The polishing process is carried out upon completion of many works. This is a rather labor-intensive and time-consuming technology. Doing it manually requires a lot of patience. In addition, to obtain a high-quality result, you must have at least some experience and skills.
For example, after painting a car, final polishing is carried out. After the cutters are completed, they are sharpened. A felt wheel for sharpening is a good assistant in these matters. But, without knowing the technology, you can ruin the previously done work. Let's try to understand all the features.
A little about the material
As noted above, an indispensable assistant in the polishing business is a felt polishing wheel. Most often, circles are made from well-pressed, high-quality wool.
This is a fairly effective method of grinding, which is ensured due to the protein nature of the material used. Wool fibers are rich in a substance called keratin. It is characterized by the enrichment of basic carboxyl and amino groups. It is thanks to this that the possibility of chemical interaction with various components of the processed material is ensured. During the process, various suspensions or pastes can be used to enhance the polishing effect.
The protein origin of the material increases grinding efficiency, which is not achieved when using non-protein polishing materials.
How are these forgings done?
Forging a knife from a drill that is made of high-quality tool steel will bring good results if it was previously intended for metal. Such drills do not require high heat during alterations, and are also fast-cutting materials.
The forging technique is simple:
- the drill is placed in an incandescent oven, it should turn red;
- it is taken out and the tail is clamped in a vice for the alignment procedure;
- they are already starting to make the shape of the cutter and handle;
- Sharpening is done using a hammer or grinder. The grinder is the fastest to work with;
- forging a knife from a drill is done in several stages so that the product does not crack or break.
Forging a knife from a spring is a delicate process that requires attention. The main thing is not to overheat the steel, otherwise the product will become weak and damaged.
If the forging of a knife from a spring is made from high-quality Soviet raw materials, the product will be strong and durable. The use of spring material will make the product durable and strong.
What fibers are used
Felt, which is used for polishing wheels, is divided into the following types according to its composition: fluff, awn, transitional hair and dead hair. Down felt contains fibers with the highest elasticity and has the largest number of flakes. The highest degree of coarseness is present in dead hair; here elasticity indicators are completely absent.
Some main composition characteristics are provided in the table.
| Name of felts | Fiber content percentage | |||
| Pooh | Transitional hair | Ost | Dead hair | |
| Fine-haired | 0,9 | 0,5 | 0,05 | — |
| Semi-coarse-haired | 0,3 | 0,3 | 0,35 | 0,05 |
Steel grades for power transformers
The magnetic cores of low frequency transformers (50 Hz) are usually made of sheet electrical steel containing from 0.5 to 5% silicon (Si), up to 1% carbon (C), and the rest iron (F). Due to the fact that their losses increase significantly with increasing frequency, they are usually used within the range of no higher than audio frequencies. Grades of electrical steels produced in accordance with GOST 802-58 are designated by the letter E, which means electric steel. The first number indicates the average percentage of silicon content, the second characterizes the electromagnetic properties: number 1—normal losses, 2—reduced, 3—very small, 4—normal at 400 Hz. The second numbers 5 and 6 indicate increased magnetic permeability in weak fields (less than 0.01 av/cm), 7 and 8 - in medium fields (0.1-10 av/cm). The third digit 0 indicates that the steel is cold-rolled, textured. The third and fourth - 00 - indicate cold-rolled low-textured steel. The letter A after the numbers indicates particularly low specific losses. For steel with increased rolling precision and surface finishing, the letter P is introduced at the end. Cold-rolled steels E310-E380, in addition to silicon (3-3.25%) and carbon (0.0003%), contain sulfur (0.003%), manganese and phosphorus ( less than 0.1%,). These steels differ from others in that they have high permeability along the rolled product and low permeability across the rolled steel. One of the main parameters of steel is losses in steel, consisting of losses due to hysteresis, eddy currents and aftereffects. Hysteresis losses are the work spent on reversing the magnetization of steel. It is usually accepted that hysteresis losses do not depend on sheet thickness, but when rolling sheets 0.2 mm or thinner, the steel becomes compacted (since finishing to the required values for hot-rolled steels is carried out on cold sheets) and hysteresis losses increase. Hysteresis losses per magnetization reversal cycle (at constant induction) within the limit of a 10-20-fold change in frequency (50 - 1000 Hz) can practically be considered constant. Consequently, when referred to a unit of time (1 second), they increase in proportion to the increase in frequency. Eddy currents are currents that appear in steel under the influence of e. d.s. induced by magnetic flux (in planes perpendicular to the direction of flux). These currents lead to losses. As the plate thickness decreases, e.g. decreases. d.s. plates and the ohmic resistance of steel increases. The total losses in the steel of the magnetic core due to eddy currents decrease approximately in proportion to the decrease in the thickness of the plate. But currents can also close in the thickness of the magnetic circuit through the contacting surfaces of the plates, so there must be insulation between the plates, especially as the width of the plates increases and the induction increases. In addition to the thickness of the sheets, the magnitude of eddy currents and losses is affected by the ohmic resistance of the steel (not to be confused with magnetic resistance). The ohmic resistance of steel (as well as wires) in Ohms corresponds to the resistance of 1 m of length with a cross section of 1 mm 2. As the percentage of silicon increases, the ohmic resistance of steel increases. Losses increase in proportion to the square of the frequency increase. Aftereffect losses are caused by the magnetic viscosity of the material and depend on the processing of ferromagnetic materials. They are determined by the difference between the total losses and the losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents. As the frequency increases, these losses increase proportionally. The total active losses of electrical steels with changes in induction (within operating values) change in proportion to the square of the induction; at inductions below 0.5-0.7 tl they are slightly overestimated against this ratio. The total active losses in steel and the reactive component determine the magnitude of the magnetizing current. Table 1 shows active losses at a frequency of 50 Hz for the main electrical steels.
Table 1 - Active losses for main electrical steels at a frequency of 50 Hz
Source
Types of circles
The felt polishing wheel is divided into several types according to the percentage composition of fibers:
- fine-haired;
- semi-coarse-haired;
- rough-haired.
The best polishing wheels are obtained with higher density felts as they are more resistant to wear. Other types quickly become unusable. But it should be noted that their use when grinding, for example, the surface of a car is not permissible. The best in this direction are fine-wool felt circles. They are also good for polishing products made of non-ferrous metals or aluminum.
As for semi-coarse wool products, their area of application is mainly aimed at sharpening delicate instruments. For example, surgical scalpels, parts for precision measuring instruments, etc.
Main manufacturers
Olympus Corporation
A Japanese company known for its products in the field of optics and photographic equipment. Its metal analyzers are popular because they are considered reliable in Japanese and are in the middle price segment.
The company invests money in scientific and technical development and software improvement. Delta X-act Count technology has been created for portable analyzers, thanks to which the speed and detection limits have decreased.
FPI (Focused Photonics Inc)
A Chinese company founded by graduates of prestigious American universities. It is considered one of the leaders in the production of all kinds of systems for monitoring the ecology of the environment. Their metal analyzers are also in demand.
The FPI portable metal analyzer is slightly less expensive than its main competitors.
Bruker
German company founded more than 50 years ago. Production, laboratories and representative offices are located in 90 countries. It consists of four divisions that deal with different areas. The development and production of metal analysis systems is carried out by Bruker AXS and Bruker Daltonics.
They are considered to be of high quality and are quite common in the Russian market due to the good work of their representative offices.
You need to look for them depending on your location.
Features of the technology for using felt discs
Ensuring high-quality execution of the process is determined by the speed of rotation of the felt disk. The best option is if the machine develops a rotation speed of 5 – 10 m/s. Otherwise, the following problems arise:
- artificial hardening of the treated surface occurs, it becomes harder and less amenable to grinding or sharpening;
- When the rotation speed increases, polishing fibers are torn off the surface of the wheel under the influence of centrifugal forces, and the material is wasted.
Determination of high-speed steel by spark
Every experienced scrap metal acceptor has one very valuable skill, the ability to determine the grade of steel by spark. Of course, almost any metal today can be determined in one minute if you have analytical equipment, but not everyone can afford it. However, even if you have equipment, work goes faster with an experienced technician than with equipment alone.
To determine the grade of steel by spark, it is enough to have a small cutting tool on hand, such as a grinder with a cutting disc. The cutting disc must be without any organic bond. The most common one will do. It is better to check the steel grade for a spark in the shade, so that you can clearly see the entire structure of the spark, the length of the rays in the beam and its color.
The sparks that occur when cutting metal carry certain information. The information lies in the structure of the spark, i.e. in molten metal micro particles that are thrown away by the centrifugal force of the cutting tool. Flying at high speed from the point of contact during cutting, the sparks become even hotter in interaction with oxygen. And depending on the chemical composition of the alloy, the spark during combustion gives its characteristic structure, length, color, beam.
Steel with a high carbon content when cut produces a large beam of bright yellow sparks with short rays and a large number of stars. When interacting with oxygen, hot particles are oxidized and carbon turns into carbon dioxide. Inhaling carbon dioxide vapor is very harmful, so during such work you should use all safety equipment.
If, during cutting, a glass plate is placed in the path of the spark near the contact, it will be strewn with molten metal particles, which will tightly weld to the surface of the glass, forming bizarre shapes when solidified. These shapes have their own unique pattern. The length of the rays in a beam of sparks is uneven. The smaller the particle, the closer its path, and accordingly, the larger the particle, the further its path.
The structure of the beam in the beam, the color and shape of the spark mainly indicate the chemical composition of the steel. Please note the figure below for examples of sparks to identify different types of steels.
Fig.1
Types of sparks when cutting various types of steels:
a - soft carbon, 0.12% carbon, straw-yellow color;
b - carbon of medium hardness, 0.5% carbon, light yellow color;
c - carbonaceous solid, 0.9% carbon, bright yellow color;
g - carbonaceous solid, 1.2-1.4% carbon, white color;
d - manganese solid, 13% manganese, dark yellow shiny color;
e - high-speed, 1-18% tungsten, dark red color;
g - tungsten, dark red color;
h - siliceous, light yellow color;
and - chromium, color depending on carbon content (non-magnetic);
k - chrome-nickel, 3-4% nickel, 1% chromium, yellow;
Carbon steel
- gives a beam of yellow sparks with an asterisk on each ray, while the higher the carbon content in the steel, the more numerous and shorter the rays, and accordingly, the more stars and the brighter their glow
Margonal steel (hard)
- 10-14% manganese, emits dark red rays with star-shaped leaves, the shape and color of which depend on the amount of carbon content
High speed steel (tungsten content)
- quick cut, P6M5 - P9 - P12 - P18 (P% tungsten content in the alloy), forms a relatively small beam of sparks of a dark red color (strokes, dust) almost without stars, the end of the spark looks like a smeared drop. The lower the tungsten content of the high-speed steel, the more red the spark has an orange tint. Spark length is relatively short
Chrome steel
- has a long beam of reddish sparks with thickening stars at the end
Silicon steel
- forms a particularly bright thickening of the beam, white color, releases a large amount of heat as a result of silicon combustion at high temperatures due to carbon oxidation, which explains the bright white color of the spark
Cast iron (iron)
- produces sparks of various shapes, types and colors, which are determined by the main impurities depending on the chemical composition, for example, the content of carbon, manganese, etc.
The entire list of available felt circles
| № | Name | List of sizes, cm | Density degree |
| 1 | Coarse wool felt circles | 10-2-3,2 12,5-2-3,2 15-2-3,2 20-2-3,2 20-2,5-3,2 20-4-3,2 | 0.30-0.45 g/cm3 |
| 2 | Semi-coarse felt circles | 12,5-0,8-2,2 12,5-2-2 12,5-2-3,2 15-2-3,2 20-2-3,2 20-2,5-3,2 20-4-3,2 | 0.33-0.48 g/cm3 |
| 3 | Fine wool felt circles | 12,5-2-3,2 15-2-3,2 20-2-3,2 20-2,5-3,2 20-4-3,2 | 0.38-0.50 g/cm3 |
Manufacturing procedure
Having decided on the materials and steel grade of the future blade, it’s time to get to work and make a knife from a drill. Don’t forget about fireproof gloves and goggles; scale will fly when forging:
- A mandatory process that is rarely mentioned is annealing. During production, the workpiece undergoes hardening; it is necessary to relieve the stress from the metal. After heating the oven to 600-700 °C, you need to put a drill in it and hold the part for 3 hours. Afterwards, let it cool on its own.
- After cooling, the workpiece is ready for use. Heat the oven to 1000 °C and place the drill in it. Having acquired an orange color, the workpiece is heated, we take it out with pliers and clamp it in a vice with the shank. Use a wrench to grab the top of the drill and turn the metal into a straight plane. All movements must be performed quickly - cooling of the workpiece is unacceptable.
- The product cannot be allowed to cool down; by constantly heating it, we begin to forge. Keep an eye on the color of the metal; if it has tarnished a little, put it straight into the oven. We cut it into a strip of the required thickness of 3-4 mm. We extend the shank in length.
- Having reached the desired butt, we begin to work on the tip and blade. We gradually round it in the area where the blade rises, pulling the metal towards the tip. The process is complex and requires certain skills.
- Forging of the RC is carried out with a small hammer; with careful blows, you need to achieve the minimum thickness.
The process of making a knife from a drill.
Features of caring for felt circles
When working with felt circles, you must adhere to certain rules, since their surface is very susceptible to any contamination.
In the case when the felt is clogged, the quality of grinding will decrease significantly, and scratches or chips are likely to form:
- If the disc is not in use and is attached to the machine, it must be covered. You can remove the disc from the sharpener and wrap it tightly with paper;
- It is better not to use additional pastes and other additives unless absolutely necessary;
- The circle should be cleaned carefully; while rotating, you need to bring pumice to its surface, but do not put too much pressure on it. Using the same method, you can trim the surface of the polishing disc. Keep an eye on it while cleaning. So that the flaking particles do not clog the surface, but flake off.
The most expensive types of stainless steel
The cost is affected by the amount of nickel in the alloy: in the cheapest types its content does not exceed 5%. The most expensive are high-alloy alloys containing nickel from 12%. The expensive scrap includes plumbing fittings and rings, wire and various electrical connectors (connectors, adapters, etc.). Matte (a by-product of non-ferrous metallurgy) with a nickel content of over 35% is also highly valued, although it is classified as slag.
But the most common steel grade is A2, containing approximately 10% nickel and 18% chromium. It is usually used to make household items. To find out the exact price, visit our collection point: to evaluate scrap, specialists must inspect the metal, assess the degree of contamination, composition and properties.
Source of the article: https://npfgeoprom.ru/materialy/marka-stali-po-iskre.html
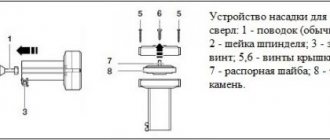
DIY felt disc
If desired, you can prepare a grinding wheel at home with your own hands from felt or felt material. For example, if there are old felt boots in the house, then from their tops you can cut out circles of the required diameter. Typically, the diametrical section size varies from 50 mm to 250 mm.
Discs with a diameter of 200 mm are in particular demand. It depends on the area of its application and the technical characteristics of the machine. The thickness of the discs should be from 30 mm to 50 mm. Although this is not mandatory. The number of blanks depends on the size of the future disk.
Sequencing
Next we perform the steps in the following order:
- We pay special attention to the technology of gluing workpieces. They need to be lubricated with glue, but the adhesive composition cannot be brought to the edges, since when it dries, abrasive particles may form. During polishing they can damage the surface;
- After all the layers are coated, we connect them to each other and press them with a weight until the glue dries completely;
- After this, a hole of the appropriate diameter is drilled in the center of the resulting disk;
- Next, install the disk on the sharpening machine and clamp it with two nuts. The rigidity of the disk installation is ensured by washers, but it should be remembered that their diameter should not exceed a third of the diametrical section of the disk;
- In order to make the circle removable, you can fix a small rod in its hole. In this case, it can be mounted on a drill.
Video
Body polishing
The polishing process can correct only some defects. If there is corrosion, chips or damage on the body through which the steel frame is visible, then a major repair will be required.
Before starting the polishing process, you should carefully inspect the vehicle to ensure that any imperfections can be eliminated.
Treatment of the body with a special device will give a positive result if:
- slight difference in shades that resulted after partial coloring;
- the presence of roughness, scratches and cloudy stains;
- faded layer of paint;
- the appearance of graininess and streaks of enamel.
You need to know that you can’t overuse polishing, because when you do it, the paint layer becomes smaller by 5 micrometers. From the date of manufacture of the vehicle, no more than 20 polishing procedures can be performed. At this time, you need to use a thickness gauge, especially if the car is used.
Curved descent at the tip
0 I removed the curved trigger at the tip and the part of the blade that is adjacent to the bolster/guard. Ganz. ru tells you that this is called the edge of the trigger and the sub-finger radius. Well, or a rounded rectangle in my case.
0
0
This is what the blade profile looks like now.