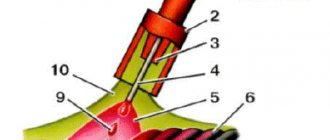
When welding with a non-consumable electrode, an arc occurs between the electrode located in the torch, from which shielding gas is supplied, and the workpiece. To form a seam, filler material is fed into the weld pool. If the welding is manual, then the additive is supplied directly by the welder; if it is automatic, the process occurs without his participation.
This welding method is used for welding non-ferromagnetic materials, including: magnesium, aluminum, zirconium, nickel, titanium, bronze, copper, stainless steel and others. This welding method allows the welder to finely sense the depth of penetration of metals, which contributes to good quality of the weld. During manual welding, the specialist himself controls the torch and filler material, which eliminates the product from lack of fusion and other defects in the weld.
Peculiarities
Non-consumable arc welding typically uses non-consumable consumables to produce high quality welds. However, it is worth considering that technology with coated electrodes has low productivity.
The main advantage of welding in inert gases with a non-consumable electrode is that it is possible to fuse ferrous metal with workpieces that may differ from it in structure, including products made of high-alloy and low-carbon steels. This method can be used for welding metals of dissimilar composition.
Welding, which uses non-consumable electrodes, has several characteristic features. One is to use special elements that cover the electrodes - tungsten, graphite and other types.
The second feature is the use of inert gases. They limit oxygen access to the welding area. They also protect the electrode and weld pool from oxidation.
Advantages and disadvantages
Many novice welders often ask the question - what is arc welding with a non-consumable electrode? This is a convenient technology that allows you to weld different metal workpieces. It is simple to carry out and does not require special skills or experience.
Non-consumable electrodes can be used when welding at home, but they are also often used in industry to fulfill the following conditions:
- They can carry out high-quality welding of thin metal sheets;
- They are excellent for welding work with steels of all classes, non-ferrous metals, as well as their alloys;
- Consumable electrodes make it possible to obtain high-quality welds when welding different types of metals.
In addition, it is worth paying attention to the fact that welding with a non-consumable electrode in an argon environment has some advantages and disadvantages. The positive features of this technology include:
- The arc has high stability, which does not depend in any way on the current polarity;
- It provides the opportunity to obtain welds with a base metal content from 0 to 100%;
- It is possible to regulate the chemical composition and geometry of the connection while changing the feed rate, inclination angle, profile, and brand of filler material.
But do not forget about the negative qualities:
- Has low efficiency indicators for the electricity used;
The use of special devices is required to ensure the initial initiation of the arc; A high cooling rate of the manufactured seams is observed.
Safety regulations
When welding, we must not forget about safety rules. It is necessary to use protective equipment for the welder: a mask or shield, gloves or leggings, special clothing and shoes.
All masks can be divided into active and passive. The sight glass of passive masks is permanently darkened. In active ones, darkening occurs only as a reaction to a light flash from the arc. The advantage of this option is that while the welding process is stopped, the glass becomes transparent and the welder can clearly see the object. There is no need to lift the glass, which is quite convenient.
Main types of welding gaiters:
- Canvas . They are not in demand because they do not perform well the main function of protecting hands from high temperatures and sparks. They easily burn when exposed to sparks.
- Split fibers . Made from specially treated leather from pigs or cows. Resistant to flying sparks. Durable, elastic, hygienic. Does not restrict hand movements. If there is a cotton layer inside, it keeps your hands warm.
- Felt . Convenient for welding work.
There are combined models that use different types of materials. Welding gaiters come in length up to the elbow and cover only the hand. The possibility of tightening the edge of the glove provides additional safety.
A welder's suit must be made of high quality materials. It must be resistant to splashes of molten metal. The requirements for a welder's suit are specified in GOST 12.4.250. The main parts of the suit are the jacket and trousers. The material from which they are made must have great heat resistance. According to the regulatory material, the jacket must cover the trousers by more than 20 cm. The fasteners are closed with flaps. The maximum distance between them on the jacket is 15 cm.
Safety regulations include electrical safety. The argon cylinder must be located at a distance of at least 5 meters from possible sources of fire. The cylinder must be placed vertically and secured to prevent it from falling. Before work, it is necessary to check the condition of the hoses.
Types of electrodes
When carrying out automatic or manual arc welding with a non-consumable electrode, consumables may be used, which may have different compositions. They help to obtain a high-quality and durable connection.
Typically, the following types of non-consumable electrodes are used during the welding process:
- From coal;
- Made from pure graphite;
- Made from tungsten base.
Moreover, each type of electrode may have important features and qualities that must be taken into account when carrying out the welding process.
Coal
Carbon consumables are often used during the air arc welding process. They can also be used to eliminate various defects and damage that exist on the surface of workpieces.
Manual argon arc welding with a non-consumable electrode, which has a carbon coating, can be carried out in modes with currents with voltage values of 500-600 Amperes. It is quite sufficient for connecting massive steel structures and for correcting defects in cast products.
The welding process itself can be carried out using filler wire, which is fed into the area where the weld is formed, and also without it.
Graphite
Pure graphite electrodes are often used when working with non-ferrous metals - aluminum or copper. They can also be used during welding of alloys and these metals. This type of non-melting material, in contrast to coal samples, is economical and beneficial to use in practice.
Graphite rods have some important advantages:
- They are resistant to high temperatures;
- Have good wear resistance;
- They have simple preparation for the work process.
Tungsten
Non-consumable tungsten rods are often used when carrying out the welding process in production and at home. They allow welding with a non-consumable electrode in protective gases of aluminum and other types of metals and alloys.
This consumable is manufactured in the form of a long coated rod with a diameter of 1 to 4 mm. They have a refractory structure. The melting temperature of tungsten-based electrodes is much higher than that of a working arc. This is what makes the rods universal and they can even be used for welding stainless steel, which has complex processing.
Often, during the manufacture of tungsten electrodes, various components are added to their composition - thorium, lanthanum oxide, yttrium. Each rod with the addition of one of these substances is intended for a specific type of welding.
Areas of application
If welding is done end-to-end without a gap, then it is enough to melt the edges of the products being welded under the protection of argon and you will get a good sealed seam.
If there is a gap, then it is necessary to introduce a filler wire made of the same material into the welding area, the result will be a strong seam with high resistance to tearing and fracture.
When it is necessary to use TIG welding on refractory materials, helium is used. In the environment of this gas, an electric arc produces 1.5-2 times more heat than in argon. Therefore, the seam is welded deeper and the welding speed increases.
The use of argon and helium in a 40/60 ratio allows you to obtain the advantages of both: arc stability thanks to argon, deep weld penetration thanks to helium.
TIG argon arc welding has become widespread in mechanical engineering, in the food industry for the manufacture of tableware, in the chemical and oil refining industries for the production of containers. It is difficult to imagine an auto repair shop or the production of aluminum products without TIG welding.
If desired, anyone can do TIG welding from an inverter with their own hands; to do this, it is enough to equip the equipment with a TIG welding torch and argon cylinders. A valve gas supply system is also needed.
Equipment used
What equipment is used when carrying out manual, automatic and argon-arc welding with a non-consumable electrode? It all depends on the volume of welding work and the size of the assembled structures. Typically, welders use two types of equipment - universal and special.
The first class of devices is often used, because the second is most suitable for large volumes and often mechanized ones. Versatile manual and automated welding machines are easy to use and easy to maintain. For this reason, they are often used for welding in small workshops and large production facilities.
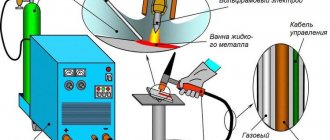
Devices for manual arc welding with a non-consumable electrode in shielding gases have the following components:
- They contain a source of direct or alternating current. Sometimes there are devices that can produce two different types of current;
- Burners of various sizes. They can be used for different current indicators;
- An oscillator that ignites the primary arc;
- Components that provide argon gas supply;
- Elements that control the welding process.
Settings
First of all, the optimal mode is selected, thanks to which the quality and efficiency of welding is higher. The direction of the current and polarity are chosen taking into account the properties of the metals being welded, and the magnitude of the current depends on the brand and chemical composition of the parts, and the diameter of the electrode used is also taken into account. Experienced craftsmen select the correct parameters using the reference book .
The voltage directly depends on the length of the arc, so work is carried out with a minimum of similar dimensions and a reduced voltage, since with an increase the quality of the connection deteriorates.
Requirements for argon arc welding with non-consumable electrode
Argon arc welding with a non-consumable electrode is often used for welding workpieces made of different types of metal. With its help you can obtain strong seams with high wear resistance. But in order for the workpieces to melt normally under the influence of a consumable electrode and argon during the welding process, it is imperative to fulfill the important requirements of the argon arc welding process.
The main requirements of argon arc welding include:
- When welding, the non-consumable tungsten rod can penetrate deeply into the gap area between the workpieces. A short arc should be used for the process. This will allow for deep melting, which may affect the quality of the connection. It will turn out small and durable;
- When mechanized argon arc welding with a consumable electrode, the movement of the rod should be carried out along the central part of the gap and in the middle. Even small violations can lead to a decrease in the strength of the connection, they can negatively affect its appearance;
- The filler element must always remain in the area with argon; it must not go beyond the welded zone. This is what protects the weld pool from the negative effects of oxygen and nitrogen that are present in the air. The influence of these substances can lead to increased brittleness of the joint. These requirements also apply to a non-consumable electrode;
- Under no circumstances should you sharply feed the filler wire into the weld pool area. This will cause severe spattering of the metal and, as a result, there will be excessive waste;
- When performing manual welding, the filler material must be fed at an angle. There should be no transverse irregularities;
- At the end of the welding process, you should not break the connection by removing the electrode from the welding area. It is enough to extinguish the arc with a rheostat;
- The supply and shutdown of shielding gas after the end of welding should be carried out within or within 10 seconds. This will protect the uncooled melting metal base, which upon contact with air is quickly covered with an oxide film;
- Before starting automatic argon arc welding with a non-consumable electrode, you need to prepare the workpieces to be joined from a metal base. All joining areas must be cleaned of dirt, rust and other contaminants. For cleaning, it is recommended to use an iron brush or an angle grinder with a metal brush attachment. It is necessary to clean until a metallic shine appears. If there are stains of oil or grease, then additional treatment with a solvent should be carried out;
- It is imperative to compare the modes of argon arc welding with a non-consumable electrode with the thickness of the workpieces being joined. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the diameter of the non-consumable electrode.
Melting view
Manual arc welding using a consumable electrode is classified as a universal approach, since it can be carried out in almost any conditions.
This method of organizing the welding process allows the operator to work comfortably even in the most inaccessible places. However, along with these advantages, this method has a number of significant disadvantages, manifested in the following:
- small depth of penetration of the processed metal;
- low productivity of the welding process, which is explained by low levels of operating currents;
- instability of manual welding, which is noticeably inferior to automated fusion techniques.
The essence of this metal processing method is to use the energy of an electric arc artificially created between the workpiece being welded and the electrode.
Under the influence of high temperatures, the metal in the welding zone intensively melts and forms a so-called “welding pool”. At the final stage of work, a neat seam should be obtained at the site of the melt (after it has cooled).
In appearance, a consumable electrode is a typical metal rod with a coating of a certain structure and thickness applied to its surface.
The main parameters that determine the dimensions of the so-called “coated” electrodes, their breakdown by type and the requirements for them are regulated by current standards (GOST 9467-75, in particular).
According to these data, the most common diameter of electrode rods is in the range from 3 to 6 millimeters. The indicated indicator is defined as the thickness of the rod, without taking into account the existing working coating.
With a decrease in this value, as well as with an increase in the total length of the electrode, its conductivity also changes, which naturally leads to strong heating during the welding process.
If overheated, the rod quickly melts (it is said to begin to “flow”). At the same time, the organic components included in the coating burn, losing their protective properties.
Results
Welding work with a non-consumable electrode must be carried out correctly; the quality of the resulting welded joint depends on this. First of all, it is worth understanding what gas shielded arc welding with a non-consumable electrode is and why it is carried out.
This method is considered popular among professionals and novice welders. It can be used to weld large structures made of different types of metals. This method is used in domestic and industrial settings.