to escape, which remains in the mixer after checking. The valve must be turned until gas can be heard escaping. The lighter placed in front of the cutter should touch the mouthpiece. After pressing the lever, sparks ignite the gas.
You need to open the oxygen valve immediately. Its sufficient volume is indicated by a change in the color of the flame to blue. In order for the torch to increase in size, more oxygen must be supplied. The pressure of gas and oxygen when cutting metal depends entirely on the thickness of the workpiece.
Important! If the flame is unstable and “spitting,” there is too much oxygen. The volume must be reduced so that the flame is in the shape of a cone.
According to the technology of gas cutting of metal, the flame was brought to the material with the tip, heating the surface. After the molten metal appears, the supply of oxygen begins, igniting it. The jet increases until the material is completely cut through. At the same time, the mouthpiece moves along the cutting line. Sparks and slag are removed with a jet.
Metal cutting with oxygen and propane
If there is a need to work with thick-layer metal, a gas cutter is used. It cuts a metal sheet using a hot flame jet. It is formed by mixing two gases - propane and oxygen.
It is impossible to cut high-carbon metals, copper and its alloys, and aluminum with an oxygen-propane cutter. The range of materials that can be affected is limited to low-carbon steel grades from 08 to 20G according to GOST (1050-60) and medium-carbon steel - from 30 to 50G2 (GOST 1050-60).
A propane cutter cuts metal with a thickness of no more than 300 mm.
To work you must have
- high pressure oxygen hoses
- propane and oxygen cylinders
- mouthpiece
- cutter
All parts of gas equipment are standard and can be replaced if damaged.
Preparing for work
Before starting work, you need to make sure it is safe: there should be no traces of oil or other flammable substances on your clothes, floor, and surrounding surfaces. Next, you should inspect the gas equipment for completeness and serviceability. The following steps will help get your equipment ready:
- Flush all high pressure hoses with gas to remove dust and dirt before connecting them. Check for suction in the cutter channels. Attach the oxygen hose to the right-hand thread fitting using a nipple and nut. Attach the propane hose to the left fitting;
- Check for gas leaks in detachable connections;
- Check the serviceability of the pressure gauges. Pay attention to the tightness of gas reducers.
Beginning of work
Oxygen consumption when cutting metal is 10 times higher than propane consumption.
- Close all cutter valves and set the operating atmospheres on the gearboxes: oxygen - 5, gas - 0.5.
- Open the propane tank a quarter of the way and light it.
- Place the torch nozzle at an angle against a metal surface and slowly open the oxygen control.
- Proceed with the process of adjusting the flame: alternately open the oxygen and gas until the flame turns blue and has a crown.
- Select the flame strength based on the thickness of the metal.
Cutting process
- Start cutting the metal from the point where you want the cut to start.
- Heat this point to the ignition temperature of the metal (1000-1300 C). When the metal ignites (the surface will look wet), open the cutting oxygen valve and release a narrowly directed stream.
- Smoothly move the oxygen torch along the cutting line, at an angle of 84-85° in the opposite direction from the cut. If the metal thickness is more than 95 mm, make a deviation of 7-10°.
- After the cut line has reached 15-20 mm, change the inclination angle to 20-30°.
With the correct choice of the speed of movement of the cutting torch, a stream of sparks and slag flies out of the cut straight down, and the edges are clean and there are no smudges or deposits.
If your oxygen hose breaks during work, don’t panic. Close the propane supply and then both tanks. The flame that disappeared during the adjustment process must be re-ignited by first closing the cutter valves.
Safety precautions when cutting and welding
The developed clear safety rules made it possible to make the process controllable, the life and health of carvers and others became out of danger:
- Using a special mask with light filters, a respirator and a protective suit.
- Admission to work for persons who have reached the age of 18 and have completed a special course in gas work and have a certificate with a mark for carrying out this type of work.
- Cleaning the tightness of all connections of equipment, pipelines and fittings to prevent gas leaks.
- Use of special carts and stretchers to move individual cylinders. No cylinders hitting each other during transportation.
- Liquefied gas, grease, and oil must not come into contact with the oxygen reducer, valve or hose.
- Do not open the reducer or oxygen cylinder valve with oily hands.
- Before starting work, it is necessary to release the mixture of gas and air formed in the hose through the cutter. This way we prevent the occurrence of backlash into the hose and reducer.
- Heating metal only with liquefied gas without oxygen is strictly prohibited.
Oxygen pressure when cutting metal
The cutter functions normally if the oxygen pressure when cutting metal is 3-12 atmospheres (depending on the thickness of the workpiece and the diameter of the nozzle). The higher the pressure for specific sizes, the more oxygen reaches the metal surface, it oxidizes better (but up to a certain limit). If the pressure for a particular workpiece and equipment is higher than normal, oxygen flows through the cut to no avail.
The second negative point is an increase in the width of the incision and excessive consumption of oxygen. The material is wasted uselessly. Therefore, the pressure is calculated separately for each nozzle and workpiece. The level is controlled by pressure gauge readings, but they are inaccurate, since the pressure decreases as it passes through the hose and mouthpieces.
The oxygen reducer is adjusted when cutting metal using a screw. To increase the pressure, turn it clockwise, to decrease it, vice versa.
Important! It is also necessary to know what pressure is on the flammable gas reducers when cutting metal. They are classified by maximum pressure (15-30 atmospheres when cutting).
The pressure is set before starting work, the role of the reducer is to maintain the level.
Metal cutting with propane and oxygen
- Metal structures
- Metal cutting Plasma metal cutting
- Oxygen gas cutting of metal
- Metal slitting
- Band saw metal cutting
- Cutting metal with a guillotine
- Artistic metal cutting
- Shaped metal cutting
- Cross cutting of metal
- Longitudinal and transverse cutting of metal
- Metal cutting with gas
- Waterjet cutting
- Laser cutting of metal
- Sheet metal cutting
- Metal cutting
- Laser cutting of metal to order
- Metal cutting according to customer dimensions
- Cutting metal with water
- Metal cutting with propane and oxygen
- Electrical discharge cutting of metal
- Metal cutting prices
Professional gas cutting: metal cutting services with oxygen and propane
offers a wide range of services, including oxygen cutting of metal.
Being one of the most common types of metalworking, oxy-fuel cutting is highly efficient and productive.
In our company, gas cutting of metal with propane and oxygen is carried out in the shortest possible time, with consistently high quality.
How metals are cut with burning propane and oxygen: process technology
Cutting metals with gas requires heating the metal surface to the desired temperature, which depends on the type of metal. The material must have a combustion temperature less than its melting point. If this rule is ignored, molten but not burnt metal is removed from the cut with great difficulty, and the edges of the cut look sloppy.
Allowances for metal cutting
Allowance for cutting metal with gas is a layer that is lost during processing according to the drawing. Standards for steel blanks are defined in Minimum allowances GOST 12169-82:
- 3-5 mm with a thickness of up to 60 cm;
- 5-10 mm with a thickness of 100 cm;
- 10-25 mm for very large thicknesses.
Important! The amount of allowance for cutting metal depends on the width of the groove, errors in the equipment used, the chemical composition of the material, deviations due to deformations, and technological inaccuracies made by workers.
Safety precautions when gas cutting metal
Safety precautions when gas cutting metal determine that it is better to work in the air or in a room with an ideal ventilation system, earthen or concrete floor. The floor covering within a radius of 5 meters must be cleared of items that are easily flammable: shavings, rags, paper, leaves and plants. It is best to place the workpiece on a metal table of a convenient height. There should be no stains left by flammable substances on the floor or table.
Before starting work, you need to make sure that you have on hand:
- protective equipment (leather gloves, safety glasses, sturdy shoes);
- fire-resistant clothing (synthetics, torn edges, loose fit are not allowed);
- tools (special pencil, square, ruler);
- a special lighter (matches are not suitable).
The greatest harm to a worker occurs if the mixture explodes due to improper handling of the cylinders or burner. Explosions of cylinders filled with oxygen are considered the most dangerous. If you handle the burner incorrectly, you may get burned. The eyes are negatively affected by visible and infrared rays, sparks, and slag splashes. If you do not use safety glasses, there is a possibility of losing your vision for some time.
Source
Pros and cons
Gas cutting and welding of metals has many advantages, but we are only interested in cutting that has the following advantages:
- It is in demand when thick metal is being cut or cutting according to a stencil is needed, and the grinder cannot cope with curved sections.
- The gas analogue is much more convenient to work with, is lightweight, and operates twice as fast as equipment with a gasoline engine.
- Propane is less expensive than acetylene and gasoline, so its use is more profitable.
- The cut edge is much narrower, and the structure is cleaner than from an angle grinder or gasoline equipment.
Disadvantages - a narrow range of metals subject to similar processing.
Overall size and weight
The parameters of a manual injection gas cutter will be contained in GOST 5191−79 standards and will directly depend on its power indicator:
- P1 has about 500 millimeters.
- For P2 and P3 they are within a certain limit of 580 millimeters. But more extended models are also being produced to carry out work in appropriate conditions.
- There are special restrictions on the weight of any such power category: 1.0 and 1.3 kilograms in the ratio for P1 and P2-P3.
The same standards from GOST will determine that the P3 variety is an oxygen-propane cutter, and also P1 and P2 can perform work on absolutely any type of combustible gas. There is also a separate group of manual injection tools for oxygen cutting - insert cutters, which have a special marking PB.
According to GOST standards, they will be defined as tips for cutting on a welding torch. The main differences in such designs are that the process of separating oxygen, as well as a mixed type of combustible mixture, will occur on the tips themselves, which have a smaller weight and size than the cutter. So the weight indicator of PB1 has a special upper limit of 0.6 kilograms, and PB2 and PB3 are about 0.7 kilograms.
But this type of gas cutter cannot be called complete in terms of its metal - in the working position during the assembly process with the main body of the burner, its overall size and weight will be no less than that of special equipment. Its main advantage is that you can purchase a torch together with various types of tips (cutting and welding), and the complete complex can be easily placed in a small case. Or buy a portable backpack specially designed for the burner.
But in this case there is one peculiarity. Propane will be much cheaper in cost than acetylene. It is for this reason that the cost of using an acetylene torch will be much higher than an oxypropane torch. To weld metal, it is better to use an acetylene torch, whose total flame temperature will be as much as 300-400 degrees higher than that of an oxygen- propane torch (with an all-propane torch the total temperature will be less than 2 thousand degrees Celsius).
The compactness of the entire post for manual cutting can be ensured using the capacity of all gas cylinders.
Surface cutting
Users, of course, are interested in the following question: how to use the cutter during shape cutting. This technique is performed using a tool nozzle, while the molten slag heats the metal, but without exceeding the melting point . The cutter is positioned at an angle of up to 80 degrees, and after oxygen is supplied, the angle changes within 18-45 0.
Grooves are formed when adjusting the cutting speed; if a larger size is needed, then change the angle of the mouthpiece and slow down the cutting speed slightly, adjusting the oxygen supply. The width of the grooves is changed by adjusting the supply of a jet of burning gas through the nozzle; this parameter is equal to 1 to 6, while care must be taken to ensure that there are no backflows.
[stextbox the edges of the recess were clean, we need to increase the oxygen supply.
Necessary equipment
Cutter P101
The very first cutter was the P1-01 device, it was designed back in the USSR, then more modernized models appeared - P2 and P3. The devices differ in the size of the nozzles and the power of the gearbox. More modern manual settings:
- Change;
- Quicky;
- Orbit;
- Secator.
They differ in their range of additional functions and performance.
Quicky-E can carry out shape cutting according to specified drawings, the operating speed reaches 1000 mm per minute, the maximum permissible metal thickness is up to 100 mm. The device has a set of removable nozzles to ensure processing of metal sheets or pipes of various thicknesses.
Autogenous cutting machine Messer
This device can operate using various types of flammable gas, unlike the prototype P1-01, which runs only on acetylene.
The Secator manual cutter has improved characteristics compared to its analogues.
Cutter R2-01
With its help, you can process metal up to 300 mm thick, this is provided by additional attachments included in the kit, they are removable and can be purchased additionally as they wear out. Secator can produce the following types of cutting:
- curly;
- straight;
- ring;
- under the bevel.
The speed can be adjusted in the range from 100 to 1200 mm per minute, and the built-in freewheel ensures smooth movement of the machine along the sheet metal. The air-cooled gearbox ensures cleaner operation and reduces fuel consumption.
The above models are manual, that is, they are compact and controlled by the hands of a master. But for large volumes of processed metal, working with such
Stationary cutting unit
installations are inconvenient and ineffective. For industrial production, stationary cutting installations are used - this is essentially the same technology.
They are a machine with a table top into which a cutting mechanism is built. Its operation is ensured by electric
a compressor that requires an electrical network with at least 380 V and three-phase sockets. The technology of operation of models of stationary cutting units is in no way different from manual ones. The only difference is in productivity, maximum heating temperature, and the ability to process metal with a thickness of more than 300 mm.
Preparatory work
How to set up a cutter for cutting metal - first of all, you need to make sure that the product is in good condition and ready for work, then perform the following procedure:
- The hoses from the cylinders are connected to the cutter, having previously purged the product to remove foreign inclusions from the inside.
- Oxygen is connected to a right-hand thread fitting, and propane is connected to a left-hand thread fitting.
- Set the propane supply level to 0.5, and oxygen to 5.0 atmospheres.
- We check connections for leaks, as well as the operation of gearboxes and pressure gauges.
If gas leaks are detected, tighten the nuts or change the gaskets.
The diagram shows the correct connection of the cylinders to the cutter.
How to use a gas cutter correctly: preparatory stage
First, we will ensure security and prepare everything necessary. You will need:
- Carbon dioxide fire extinguisher. Metal cutting with a cutter is carried out at temperatures above 1800 degrees, so we need protection. Carbon dioxide will be most effective compared to powder. By the way, a bucket of sand won’t hurt either.
- Fireproof suit. In principle, the usual equipment of a gas welder will do. It is made of tarpaulin impregnated with a fire-resistant compound. You will also need protective gloves and boots.
- Glasses. It’s easy to get a “bunnies” effect from the brightness of hot gases, so you need regular filter glasses, preferably level 3.
- Marking tool.
- Ear protection. Construction headphones or earplugs.
- Lighter for cutter. Ordinary matches or lighters are not suitable - your hands are too close to the torch. You can buy what is sold in the store under the name “household lighter.”
We prepare the workplace separately. Ideally, buy or make a welding table with an exhaust hood. But a base of fireclay bricks is a good place to start. There should be no flammable objects for 2-3 meters around the work site: paper, solvents, fuel, oils.
Necessary equipment
Now let's assemble the necessary equipment. All we need is:
- Cylinders. To assemble a propane oxygen cutter, we simply buy the appropriate cylinders. This can be done at any shop with welding equipment. They are refillable and can be refilled at the same retail outlet or gas station.
- Sleeves. For propane you will need a class 1 hose with a diameter of 1 to 2 centimeters. It is desirable that it be red for convenience. Oxygen has the same diameter, but strength class 3.
- Gearboxes. They are purchased for each gas separately. We need propane (for example, BPO-5DM) and oxygen (BKO-50DM). By the way, it is impossible to confuse them, since propane has a reverse thread.
- Check valves. At the entrance to the burner, fire arresters are installed, which also have a gas gradation. It is not worth starting the cutter without them, since if there is a bang, the combustion will spread to the sleeve and may reach the cylinder.
- Oxygen-propane burner. You can buy it at any online tool store. For example, GZU 228, G2 Mini 273, R1 142.
That's all you need to start the propane-oxygen cutter.
When everything is prepared, you can proceed to working with metal.
How to use an oxypropane torch
Preparing for work
And so, let’s assemble our cutter and check for functionality. By the way, a preventive inspection should be carried out before each start-up to avoid leaks. Especially if the equipment has been idle for a long time or there is a suspicion of a leak.
Begin:
- First, let's connect the sleeves to the cylinders. The oxygen hose is connected to a nipple with a fitting to the gearbox with a right-hand thread. The propane hose is installed in the same way. We pass all connections with a sealant (anaerobic sealant, tow, fuser).
- We release the gas a little to remove dirt from the hoses.
- Nipples are attached to the reverse side of the sleeve for transferring to fire-retardant valves.
- The burner itself is already attached to them. There should be color markings on it so as not to confuse oxygen with gas.
By the way, it would be a good idea to check the air leaks. To do this, the oxygen hose must be connected to the cylinder, and the propane nipple must be left free. We set the oxygen supply to 5 atmospheres. Touch the free nipple with your hand. If it gets sucked in, everything is fine, you can work. If not, you will need to bleed the injector.
Don't forget to seal all connections.
Let's get started
Now we will look at how to properly cut metal with a cutter. It's not difficult, but you'll have to get used to the angle of the cut. To begin with, we set the oxygen reducer to 5 atmospheres. On propane we set it to 0.5. The proportion of 1 to 10 was chosen because we have gas combustion in an oxygen environment.
Let's start by igniting the propane. Open the valve on the burner slightly and light it. We rest the nozzle against the metal at an angle of 90 degrees. Now we open the regulating oxygen a little. Now we open the valves one by one until we get a torch of the required size. Its length depends on how thick a piece of metal we need to cut through.
We start heating from the point from which cutting is planned. We are waiting for the metal to melt. On average, it takes about 10 seconds to warm up. When the metal is hot enough, let in cutting oxygen. It looks like a thin needle. Then we just slowly move it along the cutting line.
The cutting oxygen valve must be opened slowly.
The pressure difference can cause the flare to backfire, called a “pop.” If there is no fireproof check valve, flames will flow to the cylinders and cause an explosion.
How to use a cutter correctly? The correct angle must be maintained. We start with 90 degrees, then slightly tilt the cutter 5-6 degrees in the opposite direction from the cut. If the metal is more than 9 centimeters, you can tilt it up to 10.
When the metal has already been cut by 20 millimeters, set the angle of inclination to 20 degrees.
Beginning of work
How to cut metal with a gas cutter - having completed the preparation, the performer slightly opens the propane valve, ignites a gas stream, and the nozzle of the product rests on the surface of the metal. Now you need to adjust the flame strength by alternately adding propane and oxygen. After setting the optimal force of the jet of the burning mixture, the product is located at a right angle to the surface of the part, the nozzle is located no closer than 5 mm.
If the cut begins in the middle of the sheet, then the starting point is set at the beginning of the cut. The surface is heated to a temperature of at least 1000 0 C, in appearance it becomes wet, then the oxygen supply is increased to form a powerful, narrowly directed jet.
Cutting Features
The cutter must be moved smoothly along the cutting line and monitor the angle of inclination, which deviates 5-6 degrees against the movement of the tool. When the metal thickness is more than 0.95 m, the deflection is increased by cutting through the metal to a depth of about 20 mm, and the deflection angle decreases again. We have already explained in detail how to cut with a cutter so that the cut is even in the previous section.
How much gas is consumed?
Gas consumption when cutting metal with a propane-oxygen cutter depends on the thickness of the structure and the configuration of the cut. For clarity, we present the table below:
| Workpiece size (thickness), mm | Hole time, sec | Cut size (width), mm | Consumption, per m 3 cuts | |
| propane | oxygen | |||
| 4,0 | 5—8 | 2,5 | 0,035 | 0,289 |
| 10,0 | 8—13 | 3,0 | 0,041 | 0,415 |
| 20,0 | 13—18 | 4,0 | 0,051 | 0,623 |
| 40,0 | 22—28 | 4,5 | 0,071 | 1,037 |
| 60,0 | 25—30 | 5,0 | 0,087 | 1,461 |
Gas consumption is significantly reduced when surfacing or soldering is performed.
Nuances
The main task of the performer is to maintain the speed correctly:
- normal mode - sparks fly at right angles relative to the surface of the workpiece;
- low speed - flying away from the performer and an angle of less than 85 degrees.
After the process is completed, the oxygen supply is turned off first, and the propane is turned off last.
[stextbox N. Ishkulov, education: vocational school, specialty: welder of the fifth category, work experience: since 2005: “Performers who perform cutting using oxygen equipment for the first time must remember that they must start a new cut after a sudden stop from a different point, and not where the process was over."
Negative deformation
Beginning welders are concerned with the question of how to properly use a propane-oxygen cutter so that warping of the surface of the part does not occur. First you need to figure out what factors contribute to the occurrence of these defects:
- with uneven heating of the surface;
- a high cutting speed was selected;
- there was a sharp cooling of the heating area.
To eliminate the occurrence of the listed factors on the workpieces, they are first securely fixed and heated, and the speed is increased gradually. If warping does occur, then the original shape can be returned by firing or tempering, and the sheets can be straightened on rollers.
Kickback hazard
If the jet burns in an incorrect mode, a bang occurs and the flame is drawn inside the product, which leads to an explosion, as the fire spreads through the hoses and reaches containers with gases. To prevent a dangerous situation, the cutter is equipped with a non-return valve, which cuts off the flame and prevents it from spreading.
Terms of use
They are similar to safety precautions when welding, but have specific additions:
- It is not recommended to neglect protective equipment, as this leads to injury in the form of skin burns or damage to the cornea of the eyes from flying sparks, so goggles and gloves with long bells up to the elbow are required.
- The performer's clothing and shoes are made of non-flammable material.
- Gas cylinders are located no closer than five meters from the cutting site.
- The flame of the cutter is directed only in the direction opposite to the hoses.
- Cutting is carried out in rooms equipped with strong ventilation or in open areas.
If the equipment is idle for a long time, it is necessary to carry out preventive maintenance before using the cutter for its intended purpose.
Design Features
A two-pipe, as well as an injection, gas cutter is the most common type of this design. Technical oxygen in the cutter will be distributed into two formats at once.
One portion of the top tube flow will pass through the tip head and exit at high velocity through the center nozzle of the inner mouthpiece. This part of the structure will begin to be responsible for the cutting phase of the process. A control valve or lever valve located outside a specific housing.
The next part will begin to flow into the injector itself. The principle of operation of this device will be that the injected gas (oxygen), entering the mixing chamber under strong pressure and at a high speed, creates a rarefaction area in this place and through the peripheral holes is drawn independently into the flammable (injected gas). Using the process of such mixing, the overall speeds are equalized, and at the exit of the chamber a special flow of a mixture of gases begins to occur at a speed much lower than that of the injected oxygen, but much higher than that of the electrified combustible gas.
After the mixture of gases begins to circulate through the lower tube into the tip head itself, exits through the nozzles between the inner and outer mouthpiece, and also creates a torch of a heating flame. Each channel has its own valve, which will regulate the supply of oxygen, current and combustible gas to the injector.
A non-injector or three-pipe cutter , which contains a more complex design - two oxygen gas flows will begin to flow to the head through separate tubes.
The displacement of the entire heating mixture will occur inside the head itself. But it is the absence of a chamber in which mixing occurs that provides a stronger safety indicator, and also does not create conditions for creating a backlash (the process of spreading burning gases into the channel of the cutters themselves and the pipes in reverse motion).
In addition to more developed structural designs and inflated costs, the disadvantage of a three-pipe gas cutter is considered to be that for its stable operation it is necessary to use a higher pressure of combustible gas (there is no ejection effect here, as well as an increase in the speed of general flows).
Safety precautions
The equipment is classified as explosive, so the work site must be equipped with the following accessories:
- fire extinguisher;
- sand box;
- fire stand with appropriate tools.
Each performer must have a set of protective clothing.
Protected clothing is not allowed to be made of easily flammable material, such as synthetics, and the edges of the sleeves must fit tightly to the body to prevent sparks from getting inside.