Design and principle of operation of a water pump and pump
In a private home, it is important to properly organize the water supply system so that it serves for a long time and with high quality. Pumping equipment is used to pump liquid. When choosing a model, they rely on the operating principle and design of water pumps and pumps. Knowing the nuances of the operation of the equipment, it is easy to decide on the choice of unit.
How the mechanism works. The device is based on a core of brass tubes that have a flat oval shape. They are arranged vertically and form 4 plates.
There are racks around it to secure the tanks from below and above. To soften vibrations at the joints between structural elements and the radiator, shock absorbers are used. There is a ventilation hood on the engine side. There is a lining on the front side of the radiator for protection. In addition to the casing, brackets are attached to the radiator stand, onto which the expansion tank is attached.
General information
To understand the principle of operation of the pump and why it is designed this way and not otherwise, you first need to define what an autonomous water supply is. This is a complex system with different effects depending on the type of product. It consists of many elements and provides water under pressure. The key element of this system is the pump, of which there are countless varieties. There is submersible and surface. The predominant manufacturers are:
- China;
- Russia;
- European countries.
But effective operation is ensured only if the equipment is complete with a battery and automation.
The pump sucks water from a source, for example, a well, collects it in a special container, and then delivers it under pressure to the consumer. The main difference between the pumps is in the characteristics and dimensional data. It is important to choose this equipment correctly so that the water supply is ensured at the proper level.
Water pump
The shape of the blades can be either straight or angled, which affects the rotation speed. In high-speed pumps, the vanes come from bushings. Wheels with such blades are fastened with keys. Simple household low-power water pumps use riveted impellers.
The rotor is mounted on a shaft, which transmits torque to it. The shaft is mounted on bearings to eliminate vibration and distortion during operation.
The material for the manufacture of shafts of simple pumps is steel; for pumps with increased loads they are made of alloy steel with an alloy of chromium, nickel or vanadium; shafts for pumps pumping various acids are made of stainless steel. If the shaft is not balanced correctly, vibration may occur, which will cause serious damage to the pump.
There are shafts:
- Flexible: used in pumps with exceeding critical speed;
- Hard: used for quiet operation pumps without high speeds;
- Solid (the pump working shaft also serves as a motor shaft): installed in household pumps in which pump impellers are installed on the electric motor rotor.
Water pump bearings are made with cast iron liners, which are filled with babbitt. They are lubricated with liquid or thick lubricant. Bearings can be roller, ball, rubber, textile, etc. The casing also belongs to the body and is part of it. The rubber gasket between the casing and the body serves for sealing.
The oil seal serves to protect the engine from water and is located at the junction of the working chamber and the rear wall. The seals have soft padding made of cotton, paper or asbestos cord. On the liquid suction side, a water seal is installed on the oil seal. The oil seal device contains a coupling and a sealing ring, to which liquid flows from the discharge pipeline, preventing air from entering the working chamber.
About water supply and its pressure
When planning to choose a liquid pump, you need to look at its parameters. All characteristics are important, but one of the key ones is the water flow rate. It is necessary to calculate how many cubic meters of water the home owner spends per hour to find out which option is suitable.
The next, no less important characteristic is pressure. It indicates with what force the unit will supply water. This parameter is calculated according to how far the water source is from the house. The pressure is lost under the influence of height and forks in the pipeline, so it is better to provide a small margin when calculating.
When looking for a model to use at home, the scope of choice narrows. There are deep and surface pumps. The first are used for wells less than 10 meters deep. They are fixed on a special platform.
The latter are suitable for use in wells and wells whose depth exceeds 10 meters. How the pump is controlled is important. It will be easiest for those whose choice falls on automatic control.
Shaft and bearings
Whatever type of wheel is used, it is mounted on a rotating shaft. The shaft must be secured in the housing with bearings in one of 2 ways:
- Console
- Symmetrical
Cantilever fastening
When the shaft is cantilevered, the impeller is fixed at one end and the bearings at the other.
This design places the suction and discharge ports perpendicular to each other, and the suction port directly in front of the center of the wheel.
Such pumps are called end suction pumps. They are widely used because they are cheap and easy to produce, but they have one drawback related to the path of fluid movement.
During pump operation, a low pressure zone is created in the suction port.
There is a high-pressure zone at the outlet of the wheel, from which the energized fluid enters the spiral casing.
Fluid flows towards the rear plate in open and semi-open wheels, which completely destroys the pressure balance. As a result, an axial force or load occurs - pushing the wheel towards the suction hole.
This can be compensated for by installing stronger bearings or drilling holes in the wheel plate to equalize the pressures. But these are not effective methods.
Symmetrical mounting
A more effective solution is to place the shaft on bearings on both sides. This is called symmetrical design .
Shaft support is improved not only by the placement of bearings on both sides, but also by the ability to use symmetrical closed wheels with double suction.
Since there are the same high and low pressure zones on both sides of the wheel, this successfully eliminates loading forces due to the balance of pressures. This design also has another advantage. The suction and discharge ports are located parallel to each other on opposite sides of the pump, and the housing is axially divided.
By simply unscrewing the bolts and removing the cover, the service technician can access the rotating part of the pump inside without removing the entire pump from the system.
Due to the separate axial design, pumps with a symmetrical bearing arrangement are called split-casing .
All of these, of course, are very good reasons to install such a pump in your mine right now. But there are some disadvantages. Because maintenance operations and sealing requirements are more complex for split casing pumps than for end suction pumps. They are also more expensive.
By the way, read this article too: How a radial piston pump works
Surface and submersible types
The surface pump is mounted outside the well. A pipe comes out from the bottom and goes to the equipment that pumps water. A significant advantage of this model is that it is easy to install and maintain. Thanks to this, if it fails, you do not have to resort to the help of specialists.
The main disadvantages of these pumps:
- Low power reserve.
- Using a fan as a cooling tool, while submersibles cope with overheating using the water around them.
- Limited functionality.
Submersible models are divided into ordinary and deep. They differ in their maximum immersion depth. The advantages of immersion-type products are ease of cooling and the fact that they do not freeze in winter. The design of a water pump of this type, its repair and maintenance are quite problematic, but the frequency with which they have to be used is quite low.
Working principle of a water pump
The main component of the water pump, which carries out the main work, is the rotor or impeller (impeller). Typically, the rotor is made of steel, copper or cast iron. It consists of two disks connected to each other. Between them are curved blades running from the center to the edges. The bend is directed against the axis of rotation of the wheel itself. In the center of the wheel there is a neck (hole), the diameter of which is equal to the diameter of the pipe through which water or any other liquid is sucked in. The pipe and the wheel have a tight connection so that the blades have contact with the incoming water. The rotor blades are located so as to prevent fluid from flowing into the cracks, and there was only free space in the disc grooves.
There are several types of rotors:
- Open (open blades located on one disk);
- Closed;
- Stamped;
- riveted;
- Cast.
To use a water pump, you do not need to have special skills.
The open type rotor differs from the closed type in that the blades are placed on one disk and do not have a covering. Open type rotors are used for pumping very thick liquids and suspensions at low pressure, because These blades are easy to clean. A closed-type rotor, made of one monolithic part, is often installed in simple pumps. Stamped rotors are installed in large and powerful pumps.
Centrifugal and vibration
Centrifugal pumps are more suitable for home use, since their operation scheme is simpler and more efficient. Its design includes a shaft on which the blades are located. In this case, all the pressure force is concentrated at the edges of the blades. But to use this equipment, it is necessary to install a filter, because it does not react well enough to pollution and loses power because of it.
Knowing well the purpose and design of a centrifugal water pump, you can choose the appropriate model. You can check the availability of additional components in the design with the seller.
Vibrating ones do not lose effectiveness due to poor-quality and sand-contaminated water, but constant vibrations lead to silting of the source. As a result, the performance of these devices is less than that of vortex devices.
Design
A pump is a machine that converts mechanical energy into kinetic energy, pumping fluid and electrically transporting it from one point to another.
A centrifugal pump consists of two main components.
- The first is a rotating disk with curved blades. It is called an impeller .
- The second is a specially shaped pipe called a volute casing , which contains the impeller and transport fluid .
There are 5 design elements that may vary:
- type of wheel;
- type of bearing;
- housing location;
- engine mount;
- number of steps.
Control option
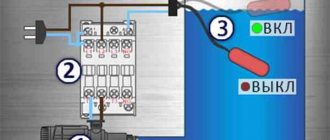
Automatic models can be used over a long period of time without intervention from the user. They have many sensors:
- pressure;
- dry running;
- short circuit protection.
If there is a threat of a short circuit, clogging or any other problem that could lead to equipment failure, the control circuit turns off the pump.
Manual type models are used in a completely different way. Their structure also differs from other species. Repairs to such a unit are required much more often. Therefore, automatic control is more suitable for domestic use. It may cost more, but over time this choice pays off.
Impellers
The impeller is designed to convert the mechanical energy received by the pump from the drive into hydraulic energy and transfer it to the pumped liquid medium (water, wastewater, sludge, etc.). Radial impellers are made for centrifugal pumps. There are several designs of impellers. Let's look at the main ones.
The most common impeller is the one-way closed impeller, which consists of a front (outer) disk and a rear (inner) disk, which goes to the center of the impeller into a hub, which attaches the impeller to the pump shaft (Fig. 27, a). Between the disks there are blades that have either a cylindrical or spatial shape. Impellers of water pumps usually have 6–8 blades, while impellers of sewage pumps have 1–4 blades.
A double entry impeller (see Fig. 25) has a higher flow rate than a single entry impeller of the same diameter.
An open-type impeller is sometimes used in small pumps; it does not have a front disk and mates with the front cover of the pump with a small gap (Fig. 27, b). Pumps with such an impeller have reduced efficiency due to increased hydraulic pressure losses.
In most cases, impellers are made by casting, pouring metal into a mold, and only in special cases, for large pumps, are the impeller disks and blades made separately by casting or other means and then joined by welding.
For the manufacture of impellers, cast iron is mainly used, which provides sufficient strength, simplifies the production technology and reduces their cost. However, when rotating in the impellers of large pumps, high stresses arise from the action of centrifugal force, which can destroy the metal. Therefore, for such pumps, impellers are made of ordinary carbon steel, the strength of which is much higher than cast iron.
For special pumps pumping liquid media containing abrasive materials, impellers are made of manganese and other alloy steel with increased hardness. In some cases, for special pumps, the surface of the flow part of the impeller is lined, that is, lined with various materials (elastic, anti-corrosion, etc.). To supply a liquid medium with increased corrosive properties, pumps with bronze impellers are used. Acid pumps use impellers made of special alloys (iron-silicon, iron-chromium, titanium). In recent years, various plastics and polymer materials have been widely used for the manufacture of impellers.
Grundfos models
It is unlikely that there is a person who has not heard of the products of this company. Now it is the most widespread and largest manufacturer of such equipment, which supplies submersible, vortex, circulation, drainage and vibration models. The buyer, in turn, gets a large selection and can choose any pump depending on his needs.
All equipment from this manufacturer is equipped with many sensors to protect against breakdowns. The range includes pumps of all types of power - both low power for wells and more powerful ones for mine wells. Models are of good quality, from parts to assembly itself.
How the pump works
The pump works like a regular centrifugal water pump, but has a few differences.
There are very compact water pumps, but they are not powerful
This:
- Creates circulation of liquids;
- Has channels for draining and driving liquids.
More powerful pumps have several wheels and are called multistage. Ceramic rotors are installed in pumps used for pumping rubber or other thick materials.
In addition to domestic needs, the water pump or water pump plays an important role in the operation of the car engine, providing cooling to internal combustion engines. It ensures forced, uniform circulation of coolant throughout the engine cooling system: from the radiator to the expansion tank.
Consumer Reviews
To select a suitable pump, you need to know well the conditions of its use and the characteristics of the model. But it doesn’t hurt to study what consumers think about them. The problem is that all manufacturers praise their products, but not everyone can boast of good reviews. Many people have bitter experiences with the chosen product. They can share it completely free of charge.
It is not worth buying equipment from a Chinese manufacturer, because the quality leaves much to be desired. This is the opinion of users. But buyers report that there will be no difficulties with equipment from Vilo, the main supplier from Europe. And SAER pumps are repaired in service centers for a long time and often. It is better to look for a middle ground when good price and quality are combined.
Frame
It is made in the shape of a spiral with a decreasing radius, similar to a snail shell. The cavity of this body does not remain the same throughout. The flow area increases as you approach the pressure pipe.
Where the volute casing ends and the discharge pipe begins there is a protruding wedge called a cutwater .
It physically separates the volute housing from the discharge port and ensures that fluid leaves the pump rather than simply spinning around in the volute housing.
The flared part of the volute casing is very important, because with the help of it the pump creates pressure.
Review of domestic products
Domestic manufacturers cannot boast of quality. An example would be the “Bison ZNVP-300−25”, popularly called “Rodnichok”. It is perfect for shallow wells - up to 5 meters. This vibration type pump can deliver 1400 l/h at a head of 60 meters. This is quite enough for home use.
Another simple model from the Russian one. It has similar characteristics to the previous model, but demonstrates low productivity - 700 liters per hour. 0.2 kW - this is its power, this explains the low productivity. The only good thing is the price: with the listed characteristics it does not exceed 1100 rubles. This is an excellent choice for those whose well is shallow (no deeper than 10 meters).
Rules for the technical operation of centrifugal pumps
Safety precautions when operating the pumping unit
Before using the pump, you must check:
- presence and reliability of fastening of the protective casing of the coupling half of the pump and electric motor;
- presence and serviceability of grounding;
- serviceability of conductive electrical wires;
- insulation resistance of the drive motor;
- the presence of a rug and a wooden stand at the electric motor starting remote control;
- availability and serviceability of control devices;
- water level in the tank;
- reliability of fastenings of all installation elements;
- absence of foreign objects on the installation elements.
Operating procedure for the pumping unit:
- study the installation, as well as the purpose of each of its elements;
- fully open the suction valve and fully close the discharge valve.
After starting the pump, you need to let it run for 1-1.5 minutes. to steady state.
After this, the discharge valve must be opened until the liquid begins to move, which is determined by the meter.
Next, you need to open the discharge valve.
When the discharge valve is fully open, the maximum pump performance is determined.
Surge
Surge or self-oscillations of the flow, i.e. flow disruption or its reversal occurs when there is a sharp change in the pump speed and a rapid change in pump parameters (flow, pressure) by the consumer. As a result, spontaneous fluctuations in parameters occur - pressure, flow and power of the pump, accompanied by pops, knocks and even shocks in the pump and pipeline.
Literature
Ship auxiliary mechanisms - Karamushko, Lukyanov [1968] Operation of ship auxiliary mechanisms, systems and devices - Popov V.V. [2021] Pumps and pumping stations - Yu. V. Anikin, N. S. Tsarev, L. I. Ushakova [2018]
- Equipment for marine diesel cooling systems
- Jet pumps - operating principle and classification
- Basic malfunctions in the operation of centrifugal pumps
- Piston pumps - operating principle and classification
- Purpose and classification of ship pumps
Equipment from Karcher and Vilo
German equipment is valued all over the world. These are good pumps with excellent performance and last a long time. The only drawback is the price. For example, SPP 33 Inox 1.645−409 costs 13,000 rubles.
Pumps from the Vilo brand used in everyday life are almost universal. The price is lower than its German counterpart , but the quality is identical. Millions of users of such equipment are convinced of this, whose messages can be seen on thematic forums and various websites.
When choosing a pump, such characteristics as pressure, power, service life, and quality are important. It is better to trust good domestic products. Buying a European pump is more expensive, but it does not always last long. It is important to pay attention to how the equipment will be installed and how well it will be maintained.
What is a water pump?
Depending on the operating principle of creating a vacuum chamber, pumps vary.
Namely:
- Centrifugal;
- Vibrating;
- Vortex.
A centrifugal water pump pumps liquid by rotating an impeller. Rotating, the impeller creates centrifugal force, which displaces flows of liquid or water over long distances. Due to this, the pressure in the center of the operating impeller decreases, resulting in an influx of liquid.
In order for the water pump to serve for a long time, it must be serviced promptly.
The working force of vibration water pumps is an electromagnetic motor. The magnet, under the influence of alternating current, attracts and releases the piston, causing it to change its position dozens of times per second. The resulting vibration vibrations contribute to the absorption of liquid into the working chamber. The liquid is then pushed into the pressure pipe through the valve. The vortex pump has a flat disk with radially arranged blades in its housing. The vacuum is created by the rotation of a rotor with peripheral blades.
One type of water pump is a water pump. A water pump is a device with a mechanical or electromechanical drive that circulates liquid and draws water from a well or well.
The pump consists of:
- Housings;
- Impellers;
- Vala;
- Pump chamber seal.
Water pumps are also used to operate transport engines, on submarines to operate ballast tanks, and on ship docks to pump and pump out water.
Circles of circulation
Installation and installation of the oil pump VAZ 2108-2109-21099
The cooling system in the car has two circulation circles: large and small. The small one is considered the main one, since when the unit is started, coolant immediately begins to circulate through it. In the operation of the small circle, only the channels of the cylinder block, the pump, and the interior heating radiator are involved. Circulation takes place in a small circle until the internal combustion engine reaches normal operating temperature, after which the thermostat activates and opens the large circle. Thanks to this system, engine warm-up is significantly reduced, and in winter, the system does not so much cool the unit as maintain its normal temperature regime.
Small and large coolant circulation circles
The operation of the large circle involves a fan, a cooling radiator, inlet and outlet channels, a thermostat, an expansion barrel, as well as those elements that take part in the functioning of the small circle. The outer circle, also known as the large circle, begins to work when the coolant temperature reaches 80-90°C and ensures its cooling.