- home
- Information
- Articles
- Countersinks and countersinks, application and differences
Back to list
Several types of tools are used to process holes, including countersinks, countersinks, and counterbores. The practice of their use is often accompanied by confusion in the names. For example, in tender documentation there are orders for “conical countersinks”, and GOST 14953-80 is indicated, which describes conical countersinks. These tools are similar in design, and there is also much in common in application, so it is not surprising that even in the technical literature there are many examples of “free” use of terminology.
Official source on the terms GOST 25751-83 “Cutting tools. Terms and definitions,” unfortunately, does not answer the questions: what is the difference between a countersink and a countersink, countersinking and countersinking and countersinking. To this end, we will consider the design and application of each of these tools.
Selection rules
Countersink drills must be selected using the same principles as traditional tools used in metalworking and woodworking.
The main focus is on the type of work to be performed. When it comes to drilling and countersinking metal products, preference should be given to models with a spiral cutting part made of tool or alloy steel - with higher strength and corrosion resistance characteristics
Visual inspection is also important. The color of the cutting part of the drill will tell a lot about what kind of processing the tool was subjected to
- Products treated with titanium nitride acquire a rich golden hue. They are very durable and have an extended service life.
- Black color is typical for countersink drills treated with steam. Typically, such products are made from high-speed tool steel.
- Products in which stress has been eliminated acquire a yellow tint, usually using the tempering method. Accordingly, the steel part has been hardened and will provide sufficient strength.
- The gray color characteristic of ordinary steel is found on tools that have not received additional processing. Their strength characteristics and capabilities are inferior to conventional ones.
An important component of choosing drills with countersinks is the type of fastener for which the hole is drilled. The conical or cylindrical type of design is determined by this factor
It is worth paying attention to the working diameter. Drills with a countersink element are produced in the most popular sizes, with the thickened part of the cut usually having a diameter of 16 mm when it comes to woodworking
Taking into account all the recommendations, you can find a suitable option for a specialized cutting tool for use in a workshop or production.
The following video talks about countersink drills.
Features and Application
A countersink drill is a specialized type of tool that can perform several operations at once. Such devices are especially in demand today in furniture production, where assembly euroscrews are used. The countersink part allows you to drill holes with variable diameters without changing the cutting tool. This element can be solid or in the form of a replaceable nozzle.
Modern drills with countersinks for metal, wood, and other materials are manufactured in a different range of diameters. The tail part can have a cylindrical or hexagonal shape, well suited for installation in a screwdriver or drill.
When using a classic drill, the hole has 1 diameter along its entire length. A traditional countersink, a separate tool used in industry and workshops, also only makes through holes of the same size. The combined option allows you to solve several problems at once, avoiding changing attachments during operation. Depending on the type and purpose of the products, the number of steps in them may change - usually there are 2 or 3. Each implies a change in diameter.
Combined countersink-drill type products allow you to achieve high quality and clean finishes. They may have both straight and helical grooves.
Countersink, countersink - what is it and technology of work
Among the metalworking tools used to create holes, countersinks and countersinks deserve special importance. With their help, openings are made with specified characteristics, for example, stability of important geometric parameters, roughness, narrowing of a cylindrical hole. Let's look at what a countersink and a countersink are.
Terminology
A countersink is a multi-bladed cutting tool used for making holes in metal parts. After processing, conical/cylindrical type recesses are obtained, you can create a reference plane near the holes, and chamfer the center hole.
Countersinking of holes is the secondary preparation of finished holes for placing hardware heads - bolts, screws, rivets
A countersink is a cutting tool with a multi-bladed surface. Used in machining cylindrical/conical holes in workpieces to expand the diameter, improve surface characteristics and accuracy. This type of processing is called countersinking. This is a semi-finish cutting process.
A - drilling with a drill B - boring on a lathe C - countersinking with a countersink D - reaming with a reamer E, F - counterbore with a counterbore G - countersinking with a countersink H - thread cutting with a tap
Countering holes is the process of reworking the top of an opening in order, for example, to remove burrs from the edge of a hole or to create recesses to hide the head of a rivet or screw and level it with the surface of the part. The tool used for this task is called a countersink.
Types of countersinks and countersinks
The production of metal cutting tools is subject to the main category of country standards (GOST) and technical regulations for the use of the finished product. On units with partially automated control, the following types of countersinks are used:
- Cylindrical, with diameters from 10 to 20 mm. This set of blades is produced with a coating of wear-resistant elements. Regulated by GOST 12489-71.
- Indivisible conical, from 10 to 40 mm. Manufactured from alloy steel with wear-resistant coating. Subject to TU 2-035-923-83.
- Whole, in the form of attachments, with a diameter from 32 to 80 mm. Regulated by GOST 12489-71.
- Conical or mounted, subject to GOST 3231-71. They are marked by the presence of special plates made from hard iron alloys.
A countersink is also a tool with numerous blades, but it has clear differences from a countersink in terms of use. These devices are divided into several types:
- Conical countersink. It has an operating head with a cone angular coefficient of 60,90, 120 degrees. It is mainly used for cultivating bases for fasteners and removing chamfers, that is, to blunt sharp edges. Regulated by GOST 14953-80 E.
- Rounded countersink (cylindrical). The device can have a rounded or conical end, having a wear-resistant coating on the base. Mainly implemented as a treatment for supporting bases.
What is a countersink, systematization
A cutting tool for metal (countersink) allows you to countersink an opening in a part up to accuracy group 5. It is widely used for semi-finishing parts before mechanical reaming. According to its structure, it is divided into types:
- holistic;
- nozzles;
- tail;
- connected.
Externally, metal-cutting devices look like a simple small drill, but have an increased number of cutting edges. The correct dimensions of the opening of the workpiece being processed is determined by the gauge. The tools are fastened in the unit's chuck with the support of the shank.
To cultivate openings with a diameter of up to 10 cm, attachments with 4 points are used. Their main feature is fastening through a mandrel. The presence of a chamfer on the teeth of the element made it possible to achieve correct adjustment of the cut.
Cone countersink design
This device is intended for passing cone-shaped openings of small depth. The main feature in the design of the element is the presence of straight teeth and an absolutely flat outer base. The number of cutting elements, in accordance with calibration, can vary from 6 to 12 units.
Countersinking holes is considered a manual procedure, carried out through a turning unit on which the countersink is mounted. The workpiece is clamped in the machine's grip, and its correct location in the recess is checked. The axial centers of the electric spindle and the rear assembly of the machine must be at the same level. This reduces the risk of the technically movable sleeve (quill) flying out. The tip of the tool is inserted into the hole to be finished manually.
To obtain an opening of the required diameter after the countersinking operation, an allowance of 2-3 mm is made during drilling. The exact allowance values depend on the calibration of the recess in the workpiece being processed. It is more difficult to implement the countersinking process for forged and dense products. To simplify your task, you should bore the countersunk hole by 5-9 mm in advance.
Countersinking can be done in cutting order. In this situation, the tool feed is doubled than when drilling, but the travel speed remains the same. The cutting recess with a countersink is laid at approximately 50 percent of the allowance for the diameter. Countersinking of holes with a tool is carried out using cooling materials. The mechanism made of hard alloys does not require the introduction of auxiliary coolant.
When processing openings, a countersink guarantees high accuracy, but defects cannot be avoided at all. The most common processing defects are:
- Increased opening diameter. The main reason for the occurrence of such a defect is considered to be the use of a device with incorrect sharpening.
- Reduced diameter of the recess. It happens that the wrong tools were chosen for the job or a damaged countersink was used.
- Defiant purity. This flaw can be caused by a number of reasons. Usually, a decrease in cleanliness lies in poor sharpening of the device. In practice, the cause of the defect can also be excessive viscosity of the product material. Therefore, the element sticks to the tool belts. Damage is also caused by the error of the turner, who made an incorrect feed and acceleration of the cut.
- Partial processing of the opening. This reason usually occurs as a result of incorrect fixation of the part or an incorrect countersink allowance saved after drilling.
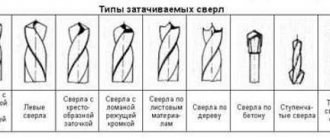
Types and purpose of countersinks
A countersink resembles a type of drill that is used for countersinking. The operation is similar to countersinking, but the final task differs. The countersinking procedure is needed in situations where there is a need to form rounded recesses to hide the marks of the fastener heads.
The cultivation of parts by countersinking is considered a semi-finishing method, and is carried out before the deployment operation.
According to the design of the countersinks, they are divided into:
A separate category includes countersinks consisting of hard alloys. They are used as grinding actions. To process openings and remove chamfers in difficult areas, another type of tool is used - a reverse countersink. To ensure the necessary processing of metal products and wood, it is recommended to purchase a countersinking kit rather than using individual tools.
The structure of the cone-type countersinks accommodates the shank and the operated element, with an angular index of 60, 75, 90 and 120 degrees. The number of teeth varies from 6 to 12 units, depending on the diameter of the tool. To ensure the alignment of the cultivated opening, a trunnion is used.
The rounded countersink has a wear-resistant coating. This mechanism is used for chamfer cutting. In design, it resembles a drill, but has a large number of blades - from 4 to 10, it all depends on the diameter of the device. There is a guiding pin at the end of the element. With its help, the position of the tools during operation is recorded. The trunnion can be detachable or integral. In practice, devices with detachable pins are used due to ease of use. You can also attach an attachment cutter to the countersink.
To process several openings into equal recesses, you should use a countersink with holders, which includes various stops. When processing a product, the cutting element is installed in the holder and moves out of the stop by an amount equal to the recess of the opening.
Countersinks are made from various types of steel, including carbide. Tools made of carbide alloys are excellent for processing metal parts, as they can withstand extreme loads for a long time. For processing products made of non-ferrous metal alloy or wood, devices made of high-speed steel are used, since it is subjected to minor loads. It is worth noting that when processing, for example, cast iron products, it is necessary to introduce additional cooling of the tools. For this purpose, special emulsion compositions are used.
The principle of countersinking metal products
When processing an opening created in a part during its casting, it is recommended to bore it several millimeters deep at once so that the countersink selects the correct initial direction.
During the period of work when processing steel workpieces, it is recommended to use emulsion cooling compounds. The procedure for countersinking non-ferrous metals and cast iron does not require additional coolant. A very important stage is the correct selection of tools for carrying out the work. In this regard, attention is focused on the following aspects:
- The type of tools is selected in accordance with the harvesting materials and the nature of cultivation. The factors of hole location and the number of processes are taken into account.
- Countersinks and a device for countersinking are selected depending on the specified parameters: the size of the recess, diameter, accuracy of work.
- The design of a metal-cutting tool is determined based on the method of its fastening on the machine.
The choice of countersink is made according to reference literature or using the normative act of the GOST 12489-71 standard:
- Blanks made from structural steel with openings up to 40 mm in diameter are processed with a countersink made from high-speed iron, including 3-4 teeth and a diameter of 10-40 mm. In holes up to 80 mm, nozzles with a diameter of 32-80 mm are used.
- For hardened iron, when boring, equipment is provided with plates made of hard alloys, with a diameter of 14-50 mm and 3-4 teeth.
- For boring blind openings of cast iron products and non-ferrous metal parts, a feather countersink is used.
A necessary condition for the countersinking procedure is the observance of allowances. As a result, the diameter of the selected tooling must coincide with the final diameter of the opening after processing. If, after countersinking, the opening is to be expanded, then the diameter of the device is reduced by 0.15-0.3 mm. If rough boring or drilling for countersinking is planned, then the edge allowance should be maintained from 0.5 to 2 mm.
Download GOST
GOST 12489-71 Solid countersinks. Design and dimensions
GOST 14953-80 Conical countersinks. Specifications
oxmetall.ru
Tips for choosing a tool
The main criterion is the type of surface being processed. For working with metal, classic twist drills made of high-speed or alloy steel are perfect.
You should pay attention to the appearance of the instrument. Color can say a lot about the degree of processing:
- Gray or steel. No processing was carried out.
- Black. The countersink was treated with steam.
- Yellow. The internal stress in the tool was relieved by tempering.
- Bright gold. The surface is treated with titanium nitride. This material is highly durable, which extends the life of the drill.
There is a wide selection of tools from various manufacturers on the market. We recommend giving preference only to trusted brands - this will guarantee the quality of the device.
countersinks
Definition
In accordance with GOST 25751-83 “Cutting tools, terms and definitions,” a countersink is defined as “an axial cutting tool for increasing the accuracy of the hole shape and increasing its diameter.” Let us immediately note that this type of tool is not intended directly for drilling holes. Also note that the definition of a countersink does not say anything about changing the shape of the hole. This is an important detail and will be useful later.
Countersink design
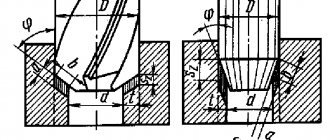
To describe the design of countersinks, it is convenient to divide them into two classes - countersinks with shanks and mounted countersinks. Countersinks with cylindrical and conical shanks The design of such countersinks is in many ways similar to the design of a twist drill (Fig. 1).
Fig.1 Solid countersink with a conical shank: a) for through holes, b) for blind holes, c) with carbide plates
The tool also consists of a working part, a connecting part (neck) and a tail part (shank). The difference from a drill lies in the shape and number of cutting edges on the working part. In particular, according to GOST 12489-77, countersinks have three blades on the end and cylindrical surface.
A countersink with a cylindrical or conical shank can be solid GOST 12489-77 (the entire working part is made of high-speed steel), or with carbide inserts (GOST 3231-71). In addition, each type is available in two versions: for blind and through holes (Fig. 1, c)). For countersinks for through holes, the angle of the main blade φ has values of 45 or 60 degrees, for countersinks with carbide plates φ=600, for all types of countersinks for blind holes φ=900.
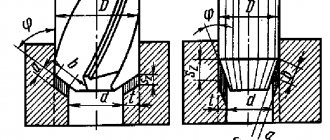
Mounted countersinks
Mounted countersinks do not have a tail section. Instead of a shank for mounting on equipment, they have an internal cone for a mandrel (Fig. 2). This type of design also features a large number of blades. In solid mounted countersinks according to GOST 12489-77, four teeth and, accordingly, four spiral grooves are provided. Further division of mounted countersinks into types is identical to the class with shanks.
Fig.2 Mounted countersink: a) solid, c) with carbide plates
Application of countersinks
Countersinking tools are used in technological countersinking operations aimed at improving the quality of holes - improving surface cleanliness, obtaining a more accurate cylindrical shape. Accordingly, the main part of a countersink is a cylindrical section of the working part. Using countersinking, holes are brought to 4–5 accuracy classes with H11 quality and surface finish corresponding to 5–6 classes. The required result is achieved due to the higher rigidity of the tool, as well as due to a larger number of blades compared to a drill.
We emphasize that all of the listed GOSTs describe countersinks with a working part of an exclusively cylindrical shape. In the descriptions of the designs of standard countersinks there is no wording “conical countersink” and there are no drawings of countersinks with a conical working part. Those. The result of using a standard countersink is a cylindrical hole of constant diameter.
Peculiarities
Wood countersink drills allow you to create holes in the material and process them. Attachments of this type are small products that create recesses for wide fastenings.
Countersinks for such tools are drills with several cutting components, they are most often used to work with conical or cylindrical holes. Such metal elements make it possible to make recesses of different types in the material.
Also, a countersink drill is often used to slightly increase the diameter of the recess and to process already made holes. The difference between a tool with a countersink and other models is that the first option uses more than two blades.
Often such attachments are needed for professional production machines. With this tool, many users grind holes made and process the ends of structures, while hiding all the roughness and other irregularities on the surface.
The rest of the product is called the shank. This element is necessary for connecting the tool to the chuck of a drill or machine tool. This part can also come in different shapes and sizes.
Shanks are available in the following shapes: cylindrical, hexagonal, triangular, tetrahedral or canonical. The first option is the most common; it must correspond to the diameter of the cutting part. So, for a countersink with a larger diameter, a shank with a smaller diameter is used. For some of the smallest drills, shanks slightly larger than themselves can be selected.
The canonical shank is used on an industrial scale. All other varieties can only be used for certain types of cartridges (three-jaw, conventional).
Any user can make a countersink on their own without buying it at a hardware store. To do this, you first need to prepare an unnecessary self-tapping screw or a regular drill; such elements will become the basis for the future product. Then these parts should be trimmed a little by adding several thin blades.
Self-made structures can be customized to an individual configuration if necessary.
Purpose and types of drills with countersinks
First of all, you need to define the concept of “countersink”. It is often confused with another metalworking tool - a countersink. Despite their similar sound, they are intended for completely different processes. Countering a surface is the recessing of the top of a pre-drilled hole.
A countersink drill is a multi-edged metal-cutting tool. It is classified as equipment for semi-finishing of existing holes. Use before applying the reamer.
Universal drills with countersinks are most often used in the woodworking industry. In the serial production of furniture, the quality of the holes comes first. The reliability of the assembly depends on this. The tool in question allows you to get a neat hole for a self-tapping screw with a countersunk head, a screw or other fastener. In addition, a countersink drill increases productivity by reducing machining operations.
The drill plays the role of a guide element, which allows you to obtain a high-precision hole.
In the process of manufacturing middle-class furniture, special fasteners are used - Euro screws. To prepare holes for these hardware, processing devices that look similar to countersink drills are used. They are also classified as combined instruments. The two-stage design allows you to drill a hole and chamfer a Euroscrew in one pass.
Basic definitions
A countersink is a special cutting tool that allows you to make canonical or cylindrical holes. It is used to process finished holes in order to chamfer the center hole.
A countersink is a tool consisting of a certain number of blades designed for cutting. Designed to improve the quality of the hole and expand existing holes, creating holes of cylindrical or canonical shape. Machining holes using a countersink is called countersinking . Countersinking refers to semi-finishing metal processing.
You can come across the wrong concept when they say that a countersink and a countersink are the same thing. Using a countersink, the technical quality of the hole is improved. And it is not intended for making recesses.
Countersinking holes - removing chips or irregularities from a drilled hole. Countering holes is the process of deepening a canonically shaped hole in order to hide the head of a bolt or self-tapping screw. You can also come across the definition of hiding a self-tapping screw in a pattai.
Countersinking a hole
Countersinking of holes - processing of drilled holes for the heads or heads of bolts, screws, hardware.