Installation of plasma surfacing PPC 250 GMR
Installation of plasma surfacing PPC 250 HG
Installation of plasma surfacing PPC 250 PTM
One of the main methods for increasing the reliability and service life of glass molds, valves, and shut-off valves is plasma cladding (Plasma transfer Arc, PTA).
The use of the plasma-powder surfacing method can significantly improve the quality of welded parts, increase productivity and impart special properties to the surface being welded.
The choice of the PTA method by the largest manufacturers and consumers of shut-off valves, mold kits for glass production, and valves confirms the benefits of using the plasma-powder surfacing method, since the resulting deposited layer with improved properties can significantly increase the service life of parts and assemblies, extend repair intervals and reduce costs for major and current repairs.
KSK plasma surfacing installations are designed for surfacing parts from rings and valves to finishing glass molds and shut-off valve parts.
- Increasing competitiveness: the methods we offer are used by all leading foreign manufacturers of fittings, glass, valves, and rolls.
- Increased overhaul cycles: the service life of parts increases from 3 to 10 times.
- Reduced downtime: reduced number of stops, and, accordingly, less time for debugging equipment to reach the desired mode.
Distinctive Process Characteristics
- minimum share of base metal in the deposit;
- high stability and arc stability;
- the increased gap between the product and the plasma torch nozzle reduces the requirements for the accuracy of its maintenance, facilitates observation of surfacing and provides freedom of maneuver with filler material;
- the smallest reduction in fatigue resistance of the deposited product;
- slight allowance for subsequent machining;
- production of deposited metal of almost any type from a relatively small range of initial powders (by mixing them), precisely specified penetration depth and coating thickness, high uniformity across the layer thickness, the ability to provide the required composition, structure and properties already in the first layer of surfacing metal, low residual stresses and deformations;
- pulsed PDN allows for precise control of the geometry of the deposited bead, obtaining a minimum width of the bead, and surfacing narrow edges of products without overheating, melting corners and melting the base metal;
−Order equipment
SBI Surfacing Equipment
SBI produces various types of plasma surfacing equipment, from simple manual surfacing kits to automatic surfacing systems:
1. Equipment for manual plasma surfacing – Series of devices PMI-350 DC– 500 DC – 350 AC/DC
Surfacing processes: plasma surfacing with powder or wire feed, TIG surfacing with wire feed
The device is universal, it can also:
- carry out welding,
— connect to a robot or automated installation,
— integrate into an automated line
Characteristics:
- Stable plasma arc
- Built-in memory – up to 999 programs
- LCD touch display
- Convenient service
- Integrated cooling unit
- Menu in Russian
- Long service life
Detailed technical characteristics are given in the section: PMI plasma welding and surfacing devices
The set of equipment for manual surfacing consists of:
- apparatus
- powder feeder
- plasma torch
Examples of application - in the section Projects - surfacing
Automatic surfacing installations. The SBI company produces surfacing installations of any configuration: column-type, portal type, and special type according to the customer’s technical specifications.
2. Automatic installation UCD-400
Designed for powder surfacing or surfacing with filler wire feeding of flat and spatial surfaces of various products:
- working surfaces of shut-off valves,
- valves (ship, automobile, power plant valves, etc.)
- stamps, molds, injection molds
- wear parts for mining and drilling equipment, e.g. surfacing of drill bits, drill feet
- wedges and working belts, etc.
Operating principle: The installation operator loads the part manually or using mechanisms, then the surfacing process occurs according to the program in automatic mode.
The standard UCD-400 deposits parts with a diameter or maximum diagonal dimension of 400 mm, the weight of the part with equipment is up to 50 kg.
The UCD-400 in its standard configuration has a control cabinet with built-in welding equipment, a control panel, a plasma torch, 3 axes of torch movement, a tilt mechanism, a rotary positioner with tilt, and protective curtains. But the installation layout and characteristics can be changed at the request of the customer.
3 Universal installation CWD 1000-3000
Application: for powder plasma surfacing and wire surfacing of rotating bodies. Standard lengths are 1-3 meters, diameters and weight of the workpiece are at the request of the customer.
4 Installation for surfacing drill pipes
Performed individually, according to the customer’s specifications.
General description:
- Programmable installation with CNC control
- Surfacing types: Plasma, TIG
- Additive: powder or wire
- Length of produced installations: up to 12 m, possibly more.
- Diameters and weight – according to the customer’s technical specifications
Application: for plasma powder surfacing on calibrator blades and for surfacing on drill pipe joints and similar rotating bodies.
5 Installation of laser surfacing of drill pipes
SBI produces various installation options according to customer specifications.
General form
"Plasmacenter" offers
- services for size restoration and application of functional coatings;
- supply of equipment and materials for the processes of welding, soldering, surfacing, spraying, deposition, additive technologies (for example, flame, plasma, high-speed and detonation spraying, plasma surfacing, electric spark alloying, powder dispensers, control devices);
- conducting R&D in the field of surface engineering, coating tribology, plasma processing methods, selection of optimal coatings and methods of their application;
- training, consulting in the field of surfacing, sputtering, hardening, modification, hardening.
Contact us by phone: +7 (812) 679-46-74, +7 (921) 973-46-74, or write to us by email.
Our managers will tell you in detail about the technologies we have for coating, hardening, restoring, imparting surface properties, as well as the cost of the company’s services.
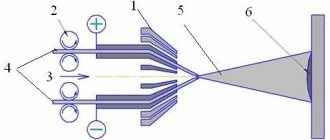
Manual arc surfacing of metal: diagram
It looks like this:
And in it:
1 – part with base metal;
2 – bath in which operations are carried out;
3 – electric arc of a certain length (preferably stable);
4 – fused layer;
5 – restorative coating;
6 and 7 – solidified and liquid slag, respectively;
8 and 9 – rod, already melted (8) and not yet (9);
10 – holder.
Minuses
- • In some cases, as a result of mixing the base material with the added material, a deterioration in practical properties is observed;
- • if the mode is chosen incorrectly, the deformation caused by high temperatures can be excessive, which requires taking additional measures to preserve the geometry of the workpiece;
- • the master solving the problem needs to have theoretical knowledge in the field of metal compatibility in order to make the coating not just uniform, but with the desired properties;
- • a small number of combinations compared to the same spraying;
- • it is difficult to cover small elements of complex shapes - the bath has to be constantly moved and it is not always possible to do this smoothly.
What is called mechanized surfacing?
In general, this is the process of applying a special layer to a worn surface, which, once hardened, will not only restore the original shape of the part, but will also become a kind of protective coating. The whole point (and the main feature) here is how this type of work is carried out, and it can be implemented in one of two options:
- • automatically – both the supply of electrode material and its movement (and workpieces too) in space are performed by equipment; many installations also provide transverse vibrations of the guided rod, which reduces the number of passes;
- • semi-automatically – mechanically, only the wire (or other additive) is delivered to the work area through a hose, after which the welder independently moves the holder with it relative to the workpiece.
Each has its own characteristics. So, in the first case, there may not be enough flexibility in positioning; in the second, much depends on the skill of the person solving the problem. Although labor productivity in both situations is much higher than with any of the manual methods (they have other advantages). The quality and uniformity of the coating are usually also better, which determines the breadth of application, especially in serial applications.
Consumption of materials
To determine the cost of the finished product, it is important to correctly calculate the consumption of surfacing materials. Calculations are carried out in accordance with accepted standards for each specific type of work and materials. Also, knowing the exact quantity of necessary consumables can ensure process continuity and create reserves of materials.
Calculation of deposited metal during welding is one of the main indicators. There is a special formula to determine the value of this coefficient. The mass is calculated per 1 meter of weld. How to determine the mass of deposited metal during welding will be analyzed further:
G = F * y * L, where: F – cross-sectional area of the weld (in mm2) y – specific gravity of the metal (g/cm3) L – length of the weld is 1 meter.
Thanks to this formula, any performer will be able to calculate the mass of deposited metal during welding.
Calculation of electrodes for surfacing is also a significant quantitative parameter. The performer does not need to perform calculations to determine this value. Each brand of welding materials has its own indicator - electrode consumption during surfacing of 1 kg. metal varies from 1.4 to 1.8 kg.
to calculate the mass of deposited weld metal per linear meter. According to GOST, each form of weld made of carbon and low-alloy steels, performed by manual electric arc welding with a metal consumable electrode and welding in carbon dioxide, has an average value of this parameter.
Surfacing of parts exposed to abrasion with impact loads and without impact loads
Products operating under conditions of intense surface wear and high shock loads must be overlaid with electrodes of the following brands:
Welding electrodes for surfacing OZN-400M
Advantages of OMG-N: they comply with state standards, deposition can be carried out with direct and alternating current of reverse polarity.
TsNIIN-4 is one of the most popular and popular brands.
Metal deposited with OZN-7M rods during multilayer deposition has increased resistance to cracking.
Advantages of OZN-400M: high productivity, deposited metal is characterized by increased hardness.
Advantages of OZN-300M: the deposited metal has increased stability of wear resistance and hardness; surfacing is performed with direct and alternating current of reverse polarity.
An example of such parts is elements of construction and earth-moving equipment.
For surfacing parts exposed to abrasion and without shock loads, the following grades of electrodes are used.
To obtain a deposited layer of special hardness, it is necessary to use surfacing electrodes T-590 and T-620. These brands are intended for repairing parts subject to intense abrasion. Thanks to a special coating, which includes ferrochrome, ferrotitanium, ferroboron, boron carbide and graphite, the hardness of the deposited metal can reach 62-64 HRC. Metal deposited with T-590 and T-620 materials is brittle and prone to cracking, and is therefore not intended to withstand significant shock loads. Fusing is carried out in 1-2 layers.
Repair of products made of various metals and alloys also has its own specific characteristics.
pros
- • it is possible to create coatings of considerable thickness (up to 2-3 mm) and thus return the original geometry even to heavily worn products;
- • productivity is 1.5-3 times higher than with any of the manual methods;
- • the equipment used is relatively reliable and easy to transport;
- • there are no restrictions on the size of objects - blast furnace cones, nuclear reactor vessels and other large objects can also be effectively protected and restored;
- • each method is quite easy to implement;
- • the applied layer can be of any composition, from pure copper to combined plastic;
- • it is not a problem to combine surfacing with other processing methods, for example, with nitriding or plasma hardening.
Surfacing of metal-cutting tools and dies
Restoration of metal-cutting tools and dies is performed by arc surfacing in three ways: manual, automatic and semi-automatic.
The first option involves the use of electrodes. Metal-cutting tools and dies operate during cold and hot stamping, so they should be restored using the following grades of electrodes: OZI-3; OZI-5; OZI-6; TsS-1; CI-1M. The layer deposited with such materials has a high level of resistance to abrasion and crushing under heavy loads and high temperatures (up to 650-850°C). The product must be heated to 300-700°C before fusing. Fusing is carried out in 1-3 layers, the thickness is 2-6 mm.
We invite you to watch a video demonstration of the Zeller 769 electrode surfacing test.
Automatic and semi-automatic methods are carried out with alloyed wire using fluxes or pastes.