Chemical composition.
Steels are usually called alloys of iron and carbon containing up to 2.14% carbon.
Depending on the chemical composition, carbon steels (GOST 380-71, GOST 1050-75) and alloy steels (GOST 4543-71, GOST 5632-72, GOST 14959-79) are distinguished. In turn, carbon steels can be:
- low-carbon, i.e. containing less than 0.25% carbon;
- medium-carbon, carbon content is 0.25-0.60%;
- high-carbon, in which the carbon concentration exceeds 0.60%.
Alloy steels are divided into:
| Table of elements MS Word, 40Kb |
- low alloy content of alloying elements up to 2.5%;
- medium alloyed, they contain from 2.5 to 10% alloying elements;
- highly alloyed, which contain over 10% alloying elements.
Purpose
Structural, intended for the manufacture of construction and engineering products.
Tools, from which cutting, measuring, stamping and other tools are made. These steels contain more than 0.65% carbon.
With special physical properties, for example, with certain magnetic characteristics or a low coefficient of linear expansion: electrical steel, superinvar.
With special chemical properties, for example stainless, heat-resistant or heat-resistant steels.
Spectral analysis of metals
This is a modern method that allows you to find out the composition of almost any mineral or finished product based on analyzed physical properties, in particular, reflection, emission, luminescence, etc. The fact is that atoms of different substances emit special wave elements characteristic only of one.
They have their own length, frequency, etc. Therefore, only the wave nature of the sample can be taken into account in order to accurately determine what additives are in its composition. And for this they use a spectral determinant of steel grade. This is the device that performs this analysis. It is available in almost all industries, but can also be used in everyday life, since it does not require any special skills to use. But there are nuances. For example, it is important to take into account the fact that during burning (as the sampling process is terminologically called), only the top layer of a few mm is determined, so it is very important that the entire bar (rod) is made of a homogeneous material. It is also worth knowing that there are four types of spectral analysis:
- Emissive – registers waves emitted by a substance.
- Absorption – takes into account how much it absorbs.
- Luminescent - determines whether additives can glow or emit light.
- Raman - focuses on the scattering of light and the excitation of molecular vibrations.
This method is very widely used in laboratories, as well as in large industries. The device uses a high-temperature spark or electric arc plasma (more than 10,000 K) as a light source, which is generated by an external storage device. Only after such excitation from the outside do atoms begin to emit their own waves, and conclusions can be drawn based on their length and features.
Degree of deoxidation
According to the degree of oxygen removal from steel, i.e. according to the degree of its deoxidation, there are:
- calm steel, i.e., completely deoxidized; such steels are designated by the letters “sp” at the end of the grade (sometimes the letters are omitted);
- boiling steels - slightly deoxidized; are marked with the letters “kp”;
- semi-quiet steels, occupying an intermediate position between the previous two; are designated by the letters "ps".
Ordinary quality steel is also divided into 3 groups based on supplies:
- Group A steel is supplied to consumers based on its mechanical properties (such steel may have a high sulfur or phosphorus content);
- steel group B - by chemical composition;
- steel group B - with guaranteed mechanical properties and chemical composition.
Depending on the standardized indicators (tensile strength, elongation, yield strength, cold bending), the steel of each group is divided into categories, which are designated by Arabic numerals.
Price for steel 5Gps
The favorable price for the 5Gps steel grade is explained by the presence of a competitive environment, low markups and loading from leading metallurgical plants directly, sometimes bypassing storage at transshipment points. Metalpro company bears full responsibility for the chemical composition of the supplied products and guarantees the quality of delivery. The cost of 5Gps steel in warehouses in Moscow and the Moscow region is determined by the costs of warehousing and logistics. Metallpro Company can also supply 5Gps steel directly from the metallurgical plant, which gives our partners an advantage to consistently save money and develop their business in a broad format.
The price for 5Gps steel is determined personally with each company, monthly needs are individually negotiated and the form of payment is discussed. Warehouse services for custom-made items and logistics to the production site also form the cost of 5Gps steel. The Metalpro company maintains an open dialogue personally with each of its clients; each transaction is accompanied by a personal manager from the production stage to the delivery of rolled metal to the customer. Full control at any stage from payment to delivery to the customer’s site gives the latter a complete picture.
Unalloyed structural steels of ordinary quality
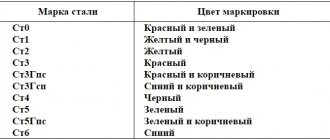
Designated according to GOST 380-94 with the letters “St” and a conventional brand number (from 0 to 6) depending on the chemical composition and mechanical properties. The higher the carbon content and strength properties of the steel, the higher its number. The letter “G” after the brand number indicates a high manganese content in the steel. The steel group is indicated before the grade, and group “A” is not included in the designation of the steel grade. To indicate the category of steel, the number corresponding to the category is added to the brand designation at the end; the first category is usually not indicated.
For example:
- St1kp2 - carbon steel of ordinary quality, boiling, grade No. 1, second category, supplied to consumers based on mechanical properties (group A);
- VSt5G - carbon steel of ordinary quality with a high manganese content, calm, grade No. 5, first category with guaranteed mechanical properties and chemical composition (group B);
- Vst0 - carbon steel of ordinary quality, grade number 0, group B, first category (steel grades St0 and Bst0 are not separated by degree of deoxidation).
| Steel designation | Carbon content |
| St0 | < 0,23% |
| St1 | 0,06-0,12% |
| St2 | 0,09-0,15% |
| St3 | 0,14-0,22% |
| St4 | 0,18-0,27% |
| St5 | 0,28-0,37% |
| St6 | 0,38-0,49% |
Characteristics of steel grade 5Gps
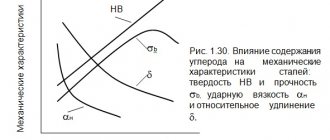
St5Gps - Structural carbon steel of ordinary quality, limited weldability, welding is carried out without heating and without subsequent heat treatment, welding methods: RDS, ADS submerged arc and gas shield, ESW. Preheating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended. CTS without restrictions. For thicknesses greater than 36 millimeters, heating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended; it is not prone to flake sensitivity and there is no tendency to temper brittleness. Machinability by cutting in the hot-rolled state at НВ 158 and σв=640 MPa, Kυ hard alloy. = 1.2 and Kυ b.st. = 1.2, has found its application in the production of beams, angle steel, and channels. Forging is carried out at temperatures from 1260 to 750 0C, cooling is carried out in air.
Unalloyed structural quality steels
In accordance with GOST 1050-88, these steels are marked with two-digit numbers showing the average carbon content in hundredths of a percent: 05; 08; 10; 25; 40, etc. So steel with a carbon content of 0.07-0.14% is designated 10, steel with a carbon content of 0.42-0.50% is designated 45, and steel with a carbon content of 0.57-0.65% is designated 60.
In this case, for steels with C < 0.2% that have not been subjected to complete deoxidation, the letters kp (for boiling steel) and ps (for semi-quiet steel) are added to the designation.
For mild steels, letters are not added at the end of their names. For example, 08kp, 10ps, 15, 18kp, 20, etc.
The letter G in the steel grade indicates a high manganese content. For example: 14G, 18G, etc.
High-quality steels with improved properties, used for the production of boilers and high-pressure vessels, are designated according to GOST 5520-79 by adding the letter K at the end of the steel name: 15K, 18K, 22K.
Mechanical properties of 5Gps steel at elevated temperature
| Test temperature, °C | σ0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, J/m2 |
| 20 | 330 | 535 | 25 | 52 | 64 |
| 100 | 310 | 500 | 20 | 54 | 69 |
| 200 | 305 | 19 | 40 | 78 | |
| 300 | 215 | 22 | 50 | 69 | |
| 400 | 185 | 500 | 23 | 64 | 59 |
| 500 | 160 | 365 | 24 | 70 | |
| 600 | 88 | 195 | 35 | 80 |
Structural alloy steels
In accordance with GOST 4543-71, the names of such steels consist of numbers and letters. The first digits of the brand indicate the average carbon content in steel in hundredths of a percent. The letters indicate the main alloying elements included in the steel. The numbers after each letter indicate the approximate percentage content of the corresponding element, rounded to the nearest whole number; for an alloying element content of up to 1.5%, the number behind the corresponding letter is not indicated.
For example, steel of composition C 0.09-0.15%, Cr 0.4-0.7%, Ni 0.5-0.8% is called 12ХН, and steel of composition C 0.27-0.34%, Cr 2.3-2.7%, Mo 0.2-0.3%, V 0.06-0.12% - 30×3MF.
In order to show that the content of sulfur and phosphorus in steel is limited (S < 0.03%, P < 0.03%) and the steel belongs to the high-quality group, the letter A is placed at the end of its designation.
Particularly high-quality steels subjected to electroslag remelting, which ensures effective purification from sulfides and oxides, are designated by adding the letter Ш through a dash at the end of the name of the steel. For example: 12×2N4A, 15×2MA, 18ХГ-Ш, 20ХГНТР-Ш, etc.
Unalloyed carbon tool steels
These steels, in accordance with GOST 1435-90, are divided into high-quality and high-quality.
High-quality steels are designated by the letter U (carbon) and a number indicating the average carbon content in the steel, in tenths of a percent. Thus, U7 steel contains 0.65-0.74% carbon, U10 steel - 0.95-1.04%, and U13 steel - 1.25-1.35%.
The letter A is added to the designations of high-quality steels (U8A, U12A, etc.).
In addition, the designations of both high-quality and high-quality carbon tool steels may contain the letter G, indicating an increased content of manganese in the steel. For example: U8G, U8GA.
Delivery of St5Gps
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to GOST 2590-88 Hot-rolled round steel, GOST 2591-88 Hot-rolled square steel, GOST 8239-89 Hot-rolled steel I-beams, GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles, GOST 19772 -93 Bent steel angles, unequal flange, GOST 8278-83 Bent steel channels, equal flange, GOST 8281-80 Bent steel channels, unequal flange, GOST 8283-93 Bent steel trough equal flange profiles, GOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality, GOST 8509-93 Steel corners hot-rolled equal flange, GOST 8510-86 Hot-rolled steel angles unequal flange, GOST 8240-97 Hot-rolled steel channels, GOST 535-88 Rolled bars and shaped carbon steel of ordinary quality, GOST 2879-88 Rolled hot-rolled hexagonal steel, GOST 19903-2015 Rolled sheets hot rolled , GOST 19904-90 Cold-rolled sheets, GOST 16523-97 Rolled thin sheets of high-quality and ordinary quality carbon steel for general purpose, GOST 503-81 Cold-rolled low-carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot-rolled steel strip, GOST 82-70 Hot-rolled steel broadband universal, GOST 3282-74 General purpose low-carbon steel wire, GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wire, GOST 10705-80 Electric-welded steel pipes, GOST 10706-76 Straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes, GOST 3262-75 Steel water-gas pipes.
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | GOST 380-2005; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 8239-89; GOST 5422-73; GOST 535-2005; GOST 8510-86; GOST 8509-93; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 2591-2006; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 19425-74; GOST 19240-73; GOST 9234-74; GOST 11474-76; GOST 8240-97; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 14918-80; GOST 103-2006; GOST 19903-74; GOST 14637-89; |
| Ribbons | GOST 3560-73; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 3262-75; |
Tool alloy steels
The rules for designating tool alloy steels according to GOST 5950-73 are basically the same as for structural alloy steels. The difference lies only in the numbers indicating the mass fraction of carbon in the steel. The percentage of carbon is also indicated at the beginning of the name of the steel, in tenths of a percent, and not in hundredths, as for structural alloy steels. If the carbon content of alloy tool steel is about 1.0%, then the corresponding figure is usually not indicated at the beginning of its name.
Let us give examples: steel 4×2V5MF has a content of C 0.3-0.4%, Cr 2.2-3.0%, W 4.5-5.5%, Mo 0.6-0.9%, V 0.6-0.9%, and HVG steel - C 0.9-1.05%, Cr 0.9-1.2%, W 1.2-1.6%, Mn 0.8-1, 1%.