Bronze is an alloy of copper and special additives that are necessary to give the metal certain technological properties. Bronze may contain the following components: Sn (tin), Mn (manganese), Be (beryllium), Pb (lead), Si (silicon), Cr (chromium), P (phosphorus), Fe (iron) and other elements.
Bronze alloy is resistant to abrasion, corrosion, and aggressive environments such as sea water. These properties are achieved by adding alloying components in certain proportions. The ratio of components is regulated by regulatory documents: GOST, industry standards, methods, enterprise standards.
Composition options
This material is a mixture of copper with alloying elements, which are non-metals and metals. However, zinc and nickel should not be the main ones among them.
By varying the ratios between the components, the properties of bronze are changed. In accordance with this, there are several varieties of it, distinguished on the basis of alloying additives. They are used as:
- tin;
- beryllium;
- zinc;
- silicon;
- lead;
- aluminum
- nickel;
- iron;
- manganese;
- phosphorus.
Tin bronze was the first to be developed (at the beginning of the 3rd millennium BC). In small quantities, this element imparts hardness, fusibility, and elasticity. When its concentration increases to 5%, ductility decreases, and at 20% bronze becomes brittle. By bringing tin to a maximum of 33%, the alloy gives a silvery-white color.
The material with beryllium is characterized by the greatest elasticity (hardened) and hardness, as well as chemical resistance. It is suitable for processing by cutting and welding.
Bronze appearance
Zinc and silicon increase fluidity, which is important for casting, and also give the surface abrasion resistance. Silicon-zinc bronze is characterized by the absence of sparks during mechanical action and good compression resistance.
Lead improves corrosion resistance, anti-friction properties, strength, and refractoriness.
Aluminum increases density, anti-friction properties, resistance to corrosion and chemical attack. Bronze of this composition is suitable for cutting.
Phosphorus is used in conjunction with some other additives to deoxidize the alloy. Its presence is reflected in the name when the content is more than 1% (tin-phosphor bronze).
The introduction of any alloying additives reduces thermal conductivity. Consequently, the fewer there are, the closer the alloy is to copper in this indicator, and the most alloyed bronzes have worse thermal conductivity.
As for copper, its content determines not only technological and operational parameters, but also the color that bronze has. Red color indicates a copper concentration of more than 90%. With a content of about 85% (the most common), bronze has a golden color. If the alloy is half copper, its white color resembles silver. To obtain gray and black colors, you need to reduce the percentage of copper to 35. This color of the material is also common, but it must be taken into account that this alloy can acquire a dark color over time as a result of exposure to various factors (temperature, water, etc.). In addition, technologies that make it possible to add alloying elements to bronze that give it a rich black color began to be used relatively recently, and products made from the alloy in question with this color have been widespread for a long time.
Thus, depending on the number of elements, these materials are divided into two-component (one alloying component) and multi-component. Their share is from 2.5%.
In addition, there is a classification of bronze based on the internal structure, namely the number of phases in the solid solution. It implies its division into single- and two-phase options.
Finally, due to the widespread occurrence of the tin type, the alloy is divided into tin and tin-free bronzes.
Story
One of the most famous places where bronze items were found was located in the Kuban River area. In this place, archaeologist Nikolai Veselovsky in 1897 excavated the so-called Maykop culture, which existed in the second half of the 4th millennium BC.
Bronze artifacts found in the Maikop burial mounds were made mainly from an alloy of copper and arsenic, so it is believed that historically these alloys, called arsenic bronzes, .
It was in no way inferior in its properties to alloys of copper with tin or lead, and even surpassed them in a number of characteristics . It was widely used in various areas of human activity of those times, from the manufacture of critical parts to jewelry.
Bronze composition
Bronze is an alloy of copper with metals such as tin, aluminum, lead, beryllium, and non-metals arsenic, silicon and phosphorus. In addition, such alloys can be additionally alloyed with phosphorus, zinc, manganese, iron and nickel.
The composition of bronze depends on the grade of the alloy and is indicated in its designation. For example, the composition of an alloy labeled BrAMts7−1 includes 7% aluminum, 1% manganese and 92% copper .
Thus, the main component of this metal is copper (from 35% to 90% and above). The second component can be either arsenic, or tin or beryllium, lead, aluminum, silicon and other components. To impart special properties, additional components can be added - zinc, iron, nickel, manganese, phosphorus and others.
Production
The raw materials for bronze are pure metals or alloys, including bronze waste. The second option is more widespread, primarily due to its lower cost. Charcoal is used as a flux that prevents excessively intense oxidation of the metal melt. A charge is made from all the starting materials, calculating its composition based on the target parameters and the production technology used.
The melting process is carried out in a certain sequence:
- a crucible with a charge is placed in a furnace preheated to the required temperature (usually electric arc and electrical devices are used due to their high efficiency);
- after complete heating and melting of the metal, phosphorous copper, which serves as a catalyst, is included in its composition;
- after exposure, binder and alloying components of bronze are added, stirring;
- in order to remove gas impurities, degassing is carried out by blowing with nitrogen or argon;
- To reduce the intensity of oxidation, phosphorous copper is added again before casting.
Throughout the entire process, it is necessary to control the temperature and the amount of components added to the melt.
Properties
The characteristics of the material in question are determined by two factors: composition and structure.
As noted, the chemical composition of bronze is developed in order to give it the required parameters. Some of the main ones are bronze’s ductility, hardness and strength. The first two characteristics can be varied by changing the tin concentration. Thus, its share in the composition of bronze is directly related to hardness and inversely related to ductility.
The concentration of beryllium has the greatest influence on hardness and strength. Some brands of bronze containing it are superior to steel in the second parameter. To impart ductility, the beryllium alloy is hardened. In this case, the main importance is not the quantitative indicators of the content of substances, but the severity of the properties they create. That is, with the same amount of two different elements, one of them can change the characteristics of the material to a much greater extent than the other.
Bronze microstructure
As for the structure, it determines the holding capacity of the material in relation to the elements. This can be seen using the example of tin. Thus, a single-phase structure contains up to 6 - 8% of this element. When its amount exceeds the solubility limit of 15%, the second phase of the solid solution is formed. This affects the balance of hardness and elasticity. Thus, single-phase options are more elastic, while two-phase bronze is harder, but brittle. This determines further processing: materials of the first type are suitable for forging, and two-phase alloys are suitable for casting.
Below, as an example, the main characteristics of cast tin bronze are considered. Its density is determined by the tin content and with its share of 8 - 4% it is 8.6 - 9.1 kg/cm3. The melting point is 880 - 1060°C, depending on the composition. The thermal conductivity of this material is 0.098 - 0.2 cal/(cm*s*C). This is a small value. Electrical conductivity is 0.087 - 0.176 μOhm*m, which is also not much. The corrosion rate in sea water is 0.04 mm/year, in air - 0.002 mm/year. That is, such bronze is highly resistant to it.
Varieties
Experts distinguish the following types of bronze:
- Lead - a composition in which the main alloying additive is lead. The finished material is resistant to high pressure. Used in the manufacture of moving elements in industrial equipment.
- Silica-zinc - in addition to the main component, this composition contains tin and silicon. The mixture has good plasticity and fluidity. It is easy to work with the material and make products of complex shapes from it. It welds well and is resistant to low temperatures.
- Beryllium bronze is a hard material. Resistant to high temperatures and corrosion. The composition includes cobalt, nickel and iron.
- Aluminum - the mixture contains 95% copper and 5% aluminum. The material has a golden hue and shines in the light. Resistant to alkalis and acids. Does not change characteristics when exposed to low temperatures, has high strength.
If it is necessary to strengthen the structure of the material, nickel is added to it. Electrical conductivity is reduced with chromium.
Treatment
There is another classification of bronze, based on the processing technology used in the production of any products from it. In accordance with this, two types of alloys are distinguished:
- foundries;
- deformable.
Casting bronzes are used to create castings of complex configurations (parts of various devices, etc.), since they are deformed only in the molten state, while deformable bronze is processed by forging, rolling, cutting, producing rolled metal in the form of wire, tape, pipes , plates, bushings, rods. In addition, bronze is suitable for soldering and welding.
Differences in the nature of the fracture and evaluation of the finished product
Many people will even say, why bother figuring out whether it’s brass or copper if the two alloys look almost the same? But the fact is that this is important for many, in particular for people who will be involved in making some kind of sculptures or melting them down. Accordingly, very often a distinction is required if you are going to sell metal for scrap.
The fact is that brass is cheaper than bronze, so at a metal collection point they can simply deceive you and offer you a smaller amount. If the weight is small, then the losses will be insignificant, but if you have a fairly large amount of goods, then you will lose a decent amount of money. It is worth noting that there is no need to conduct tests, just look at the finished products. Brass is almost never used in shipping.
Locksmith tool
This material is destroyed when exposed to sea salt water, so compasses and some parts in shipbuilding are used exclusively in bronze. Therefore, if they are trying to deceive you, insist on checking the product, or contact a certified center. They usually have collection points as well as small compact laboratories. They can conduct a quick, simple analysis and analyze the product using laboratory equipment.
It is quite easy to distinguish between metals when viewing the fracture site. Brass breaks in fairly small grains, bronze breaks off in large pieces and has a coarse grain. At the same time, the color of the bronze fracture has a reddish tint; if it is brass, then it has a whitish or yellowish tint.
Accessories skull
Unfortunately, these methods cannot be used at home due to the lack of laboratory equipment. Magnet and chip tests are available for home users. They are also very informative.
Additional processing
For a decorative effect and for protective purposes, it is possible to apply varnish, chrome, gilding, or nickel to the surface of bronze products.
In addition, for the material in question there is a specific surface treatment method called artificial patination. It is based on the natural aging process of bronze, which consists of the formation of a green-white film of carbonate or oxide composition, called patina, as a result of exposure to air and the components it contains. The artificial creation of such a coating has a decorative (giving a vintage look) and protective meaning.
This procedure is carried out by heating after applying a sulfur composition to the surface. There is also a reverse technology, that is, removing patina from old bronze products.
Advantages and disadvantages
Bronze has many positive qualities. Among them:
- variety of properties and, consequently, areas of application;
- the ability to create options for various processing methods (casting or deformation) depending on needs;
- slight shrinkage (0.5 - 1.5%);
- the possibility of repeated processing without loss of properties, that is, bronze can be processed;
- high resistance to chemical influences of the environment (water, air, acids);
- greater elasticity of many options.
The main disadvantage is the high cost of some brands, for example, tin bronze. Types of other composition, such as aluminum alloy, are much cheaper. Thus, the cost of the materials under consideration is largely determined by the alloying elements included in their composition.
Application
Tin material with 2% tin is suitable for forging at normal temperature due to its high ductility. Options with its concentration of 15% are characterized by hardness and strength. Such bronze had a wide range of applications in ancient times. Items from it were discovered during archaeological excavations. It was used for the production of dishes, weapons, money, statues, mirrors, and jewelry. However, the best known use of bronze of this composition is for the manufacture of bells, and therefore tin bronze is still called bell bronze.
Bronze bell
Hardened bronze containing beryllium is used for the production of springs, membranes and leaf springs.
For the manufacture of products used in particularly unfavorable conditions (high humidity, chemically active environments, etc.), bronze enriched with aluminum is used. It has high corrosion resistance and strength.
Lead bronze is suitable as a material for parts subject to frictional and impact loads (bearings, etc.).
An alloy containing zinc and silicon is used to produce objects by casting due to its fluidity. In addition, this material is characterized by the absence of sparks under mechanical influence.
Aluminum-nickel bronze is especially relevant for parts that are constantly in salt water due to its high corrosion resistance. This is a relatively new material that is used to produce elements of offshore oil platforms.
Decorative bronze item
Bronze parts
In addition, most grades of bronze are characterized by their lack of magnetism and low shrinkage. Because of this, they are suitable for the production of electrical products as well as decorative items.
Also, many variants of the alloy have low thermal conductivity, as a result of which they are used for the production of bathtubs, washbasins, and plumbing parts.
Finally, most bronze alloys are characterized by poor electrical conductivity. One of the exceptions is a silver alloy, which is close in this parameter to copper.
In addition to the above-mentioned spheres, bronze is used in mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, aircraft construction, for the manufacture of moving units due to wear resistance, chemical devices and pipelines due to chemical resistance.
What is stronger, brass or bronze?
When comparing maximum permissible loads, wear resistance and other parameters, it is important to consider that the characteristics are affected by the composition of the alloys. For comparison, it is worth taking the highest grade metals. This will help you find out how brass differs from bronze in terms of physical and chemical parameters. Having studied the data, you can note:
- Bronze is heavier. The reason is the presence of tin. Its mass is greater than that of zinc.
- The corrosion resistance of brass is lower. Bronze can come into contact with salt water with little or no effect, but brass alloys must be alloyed to reduce the effects of corrosion.
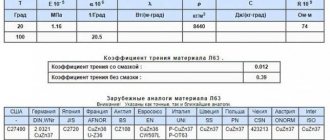
- The wear resistance of bronze products is higher, since the metal has a lower coefficient of friction.
This is interesting: Steel nitriding: process technology, equipment
Based on these properties, it can be noted that bronze is stronger than brass when considering equally high-quality alloys.
Marking
Currently, there are many brands of bronze. They differ in composition, which determines their parameters and scope of application. For convenience, a marking system was created on this basis, including alphabetic and numeric symbols. Thus, alloying additives are designated by the letters first in the name of the chemical elements representing them. The numbers indicate the content of alloy components in fractions of a percent. However, these designations do not contain data on the amount of copper. This value is calculated as the difference between the total composition of bronze and the amount of alloying additives.
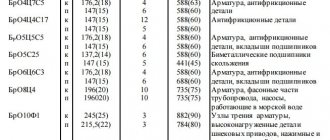
Bronze marking makes it easy to determine the grade required for a specific task. To do this, just use special tables. They contain data on the composition, parameters of the alloy and areas of its application.