Knocking and rattling in the cylinder and piston group
One of the reasons for compressor failure is a faulty piston group.
Recognizing a defect in this system is quite simple. They are usually accompanied by knocking, roaring, grinding and other metallic sounds. If the compressor knocks, then its discharge part, where there are many metal parts that interact with each other, is faulty. Due to their friction and wear, extraneous noise and unpleasant sounds appear. You should not start with such a breakdown; if possible, you should fix it as soon as you hear the first signs of their manifestation. Main malfunctions if the compressor begins to knock and operate louder than before:
- Broken, worn out bearings, connecting rod bushings
- The bearings on the crankshaft have failed.
- Worn piston, rings, piston pin
- Worn cylinder
- Loose cylinder and head bolts
- A solid particle has entered the cylinder
- The cooling impeller has become loose on the pulley
- Changing the diameter of the piston, cylinder
- Distortion of the shape of the cylinder mirror shape
- Risks, scratches, burrs on the cylinder walls
- Cracks in the main working part
- Cracks and broken flanges
During long-term operation, due to wear, marks appear on the cylinder surface, and the inner diameter of the sleeve for the eccentric shaft increases. During repairs, cylinders are restored by pressing sleeves into them. Worn bushings for the eccentric shaft are replaced. This repair is quite difficult to do with your own hands without the necessary tools and equipment. Since the most labor-intensive and critical stage is the restoration of the cylinder. Boring is performed on a vertical boring machine using a special device.
This concerns the cylinder; below we will consider the main malfunctions of the compressor crankcase.
- Cracks in the walls of the crankcase cavities
- Deviations in the size and shape of landing pads
- Warping of seats
- Seats for crankshaft bearings are broken
When these units wear out, they must be replaced with new ones. The hole for the bearings is bored on a horizontal boring machine for a larger diameter of the bearings or for pressing in a bushing, followed by boring the pressed bushing to the required diameter. Repair of a compressor of this complexity should be carried out by qualified specialists.
Below, spare parts “repair kit” for major repairs of the compressor and piston group.
The compressor gets very hot
If the compressor gets very hot, this indicates some kind of malfunction. There may be several reasons for overheating. Starting with a simple one, the air flow to the cylinder and crankcase is blocked. Check whether the impeller is blocked by foreign objects.
One of the main reasons for an overheating compressor is insufficient oil level. The working units wear out, high friction is created and as a result it gets very hot. If such work continues, the equipment will quickly fail. Check the oil level; if it is not enough, you need to add it to the required level.
Valve malfunctions due to carbonation or loosening. There may also be clogged air passages.
Look at the pressure level, perhaps the automation has broken down and the compressor is “threshing” to high pressure, this causes overheating. The safety valve may need to be repaired or replaced.
Try to locate the compressor in a cool, spacious place, especially during the hot season. Whatever cooling it has, it will heat up much less, which will affect its positive and durable operation.” Also, do not forget that the colder the air, the less moisture and oil impurities it contains.
Pressure regulation of a piston compressor
During operation of the compressor, it may be necessary to adjust the pressure according to the specified parameters or shift the on/off threshold at the lower and upper pressure. In this article we will take a detailed look at how you can do this yourself, without contacting customer service.
So, before we give specific recommendations, let's remember some of the operating features of piston compressors. One of them is that piston compressors have an intermittent operating mode, that is, they cannot operate continuously. In the passport for piston compressors you can read that a piston compressor can operate continuously for no more than 15-20 minutes per hour. However, if the compressor is selected correctly, then on average in 3-5 minutes the piston unit manages to force air into the receiver, only to then be forced to shut down. Otherwise, the piston block may overheat due to high temperatures. Therefore, having collected the required amount of compressed air into the receiver, the compressor turns off. This shutdown is carried out automatically - the so-called pressure switch. The task of the pressure switch is to open the electrical circuit that powers the engine. After this, the engine stops rotating and therefore does not drive the compressor pistons. Then, when the pressure in the receiver drops to a minimum level, the automation restarts the engine and the compressor begins to pump air again. The second feature of the operation of a piston compressor is that the difference between the minimum and maximum pressure, that is, between the lower and upper threshold, is 2 bar. This difference, as a rule, is already set by the manufacturer and should not be adjusted by the user.
But sometimes there are situations when it is still necessary to change the working pressure. Then you can call a specialist, or try to do it yourself.
However, you need to remember that you can adjust the pressure to the required value (highest and lowest) only in the lower direction. If you increase the pressure beyond the permissible limit, the safety valve will operate.
The principle of operation of a pressure switch (pressure switch) is to compare two forces, on the one hand there is an elastic spring, on the other there is gas pressure on the membrane.
Now let’s look in detail at how to adjust the working pressure on the pressure switch. To begin, record the on/off values on the compressor pressure gauge, that is, the upper and lower thresholds. Then, disconnect the compressor from the mains and remove the top plastic cover from the pressure switch.
Under it, you will see regulators in the form of two threaded bolts, one large, the other small. The large bolt regulates the compressor's upper cut-out pressure and is usually identified by the letter "P" and an arrow with "+" and "-" signs. It is necessary to turn the bolt in the desired direction: if upward, then towards “+”, if downward, then back. Next, we follow the experimental path, making half a turn and turning on the compressor using a pressure gauge and checking the upper shutdown threshold.
With a small bolt you can adjust the difference between the on and off pressure, it is indicated by “ΔP” and the corresponding arrow. Let us remind you once again that the difference between the minimum and maximum pressure, that is, between the lower and upper threshold, is 2 bar. It must be remembered that the greater this difference, the less often the compressor will turn on and the higher the pressure drop in the system. The adjustment process is similar to adjusting the upper pressure.
Another, less complicated way to regulate compressor pressure is to use a pressure regulator, or also called a pressure reducing valve.
Thus, all the rules described above for adjusting pressure on piston compressors will help you independently, experimentally, adjust the desired pressure without contacting a service center.
Source
Popular compressors according to customers
Compressor PATRIOT Euro 24-240 on Yandex Market
Compressor Denzel PC 50-260 on Yandex Market
Compressor Metabo Basic 250-24 W on Yandex Market
Compressor Quattro Elementi KM 24-260 on Yandex Market
Compressor Quattro Elementi KM 50-380 on Yandex Market
The intake (unload) valve controls your rotary screw compressor's capacity (the amount of air your air compressor sucks in). By opening and closing the air inlet, the performance of the screw compressor is regulated. When the desired pressure is reached, the compressor goes into unload mode: the unload valve closes the air intake almost completely. This way, no more air can be sucked in and compressed, so the compressor screws just spin without doing anything. At the same time, the pressure that is still present inside the screw block is released through a small hole (you will hear a hissing sound).
What to pay attention to
Before purchasing a valve, first take into account such a circumstance as the intensity of the existing air flow. In other systems it may be liquid or gas. This circumstance directly affects the startup and error-free operation of the installed valve.
In addition, you need to take into account that the performance coefficients of the air purifying unit are interrelated with the power data of the pumping device, be it a pump or a fan. When choosing a valve, take into account the temperature conditions in the room and the environment in which the device will be installed. The level of environmental pollution is also significant. For example, a unit of the “butterfly” variety, when exposed to a stream of cold air, begins to significantly slow down. This can lead to poor fusion between the duct and the mechanism as a whole. The cost of the valve can fluctuate insignificantly and directly depends on the technical parameters and the company that developed the mechanism.
Recommendations for selection
When choosing a check valve, you should consider a number of parameters. These include, in particular:
- the intensity of the air flow that will be transported through the system;
- the performance of the air exchange device on which the check valve will be installed;
- the power of the air pumping device, which can be a compressor or fan;
- the degree of contamination of the working environment that will be transported through the elements of the system being created;
- temperature operating conditions.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the type of medium with which the elements of the valve device will come into contact. This parameter has a direct impact on the choice of valve material, which must have the required durability.
Main types
Check valve mechanisms are divided into:
- straight view;
- corner;
- spring;
- ball;
- installed using flanges;
- casement;
- installed by soldering;
- produced for beading.
Still, there is one main drawback: such an air valve is placed on the absorption tank and has a very negative effect on the combined cooling capacity.
In any case, regardless of the type and intended purpose of the mechanism, you must carefully ensure that foreign particles do not fall on the clearance part. Otherwise, even when in the closed position, the shut-off valve will not be able to fully guarantee its functionality.
In order to install any of them (meaning a type of valve), you must take into account the setup and configuration of the system. In addition, these installations are distinguished based on the specifics of their shape (square and round) and the product from which they are made. Each of the products used has its own specifics. Based on this, many mechanisms are equipped with units made using plastic, and some with metal units.
Nowadays the most popular type is the plastic valve. The throughput capacity of this mechanism is up to 6 m/s. This value is achieved due to the noiselessness when switching on and off the operating components. Such a modification of the unit can operate either with the help of a valve supplied for exhaust, or independently. It should be noted that this variety is not very popular among buyers due to being replaced by more economical analogues. Today you can purchase the most popular type of valve for compressors - the so-called “butterfly”.
These devices are made using metal, and the top is treated with a thin galvanized layer. The mechanism is equipped with two rotating blades, which are attached to the central axis. When the exhaust manifold is disconnected, the parts become short-circuited. The butterfly valve is sold in several versions, the dimensions of which range from 31 cm.
From Wikipedia - the free encyclopedia
Unloading valve
- a hydraulic or pneumatic device designed to work in conjunction with a pump/compressor. Unloading valves can both relieve pressure behind the machine after it stops to facilitate restarting (as a rule, they are installed behind compressors), and transfer the machine to zero capacity in the absence of liquid/gas flow - such valves (as well as more complex devices - unloading machines) used with unregulated pumps and compressors that have a non-switchable mechanical drive (hydraulic pumps installed on aircraft engines, compressors of cars and some diesel locomotives). A device to facilitate starting is usually assembled from two conventional valves - an electromagnetic valve (the unloading valve itself), which releases air from the line behind the compressor after the compressor is turned off, and a check valve that prevents air from leaving the consumer network through the unloading valve.
Three-valve pressure regulator 3RD
installed on diesel locomotives TEM2, TEP60, 2TE10 of all indexes, TGM6 and others. On most of the listed diesel locomotives, the compressor has a permanent, non-disconnectable drive from the diesel crankshaft and the 3RD controls the unloading of the KT-6 or KT-7 compressor (transfer to zero supply), on the TGM6 the fluid coupling filling spool moves from the 3RD - as a result, oil is released from it and the compressor stops . In the cylinder heads of the KT-6 and KT-7 compressors, pneumatic cylinders are installed, when air is supplied into which the suction valve plates are pressed off their seats and the valves cease to perform their function - they do not keep air from leaving the cylinders back into the atmosphere during compression, as a result the compressor stops supplying air.
3RD consists of three valves - a shut-off valve, which rises at a pressure in the main tanks of 9 kg/cm2, an on-off valve, which rises at a pressure of 7.5 kg/cm2, and a return valve, which is pressed by the on-off valve. The shut-off valve, rising, opens the air passage to the switch-on valve, which also rises and opens the check valve, opening the air passage to the switch-on valve (so that the air supply to it does not stop immediately when the shut-off valve closes when the pressure drops below 9 kg/cm 2) and compressor shutdown device. When the pressure drops below 7.5 kg/cm2, the switching valve lowers, air leaves the compressor shut-off device, the pressure rises and the cycle repeats.
Automatic pump unloader
(for example, type GA-77) works in a similar way, but its inclusion in the system is different. Until the pressure in the system reaches the nominal value (on An-24 and Yak-40 class aircraft - 155 kg/cm2, on medium and heavy aircraft - 210 kg/cm2), the pump is connected to the system - it supplies liquid to charge the hydraulic accumulators through the return machine valve. When the nominal pressure is reached, the spool of the machine connects the pump to the drain line, the check valve closes under pressure from the hydraulic accumulators and the pump pumps liquid in a circle - from the tank back to the tank, which is necessary for cooling and lubrication of the pump, and the system is powered by the hydraulic accumulators. The moment of unloading is clearly observed at electric pumping stations - the current consumed by the engine drops sharply, and an increase in the speed of the unit is also audibly perceived.
When the pressure in the hydraulic accumulators drops to the threshold (at a nominal pressure of 155 kg/cm2 - up to 120 kg/cm2), liquid from the pump is again supplied to the check valve and through it into the system. If the machine does not operate and does not switch the pump to unloading, then if the pressure exceeds the nominal (at a nominal pressure of 155 kg/cm2 - 170 kg/cm2), the safety valve is activated and the liquid from the pump is drained into the tank through it, but the pump works with overload, energy is spent on heating the liquid.
Main varieties
The receiver valve in question can be classified according to a fairly large number of characteristics, the main one being the design features of the mechanism. The following execution options are available:
- Angular.
- Straight type.
- Ball.
- Spring.
- Attached by flange.
- Casement.
- Installed using soldering technology.
- Made for beading.
The classification is carried out according to the type of material used in manufacturing. Most often, the valve is made of metal with high corrosion resistance, but there are other options.
The locking element is also characterized by various design features. Based on this feature, the following execution options are distinguished:
- Ball.
- Membrane.
- With flat plate.
- Petalaceae.
- With gravity grid.
In addition, there are versions on sale in which the locking element is controlled by an electromagnetic element rather than a spring. They are more accurate in operation, but are much more expensive.
Safety valve
The relief valve (another name is safety) valve serves for emergency release of pressure and is the final device that protects the pneumatic equipment connected to the compressor from damage.
Experts also include the following types of relief valve:
- bypass valve;
- unloading valve.
Despite minor design differences, their operating principle is identical to a safety valve.
Operating principle of the safety valve
Compressor equipment that is not intended for use in industrial environments is equipped with spring-loaded safety valves. When such a compressor operates in normal mode, it is closed (see diagram). In this case, the air pressure on its plate is balanced by a calibrated spring, which prevents the locking mechanism from opening. If the pressure suddenly increases above the set value, the pressing force of the plate against the nozzle decreases and the valve begins to open. This releases excess air, after which the locking mechanism can return to its place.
Bypass valve
The bypass (or overflow) valve maintains the pressure of the working medium at a given level. To do this, through the existing branch there is a constant, and not one-time or periodic, as in a safety valve, removal of an excess amount of the working medium (compressed air, gas, liquid), which ensures pressure stability in the system. Such valves are used, for example, in turbochargers installed on automobile internal combustion engines.
Unloading valve
The unloading valve ensures the release of compressed air remaining in the manifold between the piston block and the return line when the compressor stops. In this case, the pressure at the compressor outlet is reduced to atmospheric pressure. In general, the presence of an unloading valve makes it possible to:
- relieve pressure in the line when the compressor is turned off;
- transfer the compressor to zero capacity in the absence of flow of working fluid;
- facilitate restarting of both the compressor and the connected pneumatic equipment.
In addition, the unloading valve is used in cases where it is not possible to turn off the mechanical drive of the connected pneumatic equipment. Install it at the compressor outlet in front of the return line.
So, the more productive and powerful the compressor equipment, the more complex the valve system. The simplest check valve for use in a household low-pressure compressor can be made by yourself. But for the installation to work correctly, it is recommended to purchase a factory-made part.
Purpose, design features and scope of application
There are quite a large number of protective safety devices that can significantly increase the service life of the compressor. The device in question has design features that make it possible to control the movement of the medium in only one direction. In other words, the valve prevents the reverse flow of compressed air, for example, when the device stops operating. The check valve for the compressor is represented by a combination of the following elements:
- Metal body. It is characterized by high resistance to environmental influences.
- Rubber ring.
- A spring that fits over the guide lugs.
- A plug that ensures the mechanism is closed.
- Sealing gasket. It significantly increases the degree of tightness of the check valve.
- Hole for connecting the compressor unloading valve.
A similar compressor check valve device is designed to relieve excess pressure in the system, as well as prevent return air flow. The design is also made by hand to achieve a similar goal. The operating principle is characterized by the following features:
- Air under pressure is supplied to the inlet. It can have a wide variety of diameters.
- The created pressure compresses the spring, due to which the passage hole opens. The spring is made of a special corrosion-resistant material, which ensures a long service life.
- When the compressor is turned off, the spring returns to its position and the line is closed. Due to this, the possibility of reverse flow of the medium is eliminated.
The above information indicates that the design of the mechanism is quite simple and reliable in operation. The purpose and features of the mechanism determine its very wide distribution.
How to make a check valve for a compressor with your own hands
The modern market offers a wide variety of check valves for compressors of various types and capacities. Meanwhile, if you want to save money, you can make a valve for the compressor yourself. In order to make such a valve, it is not necessary to know the structure of an air compressor; it is enough to understand how such a compressor works. Moreover, you will not need expensive consumables and complex equipment, as well as special knowledge, skills and experience in performing work of this kind.
To make a check air valve for a receiver, compressor, vacuum chamber or any other element of a pneumatic system, you will need the following materials and tools:
- a regular fitting or a fitting with a 15 thread;
- fittings that are equipped with hoses for connecting plumbing fixtures;
- bolt with a diameter of 3 mm and a length of 40–50 mm;
- two nuts of the corresponding diameter;
- a piece of rubber cut from an old car inner tube;
- a spring whose diameter corresponds to the transverse size of the bolt;
- standard set of locksmith tools.
The fitting for the valve can be taken from an old plumbing or gas hose.
You can make a check valve for a compressor yourself using the following algorithm.
- A rectangular plate is cut out of a thin metal sheet to act as a stop for the bolt used to secure the valve. A hole is drilled in the middle part of such a plate into which the bolt should pass freely.
- At the end of the fitting, a seat is cut out on which the fixing plate will rest.
- A valve of the appropriate diameter is cut out of a piece of a car inner tube, in the middle part of which a hole is made for a bolt.
- A metal retaining plate and a spring are put on the bolt, and then a nut is screwed onto its threaded part, a rubber valve is put on, which is secured through a washer with a second nut.
- The assembled structure is inserted into the fitting and secured on both sides with nuts removed from the plumbing hose.
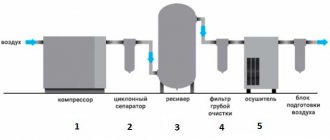
An air compressor is a unit whose operating principle is based on compressing and supplying air to pneumatic equipment under the required pressure. Such installations are an indispensable element both in everyday life and in industry, being an autonomously functioning technical unit or being included in more complex electrical appliances (for example, climate control or refrigeration equipment). The schematic diagram of any compressor includes a working chamber and a valve system. And since these devices, like any other mechanisms, can break down, you need to know how they are designed, what types of valves there are, how to choose them correctly or make them yourself. More on all this in the material below.
Purpose, design features and scope of application
A check valve installed at the outlet of the compressor head allows compressed air to pass in only one direction - to the receiver or any other reservoir. Thus, this valve prevents the return of compressed air located in the receiver or other elements of the pneumatic system back to the compressor. The greatest risk of compressed air returning from the pneumatic system to the inside of the compressor is during breaks in the operation of the device (if the compressor discharge valves do not fit tightly to the seats), as well as at the time of its startup.
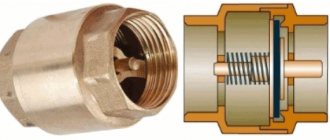
The design of a typical compressor valve consists of the following elements:
- metal case;
- the inlet hole, which is closed by a valve (to prevent the latter from skewing during its operation, guide ribs are specially made on it);
- rubber ring;
- a spring that fits onto the valve guides;
- cork;
- sealing gaskets.
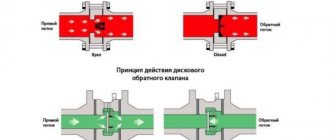
Compressor check valve device
In the check valve body, in addition to the hole through which it is connected to the compressor using a fitting, there is one more hole: the compressor unloading valve is connected to it. The purpose of such a safety valve on the compressor is to prevent the permissible pressure in the working chamber from exceeding.
The operating principle of compressor check valves is as follows.
- The compressed air generated by the compressor enters the valve inlet.
- Under the influence of compressed air pressure, the spring is compressed, opening the valve and allowing air into the pneumatic system.
- After the compressor is turned off and the air pressure in the working chamber drops, the spring expands and blocks the air line.
Working principle of the air check valve
If the air pressure in the working chamber at the moment when the compressor is turned off exceeds the permissible value, the safety valve, also installed at the outlet of the device, is activated. The design of the compressor unloading or safety valve uses a ball-type locking element, pressed against the edges of the inlet opening by a special spring. If the force created on such a ball by compressed air exceeds that to which the spring is adjusted, the valve opens, due to which the pressure is normalized.
Safety valves in pneumatic systems can also be installed on tanks, in particular on receivers. In this case, the purpose of such valves is to prevent a decrease in the pressure of the compressed air pumped into the tank.
Brass check valves for compressor installations
Devices operating on the principle of a check valve, that is, cutting off the flow of the working medium when it moves in the wrong direction, are used in various fields. In particular, they are used for installation in:
- systems designed for suction of liquid media;
- pipelines through which hot gases are transported;
- piping systems used in refrigeration units;
- air conditioning and ventilation systems;
- sewer systems.
Check valves used in systems for transporting liquid media are designed to prevent these media from entering the compressor, which may become unusable as a result. When transporting hot gases, these devices are also used to prevent gases from reaching other elements of the system.
Non-return valve (siphon) for air conditioner. Designed to connect the drainage pipeline to the central sewerage system
Exploitation
The longevity of the protective mechanisms depends on compliance with all technical operating conditions. During operation of the protective unit, the following defects may occur due to wear of the main parts:
- Seat leak. The defect may occur as a result of metal shavings and scratches on the seat. The defect can be eliminated by grinding in the seat or replacing it with a similar fitting.
- Low opening pressure of the device due to the valve spring losing its elastic properties or misadjustment of the setting. To eliminate the failure, you need to replace the spring or the fitting itself, adjust the pressure, check the operation and put a seal.
- If it is necessary to replace the unit for repair, then a plug or valve cannot be temporarily installed in its place. It is necessary, for the safety of the facility, to first select a valve with exactly the same characteristics, and only install it instead of the removed one.
- If pulsation occurs during operation, rapid opening and closing of the device valve, then such a defect can cause unwanted vibration of the pipelines, which can lead to their deformation. The reason may be a mismatch between the cross-sectional sizes of the main pipeline and the pipeline connected to the unit. To eliminate the defect, it is necessary to install pipes of the same cross-section during installation.
Productivity has dropped
A drop in performance can be due to several reasons. The suction air filter is clogged and clogged. Remove and clean the filter with compressed air or replace it. Basically, in piston compressors it is made of ordinary foam rubber.
There may be an air leak somewhere. Inspect all incoming and outgoing tubes and hoses. Just as in the previous case, wear and incorrect operation of the valves is possible, this greatly affects performance. With sufficiently long use, the piston rings wear out and sealing is lost. In more serious cases, the cylinder and pistons are worn, scratched or have other external defects, which leads to a loss of compression and the compressor stops pumping air.
It is worth checking the tension of the belt connecting the electric motor and the crankshaft of the piston system. If loosened, slippage may occur and the compressor will no longer pump air properly.
Types of check valves
There are 3 types of air returns.
- Aluminum (internal) check valve. This compressor part is considered the most durable, since it can withstand the temperature of the air passed through up to 200°C. The only drawback of this part is the rather high price, about 600 rubles.
The part is installed inside the air duct running from the cylinder to the receiver using a coupling.
Plastic return. Check valves made of plastic can be seen, for example, on the S-412 and K-24 units of the Bezhetsky class=»aligncenter» width=»600″ height=»471″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=”https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/8/9/b/89be8446429f2778614b91a235395b39.jpeg” class=”aligncenter” width=”967″ height=”763″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=”https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/5/5/5/5550aadb355338c8c69faafdb009ad8e.jpeg” class=”aligncenter” width=”933″ height=”960″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=”https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/1/e/7/1e7725c4a1dcb2dc0e504bf589c377fa.jpeg” class=”aligncenter” width=”2048″ height=”1536″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=”https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/2/a/f/2afadc121250905436d974714de613fb.jpeg” class=”aligncenter” width=”972″ height=”630″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=”https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/9/6/8/9680cf45fadc8c0251628ff0f003087c.jpeg” class=”aligncenter” width=”1024″ height=”730″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=”https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/f/5/a/f5a4452cd03739920062a4496e4c8b13.jpeg” class=”aligncenter” width=”409″ height=”306″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=”https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/6/0/c/60c56360c7dff16f2d91361d8bfeecf1.jpeg” class=”aligncenter” width=”640″ height=”480″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=”https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/8/5/f/85f8fba3edb2413ac3d4204e11394f44.jpeg” class=”aligncenter” width=”368″ height=”250″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=”https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/a/3/8/a38b8692531a21a25b9e86fcc49d8a8c.jpeg” class=”aligncenter” width=”500″ height=”400″|fcw3qayjh5a| src=»https://armatool.ru/wp-content/uploads/6/f/1/6f1f0536b5fe14b2e88f708ddc7a261c.jpeg» class=»aligncenter» width=»1000″ height=»1000″[/img]
Return line made of brass. It is used on most models of compressors from different manufacturers and costs about 250 rubles. Although this unit is made mainly of metal, it fails if the air temperature during compression exceeds 140°C.
Overpressure relief valve
An excess air pressure relief valve is a simple but reliable device that ensures the safety of compressors. If the permissible pressure in the system is exceeded, it will perform an emergency release of air into the atmosphere. Safety valves must be installed and operated correctly - only then can they protect you from an accident.
Application of safety devices
To ensure safe operation, a safety fitting is a must for any pressure system.
Depending on their purpose, they can be installed in the following places:
- Hot water supply and heating. The safety valve for the heating system is installed on the pipelines after the supply pump. Since hot water is corrosive, the discharge must be directed to a safe location, usually a drain. At high costs, the number of units can reach 2 or more.
- The plumbing fitting for cold water supply is installed in drinking water supply pipelines. The discharge is made directly to the ground.
- Hydraulic system. Hydraulic oils are used as the working fluid. The hydraulic system serves to drive working mechanisms: hydraulic motors, hydraulic cylinders. The safety fitting is installed on pipes, or can be part of a pump or hydraulic distributor. The oil is discharged into the drain line.
- Gas supply pipelines. An increase in pressure in the pipes can lead to an emergency situation - flame separation from the burners, accumulation of excess gas and an explosion in the room. Therefore, the fittings are installed immediately after the pressure regulator, and the discharge is carried out into the atmosphere.
- Air system, compressors. A protective device is installed in the compressor housing and is discharged into the atmosphere.
Compressor safety fitting
Design and principle of operation of the pressure regulator
A gas pressure regulator or pressure reducing valve is designed to reduce the pressure in the line diverted from the main line and maintain this pressure at a constant level.
Pressure regulators are used to maintain the pressure required for the operation of pneumatic, gas or other equipment.
For example, pressure reducing valves are installed on gas cylinders and allow you to adjust the required pressure in the line discharged to the consumer. Reducing valves installed on cylinders are often called pressure reducers, since they reduce or reduce the pressure in the outlet line (reduction - reduction, reduction, reduction).
Purpose of the air collector or why do you need a receiver in the compressor?
Among all types of installations designed to compress various media, piston and screw units are most widespread. The former compress air due to the reciprocating movement of the piston. In this case, a vacuum or an increase in pressure alternately occurs in the cylinder. As a result, in the case of direct connection, pulsation occurs in the pneumatic system of the enterprise. When operating screw units, this effect is not so pronounced, but is also present.
At the same time, we note that a significant part of pneumatic equipment is sensitive to the quality of the compressed air supply, therefore, with constant pulsation in the system, it quickly fails. The solution to the problem was the use of air collectors, which dampen the surge and ensure a stable supply of compressed air to the tool. However, pressure equalization is an important, but not the only answer to the question of why a receiver is needed in a compressor. In addition, tanks solve other problems, including:
Air accumulation. Using an air collector, you can eliminate the problem of peak loads that arise in an enterprise when a large number of consumers are simultaneously connected. Without using a receiver, this problem can only be solved by replacing the compressor with a more powerful model, which is most often impractical due to the high cost of the units. Additional cooling and condensate removal. In accordance with the laws of physics, during compression the temperature of the working medium increases. After the air enters the plant's pneumatic system, it cools down again. In this case, the moisture contained in it falls out in the form of condensation. This leads to metal corrosion and equipment damage. The receiver solves this problem too. It is built in between the compressor and consumers. A decrease in the temperature of the working environment and condensation occurs precisely in the air collector, as a result, the equipment is reliably protected from moisture. The latter, by the way, is removed from the receiver through a special drain valve. Reduced vibration. Both gasoline and diesel internal combustion engines, as well as electric motors, vibrate during operation.
It is important to note that an increase in vibration leads to an increase in the level of noise pollution in the room, as well as to the destruction of the base on which the unit is installed. The use of an air accumulator with a volume of 500 liters or more can significantly reduce engine vibration.
We have listed the main answers to the question of why a receiver is needed in a compressor. As for other significant functions of the air tank, these include:
- additional cleaning of the working environment from dust and other contaminants;
- increasing the energy efficiency of equipment;
- reduction of compressor on/off cycles;
- reduction of compressed air cooling costs;
- neutralization of turbulence that is formed during gas injection.
As you can see, air receivers solve many problems related to ensuring stable operation of consumers. Practice shows that in many cases normal operation of an enterprise is impossible without the use of air accumulators. And where it is possible to do without them, installing a receiver reduces operating costs, extends the service life of equipment, and increases the efficiency of equipment.
Note! In telling why a receiver is needed in a compressor, we did not pursue advertising purposes. The main objective of this article is to provide you with the most detailed information about air accumulators
Should I buy a receiver for the compressor or not? Each user makes this decision independently. For our part, we are ready to advise you on all issues. If after reading the material there are still any uncertainties, contact our specialists for additional information or assistance in choosing a receiver.
Prepared by: Dmitry Zaporozhtsev
Compressor (electric motor) does not start
The compressor does not turn on, the most common problem. The main and trivial thing that can happen in this breakdown is that there is no voltage in the network. The first thing you should check is the plug and wire supplying the electric motor for breaks. Using a special “tester screwdriver”, check whether voltage is supplied to all phases. Check the fuse if there is one. Make sure the starting capacitors are working (single-phase compressors have a voltage of 220V).
Pay attention to the pressure level in the tank (receiver). Perhaps the pressure is sufficient and the automation does not start the compressor; as soon as the pressure drops to a certain level, the electric motor will start automatically. This is not a breakdown; many people forget about this nuance and worry ahead of time.
The check valve can also become a problem if the compressor does not turn on. Also, a faulty automation unit (pressostat) affects the breakdown (on, off), the button on the unit itself may have become unusable.
If the electric motor does not start, hums, hums, does not gain the required speed, or stops during operation, this does not always mean it is broken.
The main malfunctions of the electric motor that may interfere with its proper uninterrupted operation:
- Low motor power (insufficient mains voltage)
- Loose connections, poor contact
- The check valve has failed (is leaking), thereby creating back pressure
- Incorrect start of the compressor (see operating instructions)
- The piston group is jammed (due to insufficient oil level, overload)
If the electric motor of the compressor does not turn on at all and does not make sounds, this indicates the following:
- The power supply fuse has tripped
- Overload protection tripped
- Poor contact in the electrical circuit (electrical wiring problems)
- The worst thing is that the electric motor burned out (there is often a characteristic smell)
Exploitation
The longevity of the protective mechanisms depends on compliance with all technical operating conditions. During operation of the protective unit, the following defects may occur due to wear of the main parts:
- Seat leak. The defect may occur as a result of metal shavings and scratches on the seat. The defect can be eliminated by grinding in the seat or replacing it with a similar fitting.
- Low opening pressure of the device due to the valve spring losing its elastic properties or misadjustment of the setting. To eliminate the failure, you need to replace the spring or the fitting itself, adjust the pressure, check the operation and put a seal.
- If it is necessary to replace the unit for repair, then a plug or valve cannot be temporarily installed in its place. It is necessary, for the safety of the facility, to first select a valve with exactly the same characteristics, and only install it instead of the removed one.
- If pulsation occurs during operation, rapid opening and closing of the device valve, then such a defect can cause unwanted vibration of the pipelines, which can lead to their deformation. The reason may be a mismatch between the cross-sectional sizes of the main pipeline and the pipeline connected to the unit. To eliminate the defect, it is necessary to install pipes of the same cross-section during installation.