08Dec
- By: Semantics
- Uncategorized
- Comments: 0
A variety of devices are used today for processing workpieces. Let us pay attention to perhaps the most popular of them - metal cutting devices: we will consider in detail the characteristics by which they are divided, and the scope of application of each of them, design features and main operating parameters. There are so many nuances - so that you understand which one to choose and use in each specific situation.
Separately, we note that they are not only still relevant, but they also remain promising. It is mechanical technology that remains in demand, largely due to its availability. The moment of unification also plays a role: the same drills and cutters are often suitable for entire series of machines and, with all their compatibility, can provide highly accurate results.
Classification of metal-cutting tools
There are a number of key parameters - let's take a look at each.
Based on the nature of processing (action), they are divided into:
- blade - cut off excess material;
- abrasive - abrade the surface, bringing it to the desired geometry by grinding.
By design they can be:
- solid - completely made from one piece;
- composite - made of several parts, all connections of which are permanent;
- prefabricated - their elements are fastened so that they are easy to separate if necessary.
According to the mounting option, there are top-mounted and tail-mounted ones. There are also options for drives (manual, machine or combined) and shape (plate, cylindrical, disk, conical), and each of them is in demand in its niche.
About tools used for milling machines
For milling, cutters are used as cutting devices, which come in various designs and have special teeth for processing the surface of parts.
All milling tools differ from each other in:
- the shape and appearance of the teeth;
- their direction and execution;
- their use and fastening.
In order to properly strengthen the cutter in the chuck of a milling machine, use its shank, which is attached to the teeth by welding or with various fasteners, for example:
- bolts;
- special wedges;
- screws.
Sometimes the cutter can be presented as a single unit with its cutting part. That’s what they usually call it – a solid cutter.
Important. Some modern CNC machines use only one-piece special end mills that have cylindrical and also conical shanks for more durable, quick fixation in the chuck of milling machines.
The following materials are most often used in the production of milling tools:
- metal ceramics;
- high-speed cutting steels;
- hard alloys with special diamond coatings to enhance hardness.
Main types of metal-cutting tools
Depending on the purpose, the operations carried out with their help and the features of their execution, all devices are divided into a number of groups. Let's look at each one, paying attention to the key points.
Incisors
There is a wide range of sizes, but each of them is single-edged and designed for processing all kinds of rotating bodies. And they all have the following configuration nuances:
- made with a holder and a working part;
- made of alloys that determine a specific material, and therefore the scope of their application;
- with a specific sharpening angle depending on the use cases.
They are also divided according to purpose - into the following options:
- cutting - for separating (some portion of the workpiece from the whole) at an angle of 90 0;
- through - straight, bent, persistent - for chamfering, including perpendicular to the axis of rotation;
- threaded - for creating turns from the inside or outside of parts;
- Boring – designed to expand blind or through holes.
In terms of their design, they can be either solid or prefabricated - with replaceable plates, providing versatility (but, unfortunately, reducing overall reliability and durability).
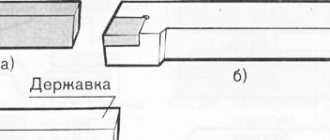
Depending on the side of fastening on the holder, cutters for lathes are divided into right and left. It’s quite easy to check which one you got. You just need to place the palm of the corresponding hand on it, with your fingers towards the top. The directions of the large and main edges should match - look at the diagram below:
Milling cutters
These are almost the most popular multi-blade cutting tools in mechanical engineering, made in the form of bodies of revolution and equipped with teeth on the working surfaces. Attention, they remove material from a fixed product. The design is more complex than the representatives of the previous group, therefore they are more expensive.
They are used to solve a wide range of problems: to give the desired geometry to the side and end planes (external), to bore holes to the required diameter, to make relatively complex shaped contours from a simple (rectangular) workpiece.
They are divided into groups according to several indicators:
- by the location of the teeth;
- according to the specifics of the edge;
- on the operations performed;
- on fastening nozzles;
- according to the material of manufacture.
The modern classification of cutting tools is very wide and varied, so we will focus on the most popular and in demand types of cutters. Using their example, one can form a correct impression of other similar devices. So, the most relevant are the following models:
End ones - needed to create contour recesses, ledges, deep grooves, smooth transitions when forming complex reliefs of body parts. They are similar in appearance to drills, but without edges at the bottom, and are often made with a conical shank, which ensures fastening rigidity.
Cylindrical - made like bushings with technological holes and grooves, due to which they are mounted on a mandrel. They have several blades at once, located along the axis, with an angle. They are used for high-precision grinding of individual sections of the workpiece; they can also be used for turning (if angular heads are installed on the spindle).
Disk - their shape is clear from the name; they are quite thin and act perpendicular to the direction of movement of the part, which allows making cuts from 1 mm. Based on the type of plates, these cutting tools for metal processing are divided into slotted, semicircular, three-sided, and modular.
Face - their edges are located at the bottom of the body, and this configuration allows you to maintain a high speed of turning the plane (the fixing table moves longitudinally); as a result, labor productivity is several times higher than with planing. They also have a cylindrical body, with a chuck, a shank and a key that transmits torque.
Worm - with shaped blades, sharpened in a reverse involute and located at a certain slope (depending on the area of application). Relevant for creating teeth on wheels, gears, and shafts. They operate on the rolling-in principle, when the workpiece is rotated with a fixed displacement step.
Corner and end - part of them is a truncated cone, and this shape allows you to quickly trim flat parts along the edge, providing a flat and smooth surface.
Saws - exclusively for cutting operations, for which their teeth are made sharp, often the same thickness as the body (in this case, they are made without transition). Attached using a groove connection. They are distinguished by economical cutting, especially in demand when processing shafts and technological profits.
Shaped - needed to give workpieces a complex and predetermined configuration (the geometry of their surface will be the opposite of the edge). Outwardly they look like files secured in cartridges by shanks.
Keyed - special, disk and finger at the same time, first acting like a drill, then with vertical working. Necessary for creating grooves.
Drills, countersinks, countersinks and reamers
The first devices of this group are well known to any person who has ever needed to make a hole in a hard surface. They are axial, they bite into the part due to the rotational movement, while the chips are removed along the helical grooves.
They differ from each other in such indicators as:
- execution material;
- shank;
- diameter (size);
- sharpening angle of the main edge.
The next popular cutting tool is a countersink, used either to widen a hole (increase the diameter) or to adjust it (increase accuracy). The conical entrance areas of the bolt seat are also machined using a special device called a countersink. Well, the roughness is reduced by a sweep - it won’t be difficult to bring the plane to the desired level of smoothness.
Broaches and firmware
The first ones have several blades at once, arranged sequentially and so that each new one protrudes above the previous one. This configuration makes it possible to remove material from the workpiece both in rotational and translational motion, and in static mode - at an angle of 90 0 to the feed direction.
They are considered professional equipment and are relatively expensive, but they have a number of advantages:
- the durability resource is high, and this is the key to low operating costs;
- During the work process, several teeth are involved at once, which allows you to increase the allowance and is a guarantee of impressive productivity;
- accuracy level – up to 6th grade inclusive;
- with their help you can effectively remove defects.
Firmware is a modern machine cutting tool that allows you to quickly make four- and hexagonal, slotted, TORX R and other holes.
If it is designed as a head, it is compatible with turning, milling, and CNC equipment, and is effective for both horizontal and vertical passes. Its supporting shaft is mounted at a given angle on ball bearings, so it successfully withstands even heavy loads. Deepening into the workpiece material occurs smoothly, so the required profile of the seat is created with high precision.
If it is aimed at creating internal holes, it is a rod with a cylindrical shank and a guide of the required cross-section. If it is used to pierce external seats, it has the opposite configuration - the desired profile is knocked out inside the disk, which is reproduced upon contact with the part.
The size range includes 7 positions, marked with the Latin letter G (from G5 to G25).
Gear cutting and grinding tools
Already from the name of the first it is clear why it is needed - to create clutch elements on splined rollers, ratchet and worm wheels and other similar parts. And its range is quite wide – it includes:
- finger and disk cutters – operate modularly;
- heads - form all the cavities simultaneously by copying (in several passes);
- combs - straight and helical, serve as planing incisors;
- cutters - wheels with edges that allow external/internal gearing.
This group also includes devices that work using the rolling method, that is, so that the edges, as a result of sliding, consistently create a surface of the required geometry.
Threading type cutting tool
It also has a “telling” name - it is needed to form helical lines of various sizes and patterns, which allow for a reliable connection. It boasts a wide range of products, including:
- heads, vortex or self-opening, made according to GOST 21760-76;
- tangential combs;
- lerks (dies);
- cutters, disk, end and others;
- taps, including nut and automatic taps, complying with interstate standards 1604-71, 3266-81, 6951-71, 8859-74.
These devices allow you to apply metric, inch, tapered, pipe cylindrical, left-handed and right-handed threads, even in through or blind holes.
Abrasive types
These are all kinds of wheels (grinding, grinding, etc.), cups, attachments used for machining parts.
The main characteristic of a cutting tool of this group is surface hardness, which must be stronger than the workpiece material in order to act on it, and not vice versa. Therefore, it is made from grains of electrocorundum, synthetic and natural diamonds, silicon carbide, randomly combined into bonds (bakelite, silicate, ceramic, magnesia, vulcanite, hyphthalic). Due to this, it acquires the ability to self-sharpen: by chipping and dulling, the upper particles make room for new layers.
All of the listed device options are rigid, but there is also a flexible category, which includes tapes and disks.
Hand-held metal-cutting tool
This is a portable alternative to machine tools - devices that facilitate human labor, and examples include:
- profile or nibblers – used to separate part of rolled sheet metal from the whole workpiece;
- panel cutters – needed for working with sandwich panels, ensuring speed and accuracy of operations;
- folding machines - allow you to automate the process of closing recumbent joints;
- molders – necessary for proper compression of rolled products;
- mobile pliers - very convenient for cold welding, they help to press the elements to be joined with great force.
The procedure for performing manipulations and rules for using the tool
The technique of plastering walls involves preliminary preparation of the surface, including:
- cleaning from the previous coating;
- treatment with antiseptic compounds;
- primer impregnation;
- installation of construction beacons.
In order for the leveling and application of the plaster mixture to be carried out according to all the rules, you will need to use a building level and prepare gypsum plaster for fixing the beacons, as shown in the photo:
- If the 2 m long rule is to be used when leveling a wall at least 5 m long, start installing the beacons from the far corner, retreating from it at least 50 cm.
- The second beacon is mounted at a distance of strictly 1 m from the first.
- The distance between all the others does not change.
You can work on beacons only after the gypsum mixture has completely dried.
After the gypsum composition on which the metal strips are installed has completely hardened, you can begin preparing the plaster mixture directly and applying it to the wall surface. When treating large areas, it is better to do this using a plaster sprayer.
The mixture intended for plastering internal surfaces consists of sand and cement, combined in a 4:1 ratio. Water is added depending on what layer of the mixture is to be applied to the surface. The plaster consists of 3 layers:
- Spray. To create it, a fairly liquid solution is used, which ensures reliable adhesion of the composition to the wall surface. To apply it, you can use equipment such as a plaster sprayer.
- The primer is applied strictly after the first layer has completely dried. This is the main thickness of the plaster layer. It can be applied in several stages, as shown in the photo.
- The final, thinnest, 2 mm layer is the covering. To create it, you will need a solution that is not as thick and durable as soil, which is spread on a leveled surface and smoothed with a falcon or a trowel.
The last of several layers of primer can be applied using a trowel.
Areas of use
We looked at what cutting tools there are, but where and when are they in demand? They are virtually indispensable in all major industries, but they can only be used effectively if certain requirements are met:
- the material they are made must be harder and stronger than the metal they process;
- the workpiece must be securely fastened;
- It is necessary to strictly observe safety precautions and the parts production scheme.
If all these conditions are met, you can count on long-term and cost-effective operation.
Another important niche is small private and home workshops. They require manual devices - all kinds of machines and machines designed for piece operations, at low speeds and with low feeds.
Planers
A planer is a hand-held woodworking tool for planing.
Using a plane, they impart the desired roughness to the surfaces of wooden parts, making them flat and straight. Planers are also used to reduce the size of parts and create long recesses of various shapes in them. With each passage along the surface, this tool cuts off a layer of material with a thickness determined by the amount of extension of the cutter, as well as its angle of inclination. The most necessary planes in a home workshop are an end plane for trimming the edges of wood and a jointer for longitudinal planing. These tools have high-quality steel knives and adjusting mechanisms that regulate the amount of wood removed. You can also supplement your tool kit with a sherhebel for straightening the edges of long boards; a chisel for cutting grooves; carpenter's scraper for cutting and smoothing curved surfaces.
Choosing the type of cutting tool for metalworking
To place the correct order, you need:
- Determine what tasks it should solve - with the help of the same cutter you can perform a wide, but still limited range of work; it will not be suitable where a drill is required.
- Take into account which machine it will be installed on - it is simply necessary that it is compatible and can receive and transmit rotation force without unnecessary losses.
- Make sure that he can maintain the required cutting parameters - carry out calculations, draw up a technological map, and compare the passport data (and other indicators) of the devices he likes with it.
- Consider the efficiency of use - all other things being equal, it is better to buy the option whose wear resistance is higher, because it will last longer, this is true even for mass production, under conditions of high loads.
About the principles of milling
When milling, using the teeth of a cutter, chips are removed from the surfaces they grind, and they are removed from the cutting zone by special grooves along the cutter itself. Therefore, the location of the teeth relative to each other is of particular importance. Correct geometric relative position affects:
- cutting speed;
- quality of processed surfaces;
- wear resistance of the cutter;
- saving energy costs;
- price of finished products.
Attention. Each type of intended workpiece, be it wood, stone, metal, plexiglass, for example, requires a certain type of milling device.
Techniques for making tools for working with metal
First of all, the tool must meet high requirements that allow you to work with strong and durable material. Tools for metal processing are made using the following methods:
- burning;
- hardening;
- forging using a press;
- grinding;
- hot stamping of hardened steel;
- induction hardening;
- metallization.
Such methods are necessary to give the working surface of the tool additional strength. The resulting equipment must have excellent cutting properties, as well as increased strength.
Main types of instruments
All equipment for metal processing is divided into several main groups, according to the method of influence:
- Pipe cutters. This is a group of equipment that is designed for cutting pipes of various thicknesses and diameters.
- Cross mixer - necessary for creating grooves in metal workpieces.
- Drill stand. There is a drill in it and it is possible to fix the workpiece.
- A die is used to cut external threads. A die holder is made for them.
- Goniometer. This is a measuring device, an analogue of the well-known protractor.
- A soldering iron is used to join metal parts.
- Hand hacksaw for metal. Designed for cutting metal, both sheet metal and small pipes.
- Metal scissors. Designed for cutting sheets that are not too strong.
- Vise - necessary for fixing the workpiece.
- Milling cutters. They work with different surfaces and can be cylindrical, end, disk, end, or conical.
All tools are used in industry and in everyday life. Many of them are used in combination.
Repair tool. Measure seven times - cut once
Let's consider what list of tools will be needed at the initial stage, and determine the purpose of each type.
At the beginning of a renovation, measuring tools are the first in importance. Among them, the most popular tool is a tape measure, with which all measurements are taken before drawing up an estimate.
A tape measure determines the exact height, length and width of any object.
A metal ruler is the simplest means for applying markings to wood, plastic, and metal. Useful in making drawings. To correct the position of significant objects, a building level is used. It is used when leveling floors, laying ceramic tiles, and checking the evenness of plastered walls.
Important! Buy a level that combines horizontal, vertical and rotating ampoules. A plumb line marks straight lines parallel to the horizon
It guarantees smooth walls during plastering work. To ensure right angles of 90º, it would not be superfluous to use a construction square
A plumb line marks straight lines parallel to the horizon. It guarantees smooth walls during plastering work. To ensure right angles of 90º, it is a good idea to use a construction square.
In a major renovation, there is always a need to remove doorways, windows, and remove old concrete floors when replacing them with new ones. At this stage, tools for dismantling are simply irreplaceable. A basic set includes: pliers, nail puller, hammer drill, crowbar, sledgehammer, screwdrivers, saw.
Wood cutting tools
The set of carpentry tools for cutting wood includes:
- saws and hacksaws;
- jigsaws;
- knives, cutters, scalpels;
- woodworking machinery.
Saws and hacksaws
Application of saws:
- longitudinal and transverse cutting - classic hacksaws;
- cutting holes - circular saws;
- production of connecting tenons - tenon saws.
Saws are distinguished by design:
- two-handed, used for sawing large logs;
- one-handed – hacksaws;
- bow - with stretched fabric;
- rewards - short saws.
Hacksaws for longitudinal cutting have teeth inclined forward, for transverse cutting - symmetrical teeth. Saws with large teeth (4 - 6 mm) are used for sawing logs and bars, with medium teeth (3 - 3.5 mm) - for cutting medium-sized parts, with small teeth (2 - 2.5 mm) - for precision manufacturing of small parts .
According to the international classification in the marking PPX or EPX, the number X indicates the number of teeth per inch. The fewer teeth, the larger they are. For cutting raw wood, hacksaws are used, the teeth of which are arranged in groups of 5–7 pieces. The spaces between the groups are needed to remove sticky raw sawdust.
Jigsaws
A jigsaw is a type of bow saw with a narrow blade and a large distance between it and the frame. The frame has a U or U-shape. The jigsaw is used for curved cuts. It ensures high quality cuts and precision manufacturing of parts.
Woodworking machinery
When sawing wood use:
- circular saws for longitudinal and transverse cutting;
- machines for cutting bars;
- jigsaws.
Manufacturers of metal processing tools
There are manufacturers who have been making high-quality equipment for metal blanks for several decades. At the same time, both domestic and imported companies are represented.
Domestic
The equipment of JSC NIR is most widespread in Russia. To produce equipment, the company uses alloys of special hardness. The main advantages of their products:
- high wear resistance;
- it is possible to quickly change tools;
- there is a nano-coating;
- low sharpening costs.
The Moscow Tool Plant is not lagging behind in terms of performance. Products have been based on world standards for several decades. Using such equipment, you can easily create the most non-standard threads, machine a coupling, pipe and any other part on a lathe.
Imported
Foreign factories produce high-quality tools that are used all over the world. One of the leaders is the Israeli company ISCAR, which produces tools for turning, drilling, and milling.
For processing titanium, aluminum, stainless steel, cast iron, you can use strong and reliable German tools from ARNO.
The top five includes the Japanese company SUMITOMO. They make their equipment from hard alloys, diamonds and CBN. The products are used for turning and milling work of various levels of complexity.
Size differences
When choosing any tool, it is important to pay attention to its size. Files come in 6 classes, which differ in processing accuracy.
Good to know. There are more than 20 types of turning tools. They are divided into left-sided and right-sided.
The dies or dies used to cut threads differ in their measurement system. It can be in millimeters or inches.