Changing the oil in a piston compressor is an important condition for its long operation with minimal repair costs. To increase the reliable operation of units, special lubricants are used, and standards for their supply to the compressor are established. What the lack of proper lubrication of compressors will lead to, whether it is possible to use a double rate of lubricant in the cylinders, and what methods exist for lubricating units will be discussed in this article.
From this article you will learn:
- What is lubricant used for in reciprocating compressors?
- What lubrication systems exist for piston compressors?
- What qualities should a lubricating oil for air compressors have?
- Consequences of over-lubrication or lack of lubrication in reciprocating compressors
1What is lubricant used for in reciprocating compressors?
Lubricant performs several important functions in air compressors:
- Positive displacement compressors,
- Dynamic compressors.
Positive displacement compressors.
In positive displacement compressors, injection occurs due to the sequential filling of the working chamber with gas, and its further compression due to a forced reduction in the volume of the working chamber. To prevent the medium from escaping back, the compressor is equipped with a system of control valves that alternately open during the process of filling and emptying the chamber. The mechanical basis of positive displacement compressors can be different, and therefore devices of this type are divided into the following groups:
- Extends the service life of units by reducing the friction force between driving mechanisms, and accordingly increases their wear resistance.
- Removes excess heat from moving elements.
- Cools working units and cylinders.
- Smoothes out pulsations and vibrations of the compressor during operation.
- Reduces noise levels.
- Creates additional sealing in valve clearances, oil seals, piston rings.
- Cleans the surfaces of rubbing elements.
- Prevents abrasive wear of cylinder components.
- Seals and prevents compressed air leaks.
The car air conditioning compressor has failed: diagnostics and repair of the device
The purpose of the air conditioning system is to ensure a more comfortable stay for the driver and passengers in the vehicle during the trip. As with any unit, this system has mechanisms that are subject to wear and tear. From this material you can find out in what cases repair of the car air conditioning compressor is necessary.
2What are the lubrication systems for piston compressors?
The design of piston compressors uses two independent lubrication systems:
- Lubrication system for cylinders and oil seals,
- Lubrication system for movement mechanisms.
Let's take a closer look at them.
Lubrication of cylinders and oil seals
Lubrication of cylinder wear elements, such as compressor valves, piston rings, bandage rings and oil seals, must be carried out according to the recommendations specified by the compressor equipment manufacturer in the technical documentation. The service life of these components directly depends on the appropriate type of lubricant, its volume and lubrication intervals.
Lubrication of cylinders and oil seals of piston compressors is carried out in one of three ways:
1. Oil splashing from the crankcase.
This method is used in crosshead type compressors (*). From the crankcase bath, oil is captured by special sprayers and distributed over the surface of the cylinder while the piston moves. With subsequent rotations of the shaft, the piston captures the incoming oil and transfers it to other working surfaces of the cylinder. The main disadvantage of this method is the lack of regulation of lubricant consumption. In addition, contact of a large volume of oil with hot air creates an increased content of carbon deposits inside the cylinder, and uneven distribution of lubricating oil throughout all cylinder components is possible.
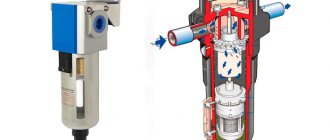
In the Figure, arrows depict the flow of lubricant distribution inside the air compressor cylinder.
(*) Crossheadless compressors are units characterized by simple design and low performance. Due to their weight and size characteristics, these devices are widely used in mobile transport installations, as well as in conditions with high requirements for compactness and low weight.
2. Injecting atomized oil into the incoming air stream.
Lubrication by injection of atomized oil into the suction gas flow is used in multi-stage crosshead compressors. This method allows you to lubricate those parts of the cylinders that are not adjacent to the crankcase. For this purpose, part of the air flow enters the cylinders through the crankcase cavity, which is filled with finely dispersed oil, and is then thrown into the cylinder with oil vapor. However, this method does not allow completely covering all working surfaces of the cylinder. In addition, close contact of some gases with oil mist significantly reduces its quality, so this method cannot be called the best.
3. Lubrication of cylinders and oil seals under pressure.
This method has another name - forced lubrication of the cylinder. It is most often used in crosshead compressors. The lubricant is supplied by a plunger pump - a lubricator. In horizontal type compressors, oil is supplied at the top point, or at two points - with a large cylinder diameter (more than 500 mm). Vertical cylinder compressors also have one or more oil entry points. Their number also depends on the diameter of the cylinders.
Oil flows from the pump through oil lines. To control the flow of lubricants, special control valves with check valves are installed at the inlets, which prevent the release of oil or compressed air from the cylinder when the valve is open. This method is the highest quality, as it allows you to completely lubricate all working surfaces of the cylinder and its components.
Lubrication of movement mechanisms
Lubrication of the moving elements of a piston compressor is carried out in two ways:
- Splashing through the crankcase
- By forced method (by circulating oil inside the compressor).
Let's take a closer look
Oil splash lubrication
along the working surfaces of movement mechanisms are used in compressors with small dimensions and intended for short-term work (for example, for working with a pneumatic impact wrench). Oil is poured into the crankcase bath, which, when the shaft rotates, turns into a mist and only then reaches the rubbing surfaces through the bearing units.
This method does not effectively remove heat, so the spray system is most often used in household or semi-professional compressor models. Another disadvantage of the method is insufficient control over the oil level in the crankcase, which may result in underfilling or overfilling of lubricant in the compressor. It is also possible for the oil to quickly become contaminated, filters become clogged, and dirt and oil enter the compressed air.
Forced lubrication
driving mechanisms is carried out through the compressor crankcase by supplying oil with a gear pump in a closed cycle. Therefore, this method has another name - circulation. The lubricant enters the pump through a coarse filter. Then, after the pump, the oil passes through a slotted (plate) filter and a refrigerator, and enters the mechanisms. Some of the oil flows through holes in the crankshaft to the connecting rod bearings and then, through drillings in the connecting rod or through special pipes attached to the connecting rod, moves to the crosshead pin. The other part of the oil flows to the rubbing surfaces of the crosshead. The forced lubrication system is equipped with pressure gauges and a bypass valve to regulate pressure.
The method of forced lubrication of moving elements is more economical, since the oil remains inside the compressor, and is also the most productive in terms of covering all components of the unit with lubricant.
In Figure 2, the dotted lines show a closed system of forced lubrication of the cylinder and seals of an air compressor.
What is the danger of a refrigerant leak?
Signs associated with a leak:
If the leak is detected on time, the refrigerant has not completely disappeared, the air conditioner did not operate without refrigerant for long, and there are no accompanying signs - repairing the air conditioner in a workshop is not necessary.
The proportion of sudden, catastrophic leaks caused by the destruction of pipelines is very small; leaks most often occur through small leaks in flared joints, and if the operation of the air conditioner is constantly monitored, leaks can be detected in a timely manner.
What to pay attention to:
Following these simple rules will help you avoid high costs for air conditioner repairs.
Moisture getting into the freon circuit most often occurs when the air conditioner installation rules are violated. One of the stages of installation, vacuuming the fren line, aims not only to make life difficult for the installer, but also to remove air and water vapor from the installed line. Such surrogates of this procedure as blowing the installed line with refrigerant cannot remove moisture at all, but only turns it into ice on the walls of copper tubes, which then melts, turns into water and does its job.
Oil acid test
| no acid | with acid |
The danger of moisture getting inside the air conditioner is that it often does not manifest itself until the air conditioning compressor fails. The fact is that all processes in an air conditioner operating in mode occur at positive temperatures, and water manifests itself only when it freezes, causing a malfunction of the capillary tube or thermostatic valve. However, by indirect signs you can determine the presence of moisture in the air conditioner:
Removing moisture from the freon circuit can also only be done in a workshop.
3What qualities should a lubricating oil for air compressors have?
Requirements for lubricants for air compressors
- Lubricating oils must have a flash point in the range of +220...+240C and an ignition temperature of about +400C.
- Sufficient viscosity of the product to create a stable film.
- The lubricant must have stable characteristics that do not change during compressor operation (no stratification, do not come into contact with gases, do not form carbon deposits, etc.)
- The lubricant must be free of water and mechanical impurities.
- Oils for lubrication of high-performance (high-speed) compressors must contain anti-foam additives.
- The average oil service life should be about 2500 hours.
- Acidity levels should be normal.
- The content of water-soluble acids and alkalis must be within the specified norm.
Requirements for the oil used
For proper operation of the mechanisms, it is necessary to fill the compressor with oil that meets certain characteristics.
Important! Manufacturers of compressor equipment usually indicate recommended brands of lubricants in the product data sheet.
For units that produce high-pressure air at moderate temperatures, not motor oils, but special compression oils are used. Compressor oil is usually obtained from heavy oil fractions that have undergone vacuum rectification and numerous purification stages. It must have a number of necessary qualities:
- resistance to oxidation at high temperatures;
- low tendency to form deposits;
- high flash point;
- chemical inertness;
- low pour point;
The most important characteristic is the kinematic viscosity of the oil, which determines its hydraulic and wetting properties . Of the domestic brands for compression equipment, it is most often recommended to buy KS-19. The products of well-known world brands with the names: Shell, Xelix, Castrol have high performance qualities. Experts recommend using the following imported oils for air piston compressors.
- Shell Corena S2 P 68, which is suitable for operation at temperatures up to 220°C and is characterized by excellent anti-wear properties, complete absence of deposits and good separation with the aqueous phase.
- Mineral oils of the Castrol Aircol PD series and synthetic Castrol Aircol PG 185, which have a long service life in harsh conditions.