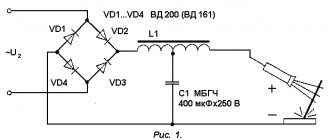
The organization of the welder's workplace is regulated by the rules and regulations of Occupational Health and Safety (OHS). These guidelines must be followed by all businesses and private workshops, and failure to comply will result in fines and injury. But there is also a Scientific Labor Organization (SLO), whose advice is advisory in nature, helping to optimize existing production in order to increase the efficiency of the work process by improving conditions and increasing employee safety. Based on all these sources, key provisions have been collected on how a welder’s workplace should be equipped in various situations.
Purpose of workplace organization
Proper placement of equipment and the creation of certain conditions for performing work contribute to the following:
- enterprise productivity increases;
- it is more convenient for the welder to do the work, therefore the quality of the result improves;
- the worker’s protection from passive harmful influences (gases, radiation) increases;
- workplace injuries are prevented;
- a favorable environment is created for the work of other employees whose activities are carried out next to the welder.
To achieve all these goals, efforts are being made to introduce a number of measures and technologies into the workplace that provide sufficient space and comfort for the welder, as well as protecting the health of both the specialist himself and those around him.
Cabin
Organization of a workplace for an electric welder who works in a permanent place in the workshop begins with the arrangement of the cabin. This helps you carry out welding work calmly and protects others from sparks and flashes of light.
The cabin must have dimensions that allow products intended for welding to be brought into it. If the structures being produced are small, then the minimum area of the cabin should be 2 x 2 meters. This will allow you to place everything you need and move freely around the product. To prevent welding radiation from disturbing others, the height of the cabin walls is set to 1.8 m. Since most welding operations are performed at table level, this height will be sufficient. The cabin frame is made of profile pipes or corners. The posts are attached to the floor with anchors. It is possible to provide a door that will completely isolate the welder’s workspace around the perimeter.
To improve natural ventilation, a gap of 150 mm is set between the floor and the beginning of the booth wall. This promotes air flow and raises harmful gases from welding upward. The sides of the cabin can be made of slate sheets or thin iron. Options made of tarpaulin and even plywood are allowed, but these materials must be impregnated with fire-resistant compounds. It is advisable to paint the walls with zinc or titanium white. Yellow crown will do. These substances on the surface of the cabin will absorb ultraviolet radiation well. If you paint such a structure black or dark blue, the overall illumination will deteriorate, since the light coming from the lamp above the workplace will be absorbed.
Electrical laboratory » Questions and answers » PUE 7th edition » 7.6.33-7.6.44. Requirements for premises for welding installations and welding stations
REQUIREMENTS FOR PREMISES FOR ELECTRIC WELDING INSTALLATIONS AND WELDING POSTS
7.6.33. The premises and buildings of assembly and welding shops and areas with electric welding installations and welding stations located in them, as well as ventilation devices must meet the requirements of current regulatory documents.
7.6.34. For electric welding installations and welding stations intended for permanent electric welding work in buildings outside welding and assembly shops and areas, special ventilated rooms must be provided, fenced off with fire partitions of the 1st type, if they are located adjacent to rooms of categories A, B and C according to explosion and fire hazard, and type 2 in other cases. The area and volume of such premises and their ventilation systems must comply with the requirements of current sanitary rules and SNiP, taking into account the dimensions of welding equipment and welded products.
7.6.35. Welding stations may be located in explosion and fire hazardous areas only during the period of temporary electric welding work carried out in compliance with the requirements set out in the standard instructions for organizing the safe conduct of hot work at explosion and fire hazardous facilities, approved by the Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia.
7.6.36. In rooms for electric welding installations, passages of at least 0.8 m must be provided to ensure convenience and safety of welding work and delivery of products to the welding site and back.
7.6.37. The area of a separate room for electric welding installations must be at least 10 m2, and the area free of equipment and materials must be at least 3 m2 for each welding station.
7.6.38. Welding stations for systematically performing manual arc welding or shielded gas welding of small and medium-sized products directly in production shops in non-fire and non-explosive areas must be placed in special booths with walls made of fireproof material. The depth of the cabin must be at least twice the length, and the width must be at least one and a half times the length of the products being welded, however, the area of the cabin must be at least 2x1.5 m. When installing a welding power source in the cabin, its dimensions must be increased accordingly. The height of the cabin walls must be at least 2 m, the gap between the walls and the floor is 50 mm, and when welding in shielding gases - 300 mm. When moving above the overhead crane cabin, its top must be covered with a mesh with cells no larger than 50x50 mm.
7.6.39. Carrying out work at welding stations during non-systematic manual arc welding, submerged arc welding and electroslag welding is permitted directly in fire-hazardous premises, provided that the work area is fenced with shields or curtains made of non-combustible materials with a height of at least 1.8 m.
7.6.40. When systematically welding products weighing more than 20 kg, electric welding installations must be equipped with appropriate lifting and transport devices to facilitate installation and transportation of the welded products.
7.6.41. Natural and artificial lighting of electric welding installations of assembly and welding shops, sections, workshops, individual welding stations (welding booths) and welding places must meet the requirements of SNiP 23-05-95 “Natural and artificial lighting. Design standards".
7.6.42. When manual welding with thickly coated electrodes, electroslag welding, submerged arc welding and automatic open arc welding, gas suction must be provided directly from the welding zone.
7.6.43. At welding stations during open arc and submerged arc welding inside tanks, closed cavities and structures, ventilation must be provided in accordance with the nature of the work performed. If necessary ventilation is not possible, a forced supply of clean air under the welder’s mask should be provided in an amount of 6-8 m3/h.
7.6.44. Canopies made of fireproof materials must be built over portable and mobile electric welding installations located in the open air to protect the welder’s workplace and electric welding equipment from precipitation. Sheds may not be constructed if the electrical equipment of the electric welding installation has shells with a degree of protection corresponding to the operating conditions in outdoor installations, and during rain and snowfall, electric welding work will stop.
In the open
The arrangement of a welder's workplace for manual arc welding in an open space uses shields and fences. This is applicable in cases of constant movement of a specialist around the workshop or during field work. Shields are placed to block visual contact between the electric arc and workers who work nearby.
Such fences have two posts on legs, between which there is a sheet of thin iron or slate. The height is the same as that of the cabin. It is installed so that it does not interfere with the welder in completing the task and closes him from others. The painting is done in a zebra style (black and yellow or black and white) so that the fences are clearly visible to others. This serves as a warning about welding work.
Electric welding arc
During electric arc welding, the air is contaminated with impurities that can cause poisoning of the human body or damage to the lungs, leading to pulmonary diseases. Impurities that cause poisoning of the body include oxides of copper, lead, zinc, manganese, fluoride compounds, carbon monoxide and nitrogen monoxide. Oxides are formed during the oxidation of copper, lead, zinc, and manganese vapors released during the welding process. Copper and zinc can be part of the electrode and base metal. Manganese can be part of the base metal, electrode metal, as well as in coatings and fluxes.
Lead oxides are formed when it is welded using a carbon or graphite electrode method. Air pollution with fluoride compounds is observed during welding using coatings and fluxes containing cryolite, fluorspar or other substances containing fluorine. Carbon monoxide is produced when welding using this method, as well as when welding with electrodes whose coating contains carbon compounds or pure carbon. Nitrogen oxides are formed in all cases of manual arc welding and to a greater extent when welding with thin-coated electrodes. The content of the listed impurities should not exceed thousandths of a milligram per liter of air.
Impurities that cause lung disease include oxides of iron, silicon, aluminum, particles of free carbon and other dust released during manual electric arc welding. These impurities, when inhaled for a long time, cause damage to the bronchi, resulting in pulmonary diseases.
To prevent air pollution by impurities, it is necessary to provide thorough ventilation of the rooms where manual electric arc welding stations are installed. Ventilation can be general or local. General ventilation should be flow-exhaust. Clean air must be supplied directly to the welding areas. In winter, this air must be heated by air heaters.
According to the Academy of Medical Sciences of the USSR, when welding with metal electrodes with TsM-7 and UONII coatings, the amount of clean air supplied to the workshop should be about 4000-5000 m3 per 1 kg of molten electrodes.
Supply and exhaust ventilation must be provided in all manual arc welding rooms. Local ventilation is installed when welding stations are located in certain places. In this case, exhaust hoods are installed above the welding tables. Vessels must be provided with local supply and exhaust ventilation when welding is performed in them. In these cases, supplying air directly under the shield or mask gives good results. In this case, the amount of air should be about 25 m3/hour.
Air supply directly under the welder’s shield or mask should also be used in the case of welding non-ferrous metals: copper, brass, bronze, lead, aluminum and its alloys. The need to supply clean air is due to the fact that when welding non-ferrous metals, a significant amount of harmful metal oxides, as well as harmful gases, are released.
Places where welding work must be sufficiently well illuminated by daylight or artificial light. Good lighting of workplaces reduces eye fatigue for workers and is one of the conditions for increasing labor productivity. Illumination of workplaces should be at least 50-100 lux. To reduce the absorption of light by the walls of the cabins, they are painted in light matte colors. It is recommended to use zinc white, crown yellow, and titanium white. The listed dyes absorb ultraviolet rays well.
- Back
- Forward
Installation of electrical equipment
An electric welding transformer and other units emit quite loud noise that has a bad effect on the human nervous system. Due to irritability, the quality of the seam deteriorates and productivity decreases. Therefore, humming equipment is installed at some distance from the work site. It is better to place the transformer or converter within 5-7 meters from the welder. This will reduce the noise emitted, but at the same time will not complicate the process of adjusting the device.
The source of welding current, located in the middle of the workshop, is protected with shields for safety. If there are multi-post installations, then a permanent mesh fence is built for them or they are taken out to a separate room. The distance from the wall to the device must be at least 500 mm. Outdoors, it is necessary to provide a canopy to protect the equipment from precipitation. The cables from the device are laid over the wall to prevent people from tripping over them.
Mobile welding station
A professional mobile welding station is organized for high-quality welding work and the production of large-sized metal structures. Such a workplace is most often organized in an open area, so a canopy must be made for it, which will protect it from solar radiation and precipitation. The main material used in the manufacture of mobile post canopies is warehouse panels.
For the convenience of storing electrodes, auxiliary tools, special equipment, and other available tools, the gas welding station is equipped with special cabinets. In this case, a ventilation system is not provided, since the work is carried out in the open air, and the harmful gases released during the work quickly dissipate on their own.
Basic requirements for organizing a mobile post
- Lighting should minimize the load on the worker’s visual organs resulting from the light flux.
- Lighting fixtures are most often placed above the desktop tabletop, next to it.
- The gas welding station must have a grounding device.
- For high-quality exhaust ventilation in a natural way, gaps of about half a meter are left between the floor base and the walls.
Installation of gas equipment
The gas welder's workplace is set up according to a similar principle. The color of the walls of the protective shields does not matter here, since the gas flame does not emit ultraviolet radiation. The main thing is that the welder can clearly see all the parts in the workplace.
A significant difference is the location of the cylinders. Although a trolley is used for transportation, on which an oxygen and acetylene cylinder are immediately installed, before performing welding work they must be separated from each other by at least 5 meters. The same should be done with propane equipment. In this case, it is important to maintain a distance of 5 m between the cylinders and the area to be welded. As a result, the arrangement should look like a triangle, with the element to be welded on one vertex and gas cylinders on the other two.
It is important that there is nothing in the way of the acetylene generator or cylinders. This provides quick access to equipment in the event of a flashback. This can prevent an explosion and serious injury. The hoses are located on the side so that they are not walked on or driven on. Otherwise, the flame will go out and rubber communications may deteriorate.
Holder
The welder's main tool is the holder. Productivity and quality depend on its convenience and thoughtfulness. The holder can be of two types: to clamp the electrode like a clothespin, or to tighten it by twisting the handle. Regardless of the type, it should allow the electrode to be changed in 4 seconds.
The structure is well insulated to prevent electric shock. The cable and the holder itself constantly exert their weight on the welder’s hand. Therefore, the mass of these elements should be minimal so as not to overwork the welder and not limit movement.
If work is carried out at high current (from 500 A), then the holder is equipped with a protective pad that prevents the welder’s hand from being damaged by high arc temperatures. When the welding current exceeds 600 A, the cable is passed to the electric holder, bypassing the handle that the worker grasps. The sides that secure the electrode are subject to the adhesion of molten metal splashes, making it difficult to replace a new consumable element. This slows down the entire process and the welder gets tired faster. To prevent this effect, the surface of the holder on which drops of metal fly is lubricated with a scraper and cleaned at the end of the day with a needle file.
Table
For convenient welding operations, it is practical to place the product on the table. This increases the speed of welding and the convenience of welding in hard-to-reach places. The welder's table is made to individual sizes, based on the dimensions of future products. The legs must be height adjustable to accommodate workers of different heights.
The table should include devices for:
- safe placement of the holder during the process of rearranging the product;
- quick access to consumables and easy electrode change;
- location of tools (hammer, file, flashlight, slag separator, metal brush);
- ignition of the electrode on the rough surface;
- installation of non-standard structures with protrusions in special holes.
Hood
An important attribute of an electric gas welder’s workplace is a hood. It ensures the removal of harmful heavy gases from the melting metal and electrode coating. It is not practical to place it in the form of a large umbrella over the table, since part of the harmful mixture will pass through the welder’s respiratory system.
It is advisable to install a flexible side air suction system, which will immediately pick up harmful gases without allowing them to rise to the worker’s face. Such a line will ensure that the hood can be moved to any location within the welding cabin. At the same time, it is worth remembering that the noise of the engine disturbs the worker, so the power unit for pumping air is located outside the room.
Creating comfortable conditions for the welder improves the quality of seams and the process of producing finished products. Reducing passive harm at work and protecting personnel from injuries helps maintain a permanent team and harmonious interaction among employees.
Stationary post
It is an open-top cabin raised above floor level. In such posts, small and medium-sized parts are welded; it is not suitable for large units and metal structures. The cabin is usually made of metal sheets, which are subsequently coated with zinc-containing paints or other coatings that are resistant to high temperatures and infrared radiation (for example, titanium-based white or yellow chromium-lead salt paint, other modern substances).
The floor must be concrete (or screed). PVC coverings, wooden floors on joists and other flammable materials are not allowed. The entrance/exit is covered with a tarpaulin, or metal double-leaf doors with corrugated glass are provided.
Some requirements for a welding booth:
- Sufficient lighting for comfortable work, the presence of light sources that illuminate the post in general and the table on which all manipulations are carried out, in particular.
- The area of the post is at least 3 m2, the height of the metal walls is 1.8 - 2 m, they must be raised above the floor to a height of 20-25 cm; the ceiling height of the room in which the cabin is installed is, accordingly, more than 2 m for free air circulation.
- A table for working in a sitting position should be 50-60 cm high. The table is assembled from metal. It is advisable that a copper sheet be laid on the table cover (including at the point of contact of the ground terminal). The lid itself is made of steel or cast iron up to 2.5 cm thick. The table should have metal drawers for storing tools, fixtures, electrodes, drawings, etc.
- There must be a special hood above the table. If you are creating a post in a garage, you can build an exhaust fan into one of the walls of the garage; in this case, you will need to take care of the presence of an air supply during the winter season. In industrial conditions, a point hood has recently been often installed, the flexible “trunk” of which can be installed directly at the welding site.
Air exchange in the room is at least 40 m3/hour according to regulatory documentation. Let us remind you that with insufficient air exchange, toxic elements contained in welding smoke (aerosol) will accumulate in the lungs of welders, which will eventually lead to the occurrence of occupational diseases.
- There should be a rubber mat under your feet.
- All equipment must be grounded (some welders use RCDs).
- The welder's work chair must rotate around its axis for ease of work. The materials from which the chair is made must be heat-resistant and non-conductive. The seat and backrest can be made, for example, of wood.
- For convenient work, you should have a manipulator (or rotator) and a foot pedal at hand, which simplifies its control. The manipulator is used for welding bodies of rotation.