Compound
Nichrome contains about 20% nickel and up to 80% chromium.
In addition, the alloy may contain additives in the form of manganese, aluminum, iron, silicon, etc.
The introduction of alloys into the nichrome composition increases the performance indicators and technical parameters of the metal:
- nickel and iron improve machinability;
- iron, titanium, aluminum and manganese reduce resistance to elevated temperatures;
- In the presence of iron in the alloy, nichrome acquires magnetic properties.
Increasing additives can degrade the characteristics of the metal.
The amount of nickel determines the temperature that the heating elements can withstand.
The chromium content in the alloy should be no more than 20%. An increase in the amount of chromium increases the brittleness and impairs the machinability of the metal. When its content in the alloy is more than 30%, cold rolling and drawing of the material becomes impossible.
The strength of the protective film and oxidation resistance depend on the amount of chromium.
Properties of nichrome
The alloy is characterized by good ductility and high electrical resistance. Its value can range from 1100 to 1400 Ohm mm²/m, depending on the type of metal.
Table 1. Technical characteristics of nichrome.
| Options | Indicators |
| Strength | 650-700 MPa |
| Melting temperature | 1100-1400°С |
| Working temperature | 800-1100°С |
| Density | Up to 8200-8500 kg/m3 |
| Resistance | 650-700 MPa |
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity | 11.3 W/(m K) |
| Linear thermal resistance coefficient | 14·10¯⁶Kˉ¹ |
| Ultimate tensile strength | 0.65-0.70 GPa |
Products made from nichrome are easily deformed while maintaining the given shape.
Nichrome does not have magnetic properties, with the exception of an alloy that contains an iron alloy.
Figure 2. Heating element.
Nichrome brands
The most common brands in the industry include:
- X20N80 is a classic alloy containing about 20% chromium and 80% nickel;
- X15N60 - the alloy has reduced chromium and nickel content, increased iron content to 25%;
- Kh20N80-N (-N-VI) and Kh15N60 (-N-VI) - alloys produced in vacuum induction furnaces;
- N50K10, X25N20 - grades of nichrome used for work at temperatures up to 900°C.
Alloys produced in vacuum induction furnaces are distinguished by the fact that their electrical resistance changes little with temperature changes.
Explanation of brands:
- X – chromium (Cr);
- N – nickel (Ni);
The numbers indicate the percentage of the composition.
Additional letters mean:
- VI - vacuum induction melting;
- H - category of heating elements;
- C - use in resistance elements;
- Heating element - intended for dry type electric heaters.
For example, the brand X20N73YUM-VI indicates: chromium content - 20%, nickel - 73%, aluminum - 3%, molybdenum - 1.5%, manganese - up to 0.3%, titanium - up to 0.05%, iron - 2 %, carbon - up to 0.05%. The alloy was smelted using the vacuum induction method.
The purpose and properties of nichrome products are determined by the chemical composition of the alloy.
International designations
In the international names of nichrome you can find the following designations:
- Cronix 80;
- NiCr80/20;
- Nichrome V;
- Chromel A;
- HAI-NiCr 80;
- Ni80Cr20;
- Nikrothal 8;
- Resistohm 80;
- euronichrome.
European analogues of ferronichrome: NiCr60/15, Ni60Cr15, ChromelCN6, Nikrothal 6, Nikrothal 60, CroniferII, AlloyC.
Advantages and disadvantages
Nichrome alloys are characterized by high electrical resistance.
The resistivity of nichrome is 10 times higher than that of galvanized steel and 70 times higher than that of copper.
Other advantages include:
- high mechanical strength and hardness;
- heat resistance and absence of temperature deformation;
- low specific gravity and good ductility;
- resistance to corrosion and aggressive environments;
The material is easy to process: sharpening, stamping, welding, etc. It does not change its characteristics when exposed to high temperatures.
Due to its resistance to corrosion and aggressive external environments, the alloy has an almost unlimited service life.
The disadvantages of the material include high cost.
Reducing the percentage of chromium in the alloy makes the product cheaper, but also reduces the technical properties of the material.
Distinctive characteristics
Among the most popular electrical products on the market is nichrome wire.
The resistivity of this component of electric heating technology is extremely high, which allows it to have a wide demand. An important feature of the metal is its resistance to high-temperature oxidation under normal and aggressive conditions. Chrome plays a key role here
The element forms a corresponding oxide film on the surface, which performs a protective function. It is also responsible for the corresponding dark color of the material, which is replaced by a characteristic white-gray when the oxidized layer is mechanically removed.
It is worth noting that direct contact with acids still destroys it, even more than corrosion-resistant tungsten.
The two-component alloy has no magnetic characteristics. They arise for its multicomponent modifications, but have weakened indicators.
Nichrome wire is rigid and does not lend itself to simple force.
We systematize information on how to identify nichrome wire, mainly how to distinguish it from externally similar materials:
- White is the color of new metal, dark is the color of previously worked metal.
- Negative or minimal magnetism.
- Rigidity.
- Destruction by acids, resistance to oxidation under the influence of high temperatures.
Making wire and tape from nichrome
Almost all electric stoves and electrical appliances use nichrome wire, thread or tape as heating elements.
There are several ways to make products from nichrome:
- Wire and thread drawing with intermediate heat treatment. Immediately before drawing, wire rod with a diameter of 6-8 mm is heated in special furnaces to a temperature of 1170-1230°C and quickly cooled. The heating temperature of the workpiece depends on the composition of the alloy. The next stage is pickling the wire rod in a mixture of hydrochloric and nitric acid with water.
Nichrome wire drawing is performed using high pressure. The production of products by drawing method is regulated by the requirements of GOST 8803-89
- Drawing of a hot-rolled billet to obtain a nichrome strip. This method allows the output to be a high-quality strip that exactly matches the profile and cross-section of the drawing channel. The resulting tape is of high quality and has no sharp edges.
- Cold drawn broach. The method is used for the production of wire and threads from nichrome. It is carried out without preheating the workpiece. Regulated by GOST 12766.1-90
- Cold rolling. Used for making nichrome tape. Performed in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12766.2-90.
- Flattening - used to produce strips from precision alloys with high electrical resistance. Performed in accordance with GOST 12766.5-90.
Nichrome tape.
The dimensions, mechanical properties and other parameters of nichrome wire are regulated by state standards or technical specifications.
Production
The manufacturing technology is based on pressure treatment using expensive equipment - mills, presses, furnaces. There are 3 methods of obtaining:
- Rolling. Nichrome is quite plastic, which makes it possible to produce wire from it by “cold” rolling. Large circles are produced by “hot” rolling.
- Drawing. It involves pulling workpieces (wire rods) through a gradually narrowing hole. The operating speed of the operation does not exceed 25 m/s. After obtaining the required diameter, the wire is subjected to thermal and chemical treatment.
- Pressing. Blanks are obtained by extruding the heated alloy through holes in the fixture matrix.
Areas of use
High corrosion resistance, the ability to work in aggressive conditions, and high-quality technical characteristics allow the material to be used in various fields.
In industrial installations and electrical equipment:
- high temperature electric furnaces;
- ventilation dryers;
- boilers and heat exchangers;
- welders;
- single-core and multi-core electrical wires;
- structural elements of metal-smelting equipment;
- powder paint polymerization chambers;
- devices for cutting foam;
- resistors, rheostats.
Heating elements made of nichrome are installed in car cigarette lighters, glass and seat heating systems in cars.
Special grades of complex alloyed nichrome with a low coefficient of electrical resistance are used as a heat-resistant coating when performing thermal spraying.
At home
The material is used in almost all modern household appliances:
- electric stoves and ovens;
- heaters and boilers;
- washing machines and toasters;
- hair dryers and irons;
- electric soldering irons and wood burning devices;
- electronic atomizers and light bulbs.
The use of spirals in household electric stoves.
Nichrome threads are widely used in medicine as a suture material during intracavitary surgical and plastic operations.
For each application, certain grades of alloys with optimal technical characteristics are produced.
Self extraction
In household heating devices, a nichrome thread is responsible for heating. Where can I get wire at home, other than from them? This method is not ideal, because the cross-section and length of nichrome involved in each individual device are not known in advance.
But in case of serious need, you can resort to it. Below are examples of things from which nichrome can be obtained.
Nichrome from a soldering iron
In this case, the nichrome thread heats the soldering iron tip. In order to get the wire, you need to disassemble the tool body. As a rule, it uses very thin nichrome. It is important to know that you need a soldering iron with a copper tip, since a ceramic one has a completely different heating element.
Hair dryer
You can get nichrome from a hair dryer, no matter a hair dryer or one used for drying hair. The heating power in it is higher than in a soldering iron; therefore, there will be more wire, and, as a rule, it has a thicker cross-section. To obtain nichrome, simply disassemble the device and remove the spiral-wound wire.
In addition to hair dryers, there are electric room heaters of the same operating principle, they contain nichrome with an even larger cross-section.
Electric stoves, kettles and boilers
Probably the most difficult process of obtaining wire of all those listed. The wire in these devices is located inside the heating element - a tubular electric heating element.
In order to remove it, it is necessary to disconnect the heating element from the device body. It can be powered directly from the mains, so in some cases the wires are cut.
As a rule, the heating element is a spiral, therefore, for more convenient removal, and also so as not to tear the nichrome wire, the spiral should be bent to the state of a straight tube.
The cavity of the heating element pipe, in which the desired spiral is located, is filled with bulk insulating material, which may look like white sand or gypsum. Under high pressure, this substance is pressed into a monolithic state, so to remove the nichrome thread, you must first remove all the insulating material.
The easiest way to do this is to crumble part of it on one side of the tube, and then lightly tap the insulating material with a hammer. This is a very long and tedious process, after which the required nichrome thread is easily removed from the tube.
A simple way to determine the type of wire
Sometimes manufacturers use kanthal instead of nichrome in their devices. When removing material from tools, it is advisable to be able to distinguish between the two alloys. It's not as difficult as it might seem. The fact is that kanthal contains iron (hence the susceptibility of kanthal threads to corrosion), so it is highly magnetic. Therefore, in order to determine the type of alloy, it is enough to bring a magnet to the wire - nichrome will not react to it.
Nichrome thread is most common in heating elements due to its low cost and good physical properties. Its use in everyday life is found in the role of heating elements for hair dryers, soldering irons, kettles, electric stoves and many other appliances. Due to their high heat resistance, nichrome materials are used at elevated temperatures. In addition, nichrome, along with other alloys, is used in evaporators for electronic cigarettes.
The prevalence of wire often raises the question of where to get nichrome wire. You can take it at home by disassembling an unnecessary device, but the best option would be to purchase the material in a store. In this case, you can be sure of the good composition of the product.
If necessary, nichrome can be replaced with another type of wire , the main thing is to determine its physical properties.
It should be remembered that depending on the composition of the alloy, the physical properties may differ, so it is necessary to clarify the requirements for the material when this is of high importance.
What is Resistance Heating Alloy
Resistive materials are materials that heat up to high temperatures when current passes through them.
The reliability, quality and technical characteristics of heating elements depend on the composition of the material.
The main types of resistive alloys include:
- Nichromes are alloys of nickel and chromium.
- Ferkhali - alloys of iron, chromium and aluminum.
- Multicomponent alloys, in which, in addition to chromium, aluminum, iron, alloying elements are added - copper, manganese, silicon, titanium.
The melting point of multicomponent alloys is 1500°C, and the service life of heating elements is 2-3 times longer than nichrome products.
Resistivity of nichrome and other alloys for heaters
Electrical resistivity determines the ability of a metal to prevent the passage of current. It is calculated as the ratio of the electric field to the current density and is measured in Ohm mm²/m.
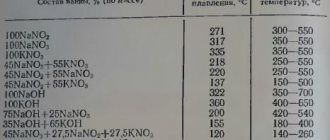
Table 2. Resistivity of main alloys suitable for heating elements.
| Alloy | Resistivity | |
| ||
| 80 – Nickel, 20 – Chrome | 1.0803 Ohm mm2/m | |
| 80 – Nickel, 20 – Chrome | 1.18002 Ohm mm2/m | |
| 35 – Nickel, 20 – Chrome, 45 – Iron | 1.01382 Ohm mm2/m | |
| ||
| 73 – Iron, 22 – Chrome, 5 – Aluminum | 1.45425 Ohm mm2/m | |
| 74 – Iron, 22 – Chrome, 4 – Aluminum | 1.35453 Ohm mm2/m | |
| 81 – Iron, 15 – Chrome, 4 – Aluminum | 1.35453 Ohm mm2/m | |
| ||
| 55 – Copper, 45 – Nickel | 0.4986 Ohm mm2/m | |
| 89 – Copper, 11 – Nickel | 0.1495 Ohm mm2/m | |
| 98 – Copper, 2 – Nickel | 0.0498 Ohm mm2/m | |
The main factors in choosing an alloy for the manufacture of heaters are the combination of high electrical resistance and the ability to withstand extremely high temperatures for a long time.
Calculation of an electric spiral made of nichrome
The parameters of the spiral can be calculated using electronic calculators on the manufacturers’ website. By specifying the heater power, supply voltage and wire diameter, you can calculate the length of wire required for the heater coil.
Resistance calculation
It is calculated based on the diameter of the wire used or the cross-sectional area of the tape.
The total length of the wire is multiplied by the resistivity of one meter of conductor with the appropriate cross-section.
If the brand of alloy is known, the resistivity of the wire is taken from tables located in technical reference books, GOST or on the Internet.
If the alloy grade is unknown, the performance of the wire or finished spiral can be measured with a multimeter.
Using an online calculator, you can make a preliminary calculation of the spiral, but to accurately calculate the parameters of the heater, many more factors should be taken into account.
Nichrome spirals.
Length calculation
The length of the nichrome spiral depends on the resistivity and diameter of the wire and is determined by the formula: L=(Rπd2)/4ρ.
- R – wire resistance;
- d – wire diameter;
- ρ – resistivity of nichrome;
- π – constant = 3.14.
We take ρ nichrome from the table GOST 12766.1-90: ρ=1.0÷1.2 Ohm mm2/m.
Table 3. The relationship between current strength, diameter and cross-section of nichrome.
| Permissible current (I), A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Diameter (d) of wire at 700°C, mm | 0,17 | 0,3 | 0,45 | 0,55 | 0,65 | 0,75 | 0,85 |
| Wire cross-section (S), mm | 0,0227 | 0,0707 | 0,159 | 0,238 | 0,332 | 0,442 | 0,57 |
Example:
It is necessary to calculate the length of the wire for the spiral of the electric stove.
Tile power P = 800 W.
Mains voltage U=380 V.
Solution:
- We determine the current strength: I = P/U = 800/220 = 3.64 A.
- We determine the wire resistance R = U/I = 220/3.64 = 61 Ohm.
- Based on these data (see Table 3), we select d=0.55 mm; S=0.238 mm.
Then the wire length l = SR / ρ = 0.238 61 /1.1 = 13.2 m = 13,200 mm.
- L—wire length (mm);
- S—wire cross-section (mm);
- R—wire resistance (Ohm);
- ρ - resistivity (for nichrome ρ=1.0÷1.2 Ohm mm²/m).
Examples of where you can get nichrome alloy
There are several ways to get nichrome. Each of them differs in the ease of obtaining and the quality of the material, but it is worth considering all possible options.
Ordering material
Nichrome, kanthal, nickel, and wire of some other alloys are sold in wholesale stores. The assortment provided by wholesalers is very large; you can order wire of any desired alloy of any cross-section and thickness. Relevant information about available stores can be found by calling the city's information service, or using an Internet search.
Even if the customer lives in a remote locality where the supplier’s organization is not located, you can request delivery, choosing the most convenient of the proposed options.
The caveat is that you will have to pay a considerable amount for delivery, and intermediaries send orders in large quantities and are unlikely to agree to supply a couple of meters of material.
Shopping in stores
Probably the most adequate option of all possible for those who require high-quality wire of a certain cross-section, especially when only a few meters of material are required.
Purchasing also has its options:
How to wind a spiral from nichrome
You can make a spiral from nichrome wire at home.
To do this, you need to select a wire of a suitable grade and calculate:
- wire length;
- spiral winding pitch;
- number of turns.
The length of one turn is determined by the formula:
l=π(D+d/2)=3.14(5+0.55/2)=32 mm.
Number of turns:
N=L/l=13 200/32=412 turns.
- d—wire diameter;
- L—wire length;
- I is the length of the turn;
- D is the diameter of the coiling rod.
The number of turns of wire when wound onto a tubular rod D=10 mm is 412 pcs.
In practice, they rarely wind spirals at home. It is easier to buy a heating element with the required parameters in a specialized store.
Homemade spiral winding.
Which devices contain nichrome wire?
Nichrome wire is not such a hard-to-find material as it might seem at first glance. Some stores charge quite an impressive price for it. However, there is no need to spend money when you can get the material completely free or for pennies.
Nichrome wire is a component of all heating elements of household appliances. A regular electric kettle contains about one and a half meters of such wire; it can also be found in old models of irons, which contain about 2 meters of nichrome. If you have a non-working fan heater, you can also remove nichrome wire from it. It is quite easy to get it out of faulty toasters and hair dryers. Nichrome can be removed from the heating element in the washbasin. You need to carefully open the tenu with a grinder and clean the wire from the white insulation.
A minimum investment will be required if you purchase the cheapest soldering iron for 50 rubles. There is a wire with a cross-section of 0.1 mm and a length of about 2 meters. In this case, the wire with the plug and other parts are also a bonus, so we can assume that the nichrome wire was received practically for nothing. Among budget purchases, it is worth noting spirals for open-type tiles, which can be selected with different sections.
There is a fairly simple way to determine that nichrome is used in the device. You need to check the wire with a magnet. Kanthal, similar to nichrome, is magnetic, unlike nichrome.
Usually, at home, such wire is very convenient for cutting foam and polystyrene. To do this as quickly and efficiently as possible, you can build a simple cutter, the main part of which will be a hot nichrome string. To do this, you need to prepare a step-down transformer, a lining made of some pipe with a thickness of at least 2 cm, and the thickness of the foam plastic should also be at least 2 cm. You also need springs for tensioning the string and the nichrome wire itself. As a base, you can take a tabletop, board or sheet of corrugated board. For shaped cutting of foam plastic, you will need a cutter made of fairly thick wire, which will be attached to an insulated handle.
Modern technology places serious demands on the compliance of its constituent materials with real operating conditions. One of the high-tech alloys is nichrome. The wire and devices containing it are resistant to aggressive operating conditions.
Temperature coefficient of resistance
The resistivity of an alloy changes when the material is heated or cooled.
The temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) of nichrome is defined as the ratio of the change in electrical resistance to the change in temperature in degrees Kelvin, taken to the minus of the first power (Kˉ¹).
TKS of nichrome is determined by the formula: α= (R1 - R2) / R1 X (T1 - T2), where:
- R1 is the resistance value at the initial temperature;
- R2 - at final temperature;
- T1—initial temperature;
- T2—changed temperature;
- (R1 - R2) - difference in electrical resistance;
- (T1 - T2) - temperature difference.
Heating by 100°C increases the electrical resistance of nichrome by 2%.
Nichrome 60 vs Nichrome 80
The properties of nichrome are determined by the quantitative ratio of nickel and chromium in the alloy.
The more nickel in the alloy, the higher its maximum operating temperature:
- for nichrome X20N80 this figure is 1200°C;
- for alloy X15N60 - up to 1125°C.
The next important indicator is plasticity. It affects the machinability of the metal.
Nichrome 60 alloy was created by reducing the amount of nickel in the alloy and increasing modifying additives to reduce the cost of heaters.
The use of the more expensive X20N80 alloy is justified when operating devices at extremely high temperatures.
How to identify nichrome wire at home
Nichrome wire is a popular material that has already taken its place as a “traditional” one among many similar products. It is obtained thanks to an alloy of nickel and chromium.
If you are also looking for such an option, then simply enter nichrome wire to buy into your search query and then look through all the proposed products.
What is nichrome
It is worth noting that such an alloy contains a large concentration of chemical elements, which ensures strength and resistance to electrical influences.
Why is nichrome in demand in various fields? Here are some features of this material:
- sustainability. The product does not rust and has excellent corrosion resistance, which cannot be said about other types of metals;
- cannot be deformed. Nichrome wires retain their properties under any influence;
- elasticity. The material can be given various shapes.
Nichrome wires are used in various fields. The product is used for the manufacture of machines and devices for wood processing.
Wire has found wide application in the creation of ordinary household heaters.
There is a certain classification of nichrome products, which is necessary if they are used in various systems. For example, marking C indicates that the product is used for the manufacture of various elements characterized by resistance.
The letter H on the wire indicates that the material is used to create heating systems.
The article number of the heating element means that nichrome wire is used in the manufacture of electrical options. Most often these are heating systems.
How to distinguish
During purchase, it is quite difficult for some buyers to distinguish nichrome wire from other products. Most often the material is confused with tungsten.
To avoid such questions, you can use the following tips:
- corrosion resistance. Nichrome has less resistance, so when exposed to an acidic environment, the wire may change color;
- heating. When exposed to high temperatures, tungsten can be deformed;
- appearance. Nichrome wire differs significantly in color.
Also, “cold” processing methods are not used to create the product, which cannot be said about other metals. Most often, during manufacturing, it is rolled into coils, which is quite convenient to use.
An option for “mining” nichrome wire is in this video:
Nichrome from used products or purchased, but not in demand, ends up through non-ferrous metal collection points for recycling.
Nichrome in any form is purchased by both small outlets and reputable companies; the price also varies.
Let's consider what nichrome and its scrap are, how much they pay for 1 kg of this alloy and why.
Properties and applications of nichrome
An alloy of nickel and chromium in a ratio of 80 to 20, obtained in 1905, thanks to its technical properties, has found application in many devices and products. Despite the high cost of the resulting material, obvious benefits were observed due to the durability and trouble-free operation of the devices.
The percentage ratio of nickel-chromium was selected experimentally and solved the set goal: to achieve properties of the metal that were not provided by any of those used in technology at that time.
Advantageous characteristics of nichrome:
plasticity (an important property in the production of nichrome products); heat resistance; low expansion coefficient when exposed to high temperatures; does not create a significant electromagnetic field when using products in electrical appliances: high current resistance (the main parameter for use in electric heating devices); small specific gravity.
Currently, the alloy composition may vary. Supplements may be added from:
The main brands of nichrome are X20N80 and X15N60.
Products made from nickel-containing alloy:
- ribbon;
- rod;
- wire;
- certain types of fasteners;
- parts for operating devices under conditions of sudden and repeated temperature changes and (or) in an aggressive environment.
Effect of temperature and processing on resistivity
Thanks to the resistance of the metal opposing the flow of electricity, nichrome heaters generate heat.
Indicators may vary depending on various factors:
- Alloy temperatures. When the temperature increases from 20°C to 650°C, the resistivity increases by about 8%.
- Manufacturing and processing methods. The resistance changes after annealing and rapid cooling:
- Х20Н80 – increase by 6%;
- Х30Н70 – increase by 4%;
- Х15Н60 – increase by 2%.
Alloy X20N35 resistivity practically does not change during processing and temperature changes.
The ability to change resistivity depends not only on the alloy composition, but also on the cross-sectional size of the heater. Elements of a smaller cross-section react more strongly to changes in the temperature of the alloy than massive parts.
Buy wire for winding vape coils in Moscow
Now we will tell you in detail how to wind a vaporizer for an electronic cigarette. Naturally, the nuances will vary depending on the type of winding, but the sequence of actions remains the same in any case.
There are also such unusual coils.
Regardless of the type of winding (pigtail, microcoil or art coil), to implement this process you will need the following tools:
- scissors or stationery knife;
- wire cutters;
- pliers;
- tweezers (preferably with ceramic legs);
- Screwdriver Set;
- a special winder on which the winding process will be quick and convenient (in the absence of such a device, you can take a drill, a large-diameter screwdriver, etc.).
The consumables you need are wire and cotton wool for the wick. In our case, this is Kanthal A1 (you can, of course, take material of any other thickness) and Chinese cotton, which, as a wick, is very convenient, since you can easily cut a measuring strip from it and immediately pull it into a spiral without additional manipulation.
The process of implementing Kanthal winding is as follows:
- First of all, you need to thoroughly wash your hands so that our winding does not pick up foreign odors, for example, food.
- Then we move directly to winding. Take a winder, or whatever you will use instead, and start winding the wire. If you are making a spacecoil, then leave small gaps between the coils, but in the case of microcoils, the coils should fit tightly to each other.
- At this stage, the microcoil is almost ready for use, and the spacecoil needs to be “springed” a little more so that it takes on the “correct” look.
We figured out the winding process. If you want to wind your atomizer with more sophisticated coils, then in one of our publications we talked in detail about the types of windings. There are also algorithms for their implementation.
6 steps.
The next step is installing the spiral. Here you need to take into account some nuances:
- First of all, you need to unscrew the fixing screws and push the edges of our spiral under them.
- After this, we adjust the position of the winding so that it is strictly in the center of the base and does not touch the nearby racks. Next we fix the spiral.
- Then we need to harden our coils. You need to burn the spiral with short and not long presses on the electronic start button. We do this until the spiral is completely warmed up and turns red. If the coils do not heat up in some places, you need to lightly run them with tweezers.
All that remains is to insert the wick into the coils and you can start tasting the new winding. Do you also wind your vape? Or do you have your own special secrets?
If you are an experienced vaper and like to control the entire vaping process, customizing the device for yourself, then you cannot do without a special wire for winding coils. By using such wire and winding it as correctly as possible, you will definitely achieve the desired effect.
In our store's assortment you can purchase single-core and multi-core wires for winding spirals. We offer models with high conductivity, pleasant taste and abundant steam. Thanks to the correct selection of wire, you can independently control the entire process and improve the quality of vaping.
Soldering nichrome
With prolonged use of electric heating devices or overheating, the nichrome spiral may burn out.
You can connect elements made of nichrome to each other, as well as to steel, copper or their alloys by soldering, using tin-lead solder POS 50 or POS 61.
In addition, a flux is used from a mixture of technical petroleum jelly (100 g), glycerin (5 g) and zinc chloride powder (7 g), mixed to a pasty state.
Soldering is performed in the following order:
- the elements to be connected are cleaned with abrasive sandpaper;
- degreasing is performed using a ten percent alcohol solution of copper chloride;
- parts are treated with flux;
- the ends of the wire are tinning;
- soldering is in progress.
Tinning can be done using regular citric acid. To do this, a small amount of it is poured onto a wooden stand, the stripped ends of the parts to be joined are placed on the powder and heated with a soldering iron. The acid melts, covering the metal surface with a thin layer.
To remove residual citric acid, the ends of the wire are tinned again using rosin.
Soldering is performed using POS 40/50/61 solders.
Repairing a burnt-out nichrome spiral using solder is not suitable for devices whose heating exceeds 300°C.
Nichrome soldering.
How can I replace nichrome thread?
A modern analogue of nichrome is fechral (FeCgAl) - an alloy of iron, chromium and aluminum.
Fechral heaters are used in mechanical engineering, foundry industry, glass and ceramics production, and other industries.
The material is supplied in the form of wire, thread, spirals of various diameters or ready-made heating elements.
The advantages of fechral heaters compared to nichrome ones include:
- no scale;
- lower density;
- longer service life (2-4 times);
- the cost is 2-3 times lower than nichrome.
Protection of fechral heating elements is provided by aluminum film. When working in a non-oxidizing environment, the protective film should be restored by annealing in air (in an oxidizing environment).
At temperatures above 900°C, the metal becomes grainy and brittle.
Fechral heating elements must be placed on ceramic tubes, since at temperatures above 800°C the spirals can deform even under their own weight.
Fechral wire 0.5 mm X23Yu5T.
Application of nichrome in medicine
Since nichrome is a 100% natural material, it is not harmful to humans and does not emit any harmful fumes. In addition, unlike its analogues, nichrome does not cause virtually any allergic reactions. This allows this mixture of metals to be used in medicine.
- An extremely thin nichrome thread is made and used for suturing.
- It is absolutely harmless to the skin and reliably fulfills its role - maintaining the wound until it heals.
- Nichrome not only does not interfere with the smooth healing of scars and wounds, but also accelerates this process.
This fact is not only confirmed experimentally, but also proven by several scientific studies on this topic. In addition to pure medicine, nichrome is used in pharmacological laboratories. It is installed in the bases of heating and cooling elements.
Nichrome insulation with silicone multi-core cable
Heat-resistant heating cable in silicone insulation based on X20N80 tape or wire is used in various heating systems and thermal treatment installations.
To insulate nichrome wire or tape, two-layer silicone insulation is mainly used.
The basis of the insulating material is silicone rubber, obtained on the basis of high molecular weight organosilicon compounds. In appearance, the insulation is similar to ordinary rubber, but differs from it in higher technical indicators:
- resistance to high voltages - breakdown voltage is 5,000 Volts;
- resistance to aggressive environments and atmospheric influences;
- fire resistance - the material does not burn and does not emit toxic smoke when burned;
- operating temperatures from -60°С to +180°С;
- increased strength and durability.
Silicone insulation can withstand short-term temperature increases up to 220°C without changing the structure and quality of the coating. It is not destroyed by ultraviolet and radioactive radiation. Does not lose its qualities under the influence of ionizing radiation up to 20 Mrad (20 x 106 kJ/kg).
For the manufacture of heat-resistant heating cables, mainly two-layer silicone insulation is used.
Nichrome in isolation.
Peculiarities
First of all, it should be noted that the high popularity of the heating cable is due to its impressive efficiency. It converts almost all electrical energy into heat, allowing you to minimize losses and achieve optimal consumption of available resources.
If we single out situations for which underfloor heating is considered the best solution, then their list will look like this:
- use of cold coatings (optionally, ceramic tiles);
- high level of humidity in rooms (most often these are bathrooms);
- inability to connect to central heating (relevant for dressing rooms and hallways, as well as insulated loggias and balconies);
- the need to heat suburban real estate.
Another remarkable feature of floors equipped with a heating cable is the ability to install them under a variety of types of coverings. It’s enough just to get acquainted with the principle of operation and arrangement of such heating systems, as well as with their main varieties.
Operating requirements
To ensure a long service life of nichrome products, it is important to follow certain rules:
- to prevent overheating, winding the heating cable on the frame in several layers is not allowed;
- the bend of the current-carrying core in the cable should not exceed five of its diameters.
The integrity of the conductor can be restored by mechanical twisting, threaded clamps or couplings, soldering or welding.
When you turn on a device with a nichrome heating cable for the first time, a small amount of smoke may be released due to the burning out of residual oil.
Nichrome spiral