Comfort and convenience in any work have never bothered anyone. This also applies to welding. Among the welding tools, there are basic ones and there are auxiliary ones. These include the smallest auxiliary part in size - a wonderful magnetic corner, or, more correctly, a magnetic square for welding.
Such corners are extremely useful for both artisans and professionals working on stream. Small in size but not in function, these special welding triangles improve the quality of products in general and welds in particular.
Magnetic square for DIY welding
Today I want to talk about a magnetic welding square that I recently made with my own hands. I have some gates and driveway gates to make soon, so I decided to make some magnetic corners this winter. They will save me a lot of time and effort when welding rectangular structures from profile pipes.
What I needed for this:
1. Old speaker. 2. Sheet metal (steel) 1 millimeter thick 3. A strip of thin aluminum. 4. Blind rivets.
Progress of work on the manufacture of a homemade magnetic square
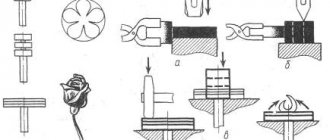
Using a hammer and chisel, I separated the "magnetic part" of the speaker. (It is secured with four rivets).
After this, all that remains is to remove the magnet.
Next I started making the plates. I cut them out of an old window sill. (I’m surprised myself, but it was made of “black” non-galvanized iron, 1 mm thick!). The metal was very magnetic, which was what I needed in the first place.
Using a mechanic's square, attaching it and the resulting magnet to the workpiece, I determined the dimensions of my future product, drew it and cut it out with a grinder:
Next I marked and cut out the corners. Corners need to be cut for several reasons:
Firstly, when cutting a profile pipe (and especially with a thick circle on a cutting machine, burrs remain on the edge. During welding, they will easily melt and will not interfere. But the square will rest against them. Therefore, after the pipes are cut to size , you will have to clean off these burrs.
Secondly, if there is not a large gap in the corner, you can accidentally weld the square itself to the workpiece.
I did not mark the second plate. I simply attached the first one to it (already with cutouts) and, according to this template, marked it and cut it out too:
Next I did some fine tuning. After all, it is not possible to cut very accurately with a grinder, and precision is needed down to fractions of a millimeter. Therefore, I had to finish it manually.
I took a piece of a wide profile pipe, spread a strip of emery cloth on it, and manually ground off the sides of my metal triangles on it, periodically putting them into a mechanic’s square and checking “for clearance.”
After that, folding the blanks evenly and squeezing them in a vice, I drilled holes in them for the rivets. (I forgot to photograph this process). And after that, just in case, I tightened them through the holes with M5 screws and once again “finished” them on sandpaper, this time two together.
Many DIYers make the angles “open”. That is, they don’t cover the end with anything! It is unacceptable. Because when working with metal, a lot of sawdust, scale, small scraps and other magnetic debris appear. Since all this debris is very light, it sticks abundantly to the magnet.
That is why its shape should be such that it can be easily cleaned. That is, its ends should be smooth planes. I made them from a thin aluminum plate. Some kind of edging from an old refrigerator shelf came under my hand.
From it I cut a strip with a width equal to the thickness of the magnet:
And from it I bent a frame around the perimeter of the plates. It will be inserted between them, and tightly clamped with rivets.
A ferrite magnet can be cut quite easily with a grinder. But, unlike cutting metal, you shouldn’t even try to use an abrasive wheel. It will slip and you will simply overheat the magnet. (By the way, if anyone doesn’t know, permanent magnets lose their properties due to overheating.). You need to cut with a diamond wheel. A diamond wheel for wet cutting is best suited.
And when cutting, the magnet must be cooled with water.
Why did I make the ends out of aluminum, and at the same time focus on another common mistake. As you know, any magnet has two poles, conventionally called “north” and “south”. Both poles are equally well attracted to the metal. Magnets of this shape have poles on planes. That is, when we apply metal plates to the planes, then these plates are the poles of the magnet. And it is with them that our square will “stick”, and not at all with the plane between them.
But, most importantly, the poles of the magnet cannot be “short-circuited” with magnetic material! This reduces its properties, and, in addition, contributes to the fact that the magnet, albeit slowly, demagnetizes!
I decided to connect the plates with blind rivets. I will only use aluminum parts:
Having inserted the rivet, I simply flare it from the back side with this core, once made from a car valve:
But before that you need to paint. I painted the aluminum frame black.
The next day I assembled the square:
For more detailed information, watch the video of making a magnetic square:
What types of clamps are there for welding work?
There are quite a large number of additional devices for fixing workpieces. They are not mandatory items for a welder, but they greatly facilitate the work and improve the quality of the resulting connection .
Next we will look at devices of various configurations.
Square corners
Magnetic corners are the simplest type of product for fixing parts to be welded at the required angle. The main advantage of such devices is the reduction of time spent on preparatory procedures, as well as the reduction in the labor intensity of the process.
The holders have a simple design - two metal plates with a magnet between them. Therefore, the possibility of failure is extremely small. Compact sizes make working with them simple and convenient. The performer has the ability to fix parts at almost any angle.
- Magnetic square BARS MF-75 is designed for fixing metal structures during welding, soldering, assembly and installation, suitable for marking and branding various parts, as well as for demagnetizing tools.
- The device is used to work with round and rectangular pipes, strips, profiles, angles, sheet, solid and other forms of metal.
- The main material - iron oxide (Fe3O4) is capable of attracting the product with a force of 75LBS (34 kgf).
- Angles: 45, 90 and 135 degrees.
- Weight - 1000 gr.
- Dimensions: 155 mm. x 100 mm. x 16 mm.
- Advantages: reliable fixation of workpieces; excellent replacement for heavy clamps; allow you to free the welder's hands; quick collection of metal shavings; facilitate installation; reduce work time; various mounting angles.
Video
Below is a promotional video, but it gives a good idea of the possibilities offered by this type of equipment.
Why is it better to buy a set at once?
Manufacturers and suppliers sell welding magnets individually. Most welding work is carried out on quadrangular structures . Therefore, it is recommended to purchase a complete set of holders - 4 pieces. Having a kit will allow you not to be distracted from work.
For complex structures, a much larger quantity than 4 pieces may be useful.
Mass holders
The ground holder (other names: ground terminal, ground clamp) is a necessary device for the welder. The ground terminal will eliminate the possibility of electric shock and will guarantee a reliable and high-quality connection. The industry provides various types of mass contact devices : clothespin, magnetic clamp, clamp and centralizer. Let's consider the pros and cons of magnetic representatives of this type of equipment (all mass clamps are discussed in more detail in a separate article).
Regardless of the type, holders have the following important
advantages : ease of use and speed of work. It should also be noted the advantages of magnetic holders :
- used for fixing workpieces of various configurations, sizes and diameters, in contrast to the “clothespin” type;
- successfully used in hard-to-reach places;
- reliability of fastening is ensured due to the large contact area with the workpiece;
- simplicity of design and absence of complex elements ensure a long service life;
- withstand significant loads and stress.
Disadvantages of magnetic holders:
- “magnetic blowing” effect and arc deflection;
- impossibility of use for working with products made of non-ferrous metals;
- if the magnet is non-switchable, various debris sticks to it, so it should be cleaned periodically;
- overheating, which occurs when the mass is attached to a dirty or rusty surface, can lead to demagnetization;
- inconvenience of attaching a magnet to small workpieces: rod or fittings.
The advantages and disadvantages of other types are presented in the article “Mass clamp”.
PROFI
- The magnetic grounding terminal PROFI is designed for connection to the grounding of the welding cable.
- The magnetic base provides excellent attachment to metal surfaces of various shapes.
- The device provides reliable contact at the connection points.
- A small contact area eliminates the possibility of overheating.
- The handle allows you to easily remove the terminal from the part.
- Weight - 400 gr.
Torch holders
The holder is a support with a magnetic base , used for storing MIG/MAG and TIG torches. The device holds the equipment when not in use.
The use of such holders allows you to avoid the possibility of damage to the burner, increase the service life of the nozzles for it, and also increases the convenience of performing work.
It is especially important to use holders when storing gas burners, since their nozzles crack when they come into contact with the cold surface on which the equipment is placed.
The magnetic base guarantees the stability of the structure , which can be placed on a welding table or can be attached to a working device.
- A simple and practical holder suitable for most burner models.
Magnetic welding mirror
The welder's magnetic mirror is designed for inspection and quality control of welds , making it easier to carry out work in hard-to-reach places . The magnet allows you to attach the mirror to any metal surface without holding it in your hands. Most models have a flexible tripod (leg), which allows you to rotate the device at any angle. Welders are offered other types of welding mirrors, which will be analyzed in a separate article.
CIMCO
- Country of origin: Germany.
- Long lasting magnet.
- Flexible brass rod with swivel joint.
- Weight - 460 gr.
- Length - 500 mm.
Switchable and non-switchable devices
Magnetic holders for welding can be permanent or switchable . The second type is attached to parts by turning on a magnetic field activator. Such devices have the following advantages in comparison with conventional magnets: quick removal is carried out with one turn of the switch; the ability to turn off the magnetic field makes it easy to clean the device from chips and other small debris. The only drawback is the higher cost .
Foxweld SHIFT-7
- The switchable magnetic square is designed for pre-assembly and fixation of parts during welding, cutting (prevents parts of the structure from falling) and installation, and is also suitable as an element for holding workpieces.
- Easy to use, allowing one person to do all the work.
- The device is suitable for any work with metal objects.
How to make a magnetic welder's square with your own hands
Dear visitors to the “ Samadekin Friend ” website, today we will look at one of the options for creating a homemade magnetic welder’s corner with your own hands, and we will also look at step-by-step photographs and videos of assembling a corner from scrap metal. Every welder and craftsman knows perfectly well that when using a welding machine to weld parts at a certain angle, small problems arise, namely, accurately setting the angle and fixing the parts to be welded. There is an excellent device called “magnetic welder’s corner”; with its help you can set an angle of 45 and 90°; under the influence of the magnetic force, the workpieces will be pressed against each other, due to which it will be convenient to weld and the angle will be accurate.
The device and operating principle are quite simple, namely the corner consists of two steel plates with angles of 45 and 90°; between the 2-3 mm thick plates there is a round magnet from the speaker, due to which a magnetic force is created that fixes the workpiece in the required position. The structure is tightened in 4 places, namely in the corners and in the center, with 3 nuts per bolt, two inside the corner and one on the outside.
Note. It is advisable to cut off sharp corners 1 cm at a time, because the parts being joined are often sawn unevenly with burrs and the corner may not fit tightly into place. Also, to protect against corrosion, the metal should be painted with metal paint.
Materials
- metal plate 2-3 mm
- bolt 4 pcs
- nut 12 pcs
- speaker magnet
Tools
- welding inverter
- Angle grinder (grinder)
- drill
- metal ruler, marker
- wrench and pliers
Step-by-step instructions for making a magnetic welding angle with your own hands.
First, you should take a 2-3 mm metal plate and measure the angles by applying a corner.
Then place the magnet removed from the speaker so that you get a triangle with angles of 45 and 90°, attach a metal ruler and draw a line with a marker.
Using an angle grinder (grinder), we saw off the workpieces.
We polish.
We place the workpiece on the plate and tighten it with a clamp to cut out exactly the same triangle.
We combine two blanks and equalize the sides using a file.
We apply a magnet to two pieces folded together at once to mark the places for future holes, so everything will be accurate and without displacement.
The workpieces are fixed with clamps and holes are drilled.
Next, a magnet is placed on the corner and covered with a second plate on top, it turns out that our magnet is located exactly in the center of the structure.
The tie is made using a bolted connection, namely a bolt and three nuts, two of them inside the magnetic corner of the welder, and one outside for control fixation.
When the structure is fully assembled and fixed, it is necessary to drill a hole exactly in the center of the corner to make an additional tie.
Pull it together carefully.
We cut off the protruding parts of the bolts with an angle grinder (grinder)
We place a corner on a piece of professional pipe
We attach another small piece of pipe.
We weld.
This is such a wonderful device; thanks to it, welding work will become much easier and more convenient.
Magnets for welding
Welding is a fast and reliable way to create permanent connections between metal parts.
The process itself does not last long; it often takes a lot of time to correctly position the workpieces relative to each other. They must be fixed accurately and securely so that there is no displacement during the welding process. Many devices have been developed for this.
Magnetic fasteners - angles and holders are very quick to install and remove and save the welder a lot of time.
Magnets for welding
Types of fasteners and their purpose
In order for the weld to be strong and reliable, the workpieces to be welded must be fixed. For this purpose, there are many different types of equipment, universal and specialized. These include:
- switchable magnets for welding;
- screw clamps;
- screw spacers;
- magnetic corners.
Switchable magnets
In this type of equipment, it is possible to control the intensity of the magnetic field, turning it on and off. This effect is achieved by rotating one magnet inside the housing relative to the other so that their magnetic fields either mutually enhance or neutralize each other, and the field does not pass beyond the housing.
Switchable magnets are placed and removed from workpieces with one finger movement. Such devices are especially convenient when it is necessary to correct the position of workpieces.
Another advantage is that after turning off such a holder, all sawdust, trimmings, shavings and other small metal waste fall off it, making cleaning easier
Switchable magnet
Clamps
The equipment is designed to reliably press the workpieces against each other.
Its outer part, made in the shape of a right (or other) angle with a cut out top, is the fixing part, and the inner part, equipped with a screw feed device, is a clamping device.
Essentially, this is a vice with jaws bent at an angle. The parts (profile or rod) are placed in a clamp and pressed against each other with a screw.
The dimensions and shape of the parts are limited by the size of the clamp. It can be used not only for welding, but for other plumbing work.
Clamp
Spacers
Spacers are used to create the required gap between the workpieces to be welded.
Home craftsmen choose for this purpose cutting pipes and profiles from a waste box, but it is much more convenient to use an industrial product. The spacer is also equipped with a screw and is a “reverse clamp”.
It can be adjusted to any required clearance within the screw stroke. Spacers and welding magnets are often used together.
Magnetic corners
One of the most commonly used devices is a corner. Its main advantages:
- Reduces the labor intensity of the welding process. The time for fixing workpieces is reduced several times.
- Parts can be fixed at almost any angle between them.
- The device is compact and does not interfere with welding work.
- The time for removing equipment is also reduced several times compared to clamps.
Magnetic corner
Magnetic corners are available with both fixed angles and freely variable angles. To do this, they are equipped with a hinged device with a lock.
Structurally, the equipment consists of two metal plates cut from sheet metal and permanent magnets fixed between them. The most popular are universal flat corners, reminiscent of a house with a cut off roof.
But there are also three-coordinate spatial clamps in the form of polyhedra or cylinders. They allow you to assemble very complex spatial structures, such as power line supports, spatial trusses, etc.
Purposes of use
The main goals pursued by the use of magnetic holders for welding work are the following:
- convenient and reliable fixation of workpieces;
- placing them in space in strict accordance with the product drawings;
- precise alignment of angles between parts;
- reducing the labor intensity of welding and improving its quality;
- replacement of obsolete screw clamps and clamps.
Magnetic corners for welding have a clamping force from 5 to 60 kg and are used with sheet metal and rolled profiles.
According to the degree of versatility, equipment is divided into two types:
- universal;
- corner magnets.
Universal equipment has one or more degrees of adjustment and allows you to work with workpieces of flat, cylindrical and multifaceted shapes, connecting them at arbitrary angles in several planes simultaneously. Such devices are indispensable when assembling complex spatial structures. They are given increased resistance to heat and splashes of molten metal.
These advantages of professional-grade equipment come at the price of a high price and limited availability in regular hardware stores.
The square is much simpler in design, easier to learn and allows you to cover most of the needs of the home craftsman.
Triangular Welding Magnets Hexagon Welding Magnets
Angles are available in three main forms:
- sagittal (“house”);
- triangular;
- hexagonal.
Arrow-shaped and triangular ones allow you to weld workpieces at angles of 45°, 90° and 135°. Hexagonal, in addition, support angles of 30°, 60°, 75°.
Using magnetic squares when working with simple structures saves even more time than using universal ones. The disadvantage of such devices, especially their budget models, is the low magnetic force.
Advantages of magnets
The main advantages of magnets compared to screw and wedge equipment are:
- Easy and quick rough assembly of the structure.
- Possibility of fixing parts at the most common angles of 45°, 90°, 135°. Advanced models of magnetic fasteners for welding will allow you to fasten workpieces at angles of 30°, 60°, 75°, and universal ones - at any angle.
- Saving time on preparatory operations several times.
- The fasteners are small in size and do not interfere with welding.
- Switchable welding magnets make it easier to install or remove.
- Easy to clean from shavings, sawdust and slag. (especially switchable ones).
The disadvantage compared to screw and wedge fastenings is their inapplicability to wood, plastic and other non-magnetic materials.
Criterias of choice
Before you start buying a magnet for welding, you should think about what specific operations you are going to use it for. In addition, the volume of this work and its frequency are important.
If you need to weld the frame of a fence or greenhouse once a year, or replace the trim of a trailer body for a walk-behind tractor, there is no point in buying a professional model with fixation at an arbitrary angle in three planes, but you can get by with a couple of squares.
If you are opening a business and the scope of welding for six months to a year is clear, then a professional device will pay for itself by increasing labor productivity.
There are also several general rules and recommendations for selection:
- The higher the class of equipment (and its price), the longer it will retain its working qualities, primarily its geometric dimensions and clamping force.
- High magnetic field power allows you to hold workpieces of greater mass or length. Mid-level models hold up to 35 kg.
- A larger number of angles will allow welding of a variety of structures.
Modern high-quality devices do not have a negative impact on the stability of the welding arc. Unfortunately, some cheap Chinese holders have this effect on welding quality and are best avoided.
Switchable magnets are several times more expensive than permanent ones. But they are also much more convenient.
It becomes possible to weld without an assistant. With them, it is possible to precisely adjust the position of parts with millimeter precision - just turn off the magnet for a second and move the workpiece.
It is also much easier to remove them from the finished product after welding. Another advantage is that when the magnet is turned off, all the iron debris stuck to it falls off on its own.
Whether such convenience and performance is worth the money requested is something everyone decides for themselves.
The quality of the switched-off magnet must be high. If it switches off spontaneously during welding, the structure may disintegrate into blanks and the work will have to be redone.
A simple DIY magnetic square
The magnetic square has a very simple structure and is quite accessible for self-production by a craftsman with metalworking skills. Usually they are made by hand in three cases:
- testing your strengths and abilities;
- There is no suitable size on sale;
- for welding non-standard products.
Do-it-yourself magnet for welding
For production you will need:
- sheet metal 2-3 millimeters thick;
- round magnet (from an old speaker);
- bushings made of non-magnetic material (plastic, hard rubber, etc.);
- nuts, countersunk head screws.
The manufacturing sequence is as follows:
- Draw the outlines of the holder on the sheet. You need to be especially careful and use only a high-quality and certified square and ruler for marking. The accuracy of the assembly of your future structures will depend on the accuracy of the angles when marking.
- Using a grinder or jigsaw, cut out the parts and align their edges.
- Cut the bushings to size. It is important that they are strictly the same in height and have smooth edges.
- Pick up a piece of elastic plastic and fix the magnet along its inner hole.
- Mark the places for fastening, drill the plates (preferably together).
- Assemble the product by putting the bushings on the screws and placing them and the magnet between the plates.
The clamping force of the product depends on the accuracy of the assembly and the magnetic properties of the metal; before welding, it will have to be determined experimentally.
Magnetic holder for DIY welding
This is another design option for a magnetic corner for DIY assembly. It will require:
- metal sheet 1-3 mm;
- neodymium magnets (so-called “screw magnets”);
- dry board;
- nuts, countersunk head screws, self-tapping screws.
Manufacturing of magnetic holders for welding
The manufacturing procedure is as follows:
- Mark and cut two identical blanks from the sheet, carefully monitoring the accuracy of the angles.
- Make the central part of the holder. Cut it out of the board so that it follows the contours of the metal plates, but recedes inward to the height of the magnets plus a millimeter to one and a half.
- Fasten the metal and wooden parts of the product together.
- Using self-tapping screws, screw the magnets to the wooden spacer around the perimeter so that they are at the same distance from each other.
Before starting work, you need to check the geometry of the resulting equipment - its angles and dimensions.
The cost of magnets for welding ranges from hundreds of rubles (household models made in China) to tens of thousands (switchable universal professional devices from well-known brands with the ability to work in many planes and arbitrarily set angles). But it is possible to make their analogue yourself:
- Cut two triangular-shaped plates from a sheet of metal (or in the shape of a house with a cut off roof). You need to carefully monitor the exact alignment of the angles.
- File the edges.
- The magnet can be used from faulty speakers or a microwave oven.
- Mark and drill through holes in the corners of the triangle and in its center.
- Using four screws and nuts and bushings equal in height to the magnet, fasten the structure so that the magnet is clamped in the center.
- To reduce contamination, plastic plugs can be placed along the end faces.
DIY switchable magnet
The shape of the magnet for welding may not be triangular. It is selected depending on the needs of the assembled welded structure.
, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Simple and ingenious: magnetic welding angles
Comfort and convenience in any work have never bothered anyone. This also applies to welding. Among the welding tools, there are basic ones and there are auxiliary ones. These include the smallest auxiliary part in size - a wonderful magnetic corner, or, more correctly, a magnetic angle for welding.
Such corners are extremely useful for both artisans and professionals working on stream. Small in size but not in function, these special welding triangles improve the quality of products in general and welds in particular.
- Clean Water Welding Gadgets
- Types of magnetic squares
- Choosing the right square: here and now
- DIY magnetic holder
Clean Water Welding Gadgets
Here's how they do it:
- While the metal workpieces are precisely and securely fixed, you have more freedom in your actions. Your hands and your attention are concentrated only on the welding seam. Hence the increase in its quality.
- Using a magnetic welding angle, you can prepare and perform all welding work yourself, without outside help. That's labor savings for you. And you also don’t depend on anyone.
- The seam will be neat and precise thanks to the optimal and reliable installation of the workpieces using corners. If your work requires special precision, then the use of angles becomes not a recommendation, but a mandatory condition for welding.
- If you have a large amount of work, you cannot escape without fixing triangles: they will allow you to save your working time to a significant extent.
- It is easiest to weld workpieces of unusual or non-standard shapes using a welding angle with a magnet.
- With corners you can cook not only on horizontal surfaces, but also on vertical ones.
- These squares are useful not only for welding and soldering, but their ability to firmly hold parts is useful when cutting metals.
Why is the correct name “squares” and not “triangles”? Because these clamps are available in multi-angle configurations, their shape more closely resembles an irregular polygon. The most commonly used angles are 45°, 60°, 90°, 135°.
Types of welding fixtures
Why are magnetic accessories used in welding? The technology of joining parts by welding may require the welder, for example, to place different workpieces at angles from 30 to 90 degrees or to precisely orient the edges in the same plane. Such magnets are especially useful for welding metal structures from profile pipes. Excellent quality can only be achieved by using various types of corners and holders.
Most often in welding practice the following devices will be required:
- Magnetic corners (permanent and switchable).
- Fastening devices (for fixing in one position).
- Clamps (used to clamp parts).
- Spacers (to create gaps).
Magnetic corners
The main advantage of such a device is that it allows you to reduce the time required to prepare parts for welding. Magnetic welding angle allows you to:
- Reduce the labor intensity of the process. There is no need to spend a lot of time fiddling with securing parts.
- Possibility to fix parts of the product at almost any angle.
- The compactness of the devices simplifies working with them.
- Automate the welding process. Switchable magnets allow you to quickly connect and disconnect fasteners.
The most basic products have simple welded joints, but more often they have complex configurations and seam shapes. And no one can deny accuracy in such work. Therefore, magnetic devices with different functionality are often used: fixed and adjustable angles, or permanent and switchable magnetic systems.
The design of permanent magnetic corners is simple. These are two metal plates with a magnet located between them. The most common form is in the form of a house with a gable roof, a cut-off ridge and a round hole in the middle. There are also others for cooking in all three coordinates of space, or more simply - tetrahedral or polyhedrons, as well as cylinders.
By placing such a magnetic square for welding between parts in the desired position, they quickly secure parts of the product.
Switchable magnets
The magnetic holder for welding can be either permanent or switchable. They allow you to secure parts by inclusion.
Their advantage is that the switchable magnet for welding can be removed with one turn of the switch, after fixing the parts with welding points. This also makes it easier to clean the magnet from chips and small scraps (unlike a permanent magnet).
Also, all magnetic angles can be standard or universal. If the standard ones have precisely fixed angles, then the universal ones will allow you to weld two parts at an angle, for example, 32 degrees.
Clamps
This device is designed to pull two parts together and temporarily fix them.
The most common form is in the form of the letter “p” turned on its side. One side serves as a permanent retainer, and the other has a threaded screw clamp.
The size of parts that can be fixed with clamps is limited by their parameters.
Such clamping devices will be useful not only for welding, but also for other types of plumbing work.
The use is simple - the parts are placed in a clamp and tightened with a screw.
Spacers
To create gaps between the parts of the product being welded, you can make a simple spacer from a piece of pipe or fittings. But to reduce preparation time, you can use factory-made products.
The operating principle of such devices, like clamps, is based on a screw thread. Only functioning, on the contrary, to unclench.
Types of magnetic squares
Welding magnets can vary in both shape and operating principle:
- A clamp is a flexible square with angles that can be adjusted. An excellent tool to help produce parts of any complexity.
- A simple welding angle with fixed angles and a permanent magnet.
- Switchable magnets for welding are an excellent technical solution for ease of work: after welding, you can turn off their action, the holders “unstick” on their own, which allows you to remove the clamps without effort or any deformation.
- Universal magnetic angles for welding with several standard angles are another excellent technological solution for performing a variety of jobs of varying complexity.
- Angles with different power of action. It is clear that fastening massive workpieces requires fasteners that are powerful in action, just as for small work that requires jewelry precision, they must be compact both in size and in terms of attractive power.
- Three-coordinate and tetrahedral squares using cylinders and ferritic heat-resistant magnets for working in difficult temperature conditions and with workpieces of different sizes and weights.
Choosing the right square: here and now
Everything is simple here: for simple home welding work, you will need holders that are simple in design. Complex processes involve fasteners with technological bells and whistles - from switchable magnets to heat-resistant options, from simple corners to 3D models.
One way or another, a high-quality magnetic holder for welding must be resistant to significant mechanical loads and have sufficient tensile strength. In the end, we are talking about fixing not fluff, but heavy metal parts. Our squares must be able to fix them completely and irrevocably. Only in such cases will welding holders make sense at all.
If you are engaged in complex welding work, and if you have the opportunity, then it is best to choose high-quality holders with on/off magnets. Such devices will help you turn on or off not just the entire square, but individual edges.
This mode makes it possible to independently work with complex tasks. Corners of this class are usually made of chrome-plated metal with increased strength.
The cost of welding holders cannot be called low; these are not cheap devices. The price depends on the number of standard angles, attraction power, adjustment mechanisms, brand, etc. The simplest copies cost about four hundred rubles, a standard set costs around a thousand rubles. Well, professional magnetic welding devices with technological additions increase in price to 3,000 - 5,000 rubles.
DIY magnetic holder
If you haven’t found a suitable welding fixture in the store or are short on funds, you can build the necessary magnet for welding yourself.
Working with a magnetic square.
Making your own magnetic corner for welding is a great idea for three reasons:
- This is a real cost savings
- This will be a device that is suitable specifically for your technical needs.
- This is a very simple device, which is quite possible to make even without much practical experience.
What you will need:
- a magnet of any shape, but preferably a round one with a thickness of about 15 mm;
- steel sheet 2 mm thick;
- M6 bolts with nuts.
Welding angle with shut-off.
The tips and steps for making a welding angle are as follows:
- This device is best made from steel manually, using a grinder or laser. The main thing is to cut the templates with extremely precise angles on the work plane. There should be two templates. Their size should be larger than the diameter of the magnet. We pay special attention to the size and grinding of the corners - the quality of your square will depend on this. It wouldn't hurt to sand the entire surface well: if rust or any defects remain, the strength of the magnet will decrease.
- The magnet will attract any metal debris in the form of sawdust or shavings. You can get rid of this with the help of a spacer - a special part made of steel, which should be slightly smaller around the perimeter than the steel corner itself. Such a spacer will add additional rigidity to the holder, which will not hurt you. A special through hole is made in it.
- A magnet can be of different shapes. He is placed inside. Under no circumstances should it protrude beyond the edges of the steel plates. To fix it, you need to make four holes: one in the middle and the other three at the edges.
- The final stage of assembly is the careful folding of the layers of our “sandwich”, which can be fixed either with glue or metal rivets. The most reliable way would be M6 bolts. Nuts should be placed not only on the ends of the bolts, but also between the layers. The tails of the bolts protruding onto the nuts must be cut off with a grinder.
You should remember the properties of a magnet. If you place a regular, rather than heat-resistant, ferrite specimen in a square, then under the influence of high temperatures it may lose its properties. This needs to be remembered and controlled.
How to make a magnetic welding corner with your own hands
The availability of inexpensive, lightweight and high-quality welding machines on sale has become the reason that welding work is now carried out independently by many home craftsmen. Unlike factory conditions, home craftsmen cannot afford a lot of complex universal equipment. And there is often nowhere to find extra hands (in the sense of an assistant).
Manufacturers
CIMCO is a German company offering a wide range of safe and high-quality tools for various fields of activity. The company is constantly working to introduce modern technologies into the production process.
ESAB is a Swedish industrial concern, one of the market leaders in the production and supply of products
Foxweld is a trading and manufacturing company offering a wide range of quality products for welders: equipment, tools, consumables, accessories.
BARS is a Russian brand of welding equipment and accessories, the impeccable quality of which is ensured by strict testing of all stages of the production process. The manufacturer is constantly improving its products.
Why do you need a magnetic angle for welding?
A good, proven clamp cannot be considered a universal equipment, and it requires a lot of time and effort to use. There was an urgent need to create something very convenient, universal and not expensive. It would be even better if you could do it yourself. The solution to the problem was a magnetic corner (square) for welding.
The vast majority of welded structures require strict adherence to angles between the elements being connected. Previously, this was achieved by using simple devices in the form of a vice, clamps and even special equipment. The emergence of a large number of holders based on permanent magnets has greatly simplified this process. Having a set of such equipment in your arsenal, you can assemble structures of any complexity yourself without resorting to outside help.
Of course, there are many similar products made industrially, but welders know how to handle metal and try to make homemade devices. Which option is preferable? You will find the answer to this question in this article.
Make or buy
After becoming familiar with the process of making magnetic devices, each performer will be able to decide to create a product with their own hands or purchase a “ready-made” one. DIY option is suitable for performers who like to make things on their own. In addition, it is not always possible to find the desired or desired model of device on sale. To perform some work, the welder needs a square of a non-standard shape to obtain the angle of the required size.
Professional welders prefer to purchase a finished product , this saves time.
Types of magnetic corners
To fully understand the issue, it is necessary to distinguish between two fundamental types of magnetic corners used in welding: corner (permanent) and switchable.
Corner magnetic holders are the most widely used. Their main advantages are ease of use and low cost. They are produced by industry to hold metal structural elements of various sizes and at various angles. Of course, it is necessary to understand that the corner cannot support a beam weighing 1000 kg. Basically, we are talking about kilograms and tens of kilograms, which is more than enough. The number of angles offered is six, which is also more than enough.
Switchable corners are several times more expensive, but they are also the most versatile and convenient to use. The essence of this product is that the magnetic field can be turned off at the user's request. Physically, this is done with one movement of the hand, moving the rotary lever from one position to another. The work becomes faster and more comfortable; no effort is required to remove the corner from the structure. Prices and the full range of magnetic angles can be viewed in the catalog of the KEDR manufacturer’s website.
To decide which type to give preference, one should proceed from the following considerations:
how often do you weld metal structures;
How critical is labor productivity to you?
Are you willing to pay for comfort or are you willing to endure inconvenience?
Dimensions
Magnetic devices are small in size , which makes them so popular. The length, width and height parameters of equipment with magnets may vary, but regardless of the model and manufacturer, they are all compact and easy to use. The average weight of the product is about 1 kg.
The most important indicator is the force of attraction (holding or pressing) of the magnetic corners. Manufacturers and suppliers may specify this parameter in pounds (LBS or lbs) or kilograms (kgf). The maximum value of this indicator is 34 kgf or 75 lbs. You can also find the following values: 11; 13; 22; 23; 24 kgf and others.
Depending on the tasks, you should choose the necessary model.
Required materials and tools
List of tools for making a magnetic square:
This is the maximum list of tools. If necessary, you can get by with a much smaller set. If you don’t have a grinder, you can cut out blanks from a two-millimeter sheet with a chisel. Drill all the holes with a drill, and the accuracy of a caliper may be excessive. In general, each master himself can choose a tool from among the available ones.
We offer a set of materials necessary for the manufacture of a magnetic square. It is not difficult to guess that this list is very arbitrary, and, in the absence of specific material, it can be replaced with a similar one.
steel rod Ф24 mm;
steel sheet 2 mm thick;
steel tube Ф15 mm;
bolts, nuts, washers M6.
Ring magnets are most often obtained from powerful Soviet speakers. Although they are keeping silent about where to get these speakers. This can become a problem, especially if you need not one square, but two or three. In this case, powerful neodymium magnets, which can be found on the market, can help out.
Manufacturing process and order
In accordance with the drawing, we mark the parts. We cut out the triangles with a grinder, and cut off three bushings from a steel tube with a hacksaw. For precision drilling, we drill two workpieces at the same time, having previously tightened them with clamps. We got a magnet with a hole in the center, so we attach it using a cylinder of the appropriate diameter, cut from a round piece of wood. We clean the resulting parts, paint them and begin assembling them.
Assembly
Assembling the finished product is not particularly difficult and does not require a detailed description. Briefly, the process goes like this:
We insert bolts into three corner and one central holes.
We put bushings on the bolts coming out of the corners of the triangle, and put a cylinder on the bolt in the center (if you didn’t forget to drill a hole in it).
We put the magnet on the cylinder.
We place the second triangle on the four bolts and secure the structure with nuts, having previously placed washers under them.
Assembly is complete, the product is ready for use.
Types of magnetic corners for welding. How to make a holder with your own hands
When welding small metal parts, it can be difficult to keep them stationary. To fix the elements in this case, the welder most often has to resort to the use of additional mechanisms and devices so that the parts do not move during welding.
The use of vices and clamps allows them to cope with this task perfectly, but the main disadvantage of such products is the need to carry out a large number of additional movements to install the part in a static position. And also the inability to fix parts at a certain angle.
A magnetic holder for welding does not have such disadvantages, so if you often have to weld parts in this way, it is recommended to purchase or make this device yourself.
Welding magnets
For high-quality welding work, it is necessary to correctly carry out preparatory procedures . The process of fixing takes a lot of time from the performer . In addition, the assembled structure may fall apart from contact with equipment or an electrode. The welder will need to spend a lot of time and effort on restoration. special magnetic accessories were created for fixing parts. Such compact devices allow you to avoid the help of colleagues and save time on creating additional devices of a larger scale (for example, a “third hand”).
Types of magnetic holders for welding
When performing welding work, magnetic devices of the following designs are most often used.
Angular: permanent
The advantage of this model of angles is the ability to quickly fix the parts to be welded in 6 positions. The device consists of 2 plates with a powerful magnet located between them.
If you often have to weld parts at different angles, it is recommended to purchase an adjustable holder.
A design with fixed angles will be much cheaper, but such a device should be purchased when the main part of the welding work involves fixing elements in the most frequently used position.
Disabled
The switchable magnetic welding holder is a device in which the magnetic field can be neutralized using a rotating lever.
Such devices cost several times more than a regular angle, but thanks to the shut-off function, using the product is easier and more comfortable.
Also, switchable models can be easily cleaned of metal shavings and other small parts.
Watch an interesting video where a person talks about a homemade switchable magnet for welding:
Which type of welding holder to choose depends on many circumstances. If the corner is needed for frequent use, it is recommended to purchase a switchable model with a tearing force of at least 20 kg.
Main selection criteria
For professional work, you should choose a high quality tool. Devices are exposed to high temperatures, which reduce the magnetization coefficient of low-quality specimens. The fixture must be free of chips, gouges and other defects where it touches the clamped product. Irregularities do not allow objects to be firmly fixed at a given angle.
- Important! The advantage of switchable corners is the ability to turn off the magnetic field both on the entire device and on its individual faces. These devices are suitable for craftsmen who often weld parts of complex configurations
Chinese angles have a budget price, but they cannot withstand temperature changes, so they quickly break. To weld products at different angles, it is recommended to choose a customizable mechanism or purchase a kit containing several types of tools for clamping at certain angles.