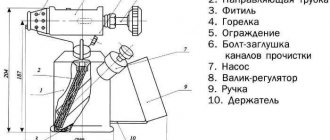
When carrying out soldering, acidic fluxes are often used to pretreat the surface of parts. The degree of activity of the material is selected depending on the type of metal and the degree of its contamination.
There are various products on sale, the composition of which is selected taking into account the specifics of the work to be done. You can make soldering acid at home yourself.
This will require certain knowledge, basic ability to make chemical compositions and a small amount of money to purchase components.
Making soldering acid yourself
First, you should take care of your own safety, because using acid is very dangerous and can cause irreparable harm to your health. If acid production is carried out in enterprises and industrial areas, then everything must be done in special-purpose cabinets. The reagents are reliably protected from outsiders, and they are poured strictly under special hoods. At home, it is recommended to use protection, gloves, goggles, respirators and other devices. Dissolving the acid should only be done in a well-ventilated area or even outside. Indeed, in the process of creating acid for soldering, hydrogen is constantly released into the air in large quantities. It is also necessary to take care, just in case, of water, with which you can quickly rinse the area of skin on which the substance has come into contact. It is best to use cold tap water because in the event of an accident, it will reduce pain and quickly clean the wound.
If this substance is spilled on the surface, it is best to wash it off with a special mixture of water and alkali. You must also remember that this material must be stored correctly, the container must be closed and sealed, storage is carried out in a dark and cool place. It is recommended to prevent unauthorized people from accessing the soldering acid to avoid danger to others. Flux is sometimes made from pure hydrochloric acid without zinc and water. However, it is mostly used only for iron products.
What can you do at home?
The degree of acidity of fluxes differs.
Active mixtures include compositions with zinc chloride. From the school course, perhaps someone remembered the properties of saline solutions. Salts tend to undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water. Zinc chloride, when exchanged with water, forms a strong acid and a weak alkali. Therefore, the solution has an active acidic character. Hydrochloric acid quickly removes oxide substances.
Typically, soldering acid is made by adding 412 g of zinc to 1 liter of concentrated hydrochloric (hydrochloride) acid. The procedure is not entirely pleasant and safe. During operation, volatile acidic vapors are released.
You should work with concentrated hodgepodge only under a hood or in a respirator, in a well-ventilated room.
With hydrochloric acid
Several formulations with zinc chloride are popular. Zinc compounds are used in the galvanizing process to protect metals from corrosion. This chemical element is known for its resistance to oxidation processes. Making soldering acids with your own hands is not difficult.
For products made of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, the following ratio is suitable:
- zinc chloride – minimum 25%, maximum – 30%;
- concentrated hydrochloric acid – 0.7%.
Both components must be quickly dissolved in water. It should be noted that hydrochloric acid is a highly volatile substance. It is advisable to work with it under a hood. The bottle with the starting reagent should only be kept closed.
With Vaseline and alcohol
For parts made of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, sometimes it is more convenient to use a paste with acidic properties instead of soldering acid.
To prepare it, you need to mix a saturated solution of zinc chloride - 3.7% and technical petroleum jelly - 85%. To give the required consistency, add a little water to the mixture.
To work with nickel, platinum and their alloys, you can make a soldering mixture with your own hands from zinc chloride - 1.4% and ethyl (wine) alcohol - 40%. Both components must be thoroughly dissolved in water and the finished soldering solution must be mixed.
After using all the above compounds, the soldering area should be rinsed well with plain water.
With rosin
For carrying out critical work with ferrous metals, soldering precious and non-ferrous metals, a paste mixture made by yourself from rosin - 24% and zinc chloride - 1% is suitable. All this must be dissolved in ethyl alcohol. At the end of the soldering procedure, you need to wash the work area with acetone.
To form a seam with increased strength characteristics, it is recommended to take:
- rosin – 16%,
- zinc chloride – 4%,
- technical petroleum jelly – 80%.
It is more difficult to rinse the soldering area after treating it with such homemade solder paste. You need to take acetone.
Experience shows that in some cases it makes sense to replace soldering acid with a corresponding acidic paste.
Homemade sour pastes
When working with aluminum parts, a flux with oleic acid is often used, the formula C17H33COOH gives an idea of the high molecular weight. Higher acid has a viscous consistency, similar to a slightly viscous liquid.
Soldering flux is made as follows: 20 ml of oleic acid, about 3 g of lithium iodide are dissolved in a glass container in a water bath. A homogeneous solution, made with your own hands, after cooling, is poured into a glass bottle for storage.
After soldering, the working area is washed with acetone, gasoline or alcohol.
To solder nichrome, you can make a composition with your own hands from 100 g of Vaseline, 7 g of powdered zinc chloride, 7 g of glycerin.
The whole mass must be mixed well. It is advisable to do this in a thick porcelain cup or a special mortar.
Hydrochloric acid
Flux based on hydrochloric acid is a complex chemical substance. Usually sold in small bottles called soldering acid. It has a yellowish tint and a sharp, specific odor. It has the ability to dissolve most metals and corrodes skin and muscle tissue. Therefore, soldering with this composition must take precautions.
Application
Hydrochloric acid can be used to solder aluminum, stainless steel, silver and various alloys. This flux is also used for tinning and soldering of galvanized steel. This method has found wide application in roofing work and the organization of external drainage.
The need to use acid fluxes
Any soldering acid - hydrochloric or phosphoric acid - is designed to create an ideal environment for the interaction of solder with elements.
Their use makes it possible to remove contaminants and oxides from the working area, prevent the resumption of the oxidation process and reduce the tension of the solder, in order for it to spread more freely.
As a result, reliable soldering of parts is ensured.
Depending on the type of metal, the flux for soldering is selected. It is worth noting here that soldering acid is not used when assembling boards.
Read also: Recipe for sea cucumber with honey
Acid belongs to the category of aggressive media and contributes to the destruction of components standing in its path.
In addition, it is an ideal electrical conductor and has the property of creating additional conductive channels.
Therefore, you should not even count on neutralizing the acidic environment after soldering.
Universal flux paste made from tallow
Paste flux is more convenient to use than liquid or solid. To prepare it you will need:
- lard (preferably unsalted) – 100 g;
- ammonia powder – 1 teaspoon;
- rosin – 2 teaspoons.
How to make flux with your own hands:
- Finely chop the lard and melt the lard. Separate it from the cracklings.
- Crush rosin into a fine powder.
- Combine 2 teaspoons of lard, 2 teaspoons of rosin powder, 1 teaspoon of ammonia.
- To stir thoroughly.
- Draw into a syringe, removing it into a needle.
Orthophosphoric acid
Another type of soldering agent is phosphoric acid. It has the formula H3PO4. It is used for alloying chromium and nickel. However, it is not used in its pure form. Acid occupies only 32% of the solution. Another 6% is allocated to rosin.
Sometimes orthophosphoric soldering acid, the composition of which is diluted with zinc chloride, can have a mass content of the latter from 50% to 0.005%. The mass fraction of insoluble residue is 0.001%, and ammonia - no more than 0.5%. The maximum pH level for such a solution is 2.9%.
Under normal conditions, the substance looks like colorless crystals with hygroscopic characteristics. It dissolves well in water. Therefore, if it accidentally gets into your eyes, you should rinse the mucous membranes for 10 minutes with running water.
Error message
Content
Preparing flux for soldering
The quality of the finished flux is determined not only by its composition, but also by the sequence of introduction of the constituent substances during its manufacture.
In mass production, fluxes are usually made from commercially pure components. When developing new fluxes, in order to eliminate the influence of various impurities, which are always present in certain quantities in technically pure substances, it is necessary to use only reactively pure components and only after clarifying the composition and test soldering, use technical substances.
Prepared fluxes and solder pastes should be stored in clean containers with a tightly closed stopper. During open storage, due to the evaporation of components and the absorption of moisture from the atmosphere, a violation of the flux composition, a change in its viscosity, color, presentation and fluxing activity may occur.
The most widely used solution for soldering with low-melting solders is an aqueous solution of zinc chloride. It is prepared by dissolving zinc metal in hydrochloric acid. For this purpose, zinc is loaded into a bath with an acid-resistant lining, then hydrochloric acid is gradually poured in.
To avoid overflow of the solution over the edges of the bath during the reaction, the acid filling level should not exceed ¾ of the depth of the bath. The amount of zinc and hydrochloric acid is taken in accordance with Table 1.
Table 1 - The ratio of the amount of zinc and hydrochloric acid when preparing zinc chloride
| Density of hydrochloric acid | Ratio of acid and zinc, l/kg |
| 1,130 | 3,70 |
| 1,135 | 3,55 |
| 1,140 | 3,40 |
| 1,145 | 3,30 |
| 1,150 | 3,20 |
| 1,155 | 3,08 |
| 1,170 | 2,77 |
| 1,175 | 2,68 |
| 1,180 | 2,59 |
| 1,185 | 2,52 |
| 1,190 | 2,43 |
The completion of dissolution of zinc in acid is determined by the cessation of the release of hydrogen bubbles. The resulting solution of zinc chloride is left to stand until transparent in the same tank, and then it is pumped into another tank to precipitate sulfuric acid ions with calcium chloride.
As the bath becomes contaminated with sludge, the latter is removed using sieves; If there are pieces of zinc metal in the sludge, the sludge is washed with water and used again. A solution of calcium chloride for the precipitation of sulfuric acid ions in the flux is prepared in a gummed tank by neutralizing quicklime with hydrochloric acid. The normal concentration of calcium chloride is considered to be 210-240 g/l in terms of calcium oxide.
After adding calcium chloride, the prepared solution is stirred with a wooden stirrer and left for 24 hours.
For soldering stainless steels and heat-resistant alloys with brass and other refractory solders with a melting point of 850-1100 ° C, fluxes F200 and F201 are used.
They are prepared as follows: in a deep metal mortar, boric anhydride is crushed into pieces no larger than 6 mm in size and ground in a porcelain mill to a powder state. Ground boric anhydride is stored in jars with rubber stoppers. If boric anhydride is not available, it can be prepared from boric acid by melting it in porcelain or fireclay crucibles. Borax is added to the ground boric anhydride. All components are mixed and thoroughly ground in a porcelain mortar or in a porcelain ball mill. The ground flux is stored in glass jars with rubber stoppers or gaskets.
Flux ligature F201 consists of 4% magnesium, 48% aluminum and 48% copper. It is prepared in the following way: first, aluminum and copper are melted, and then magnesium is introduced at a temperature of about 700 ° C while vigorously stirring the alloy.
Before introducing it into the flux, the ligature should be ground in a ball mill or ground in a porcelain mortar to a powder state.
Fluxes F200 and F201 can be used in the form of powder or thick slurry mixed with water or alcohol. In all cases, flux must be applied to the soldering area before heating the part.
After soldering, flux residues must be removed by prolonged boiling of the parts in water or by blowing them in a sandblaster, followed by drying at a temperature of 120-150 °C.
F209 flux is used for soldering structural and stainless steels, as well as heat-resistant and copper alloys with silver solders with a melting point of 600-850 °C. It is prepared in the following way: dehydrated potassium fluoride is broken into pieces no larger than 20 mm in a porcelain or metal mortar and placed in a jar with a rubber stopper. Boric anhydride is crushed into pieces no larger than 6 mm in size, and then ground in a porcelain ball mill to a powder state. The prepared components are weighed according to the recipe, mixed and ground in a porcelain ball mill to a powder state. After grinding, the flux is immediately packaged in glass jars with rubber stoppers.
For soldering steel products with low-tin solders and for processing steel products before hot coating with tin-lead solders, lead or tin, an electrical contact flux of the following composition, g/l, can be used:
| Zinc chloride | 350-400 |
| Stannous chloride | 5-10 |
| Copper chloride | 8-12 |
| Ammonium chloride | 20-30 |
| Wetting additive OP-7 | 2-3 |
| Hydrochloric acid | 35-60 |
How to solder with acid
As already noted, acid fluxes are used for soldering various metals and their alloys. Such work has its own nuances, which are discussed below:
- Surfaces that need to be soldered are cleaned of dirt and rust. This is done with a file or sandpaper;
- Next, acid flux is applied to both surfaces. This can be done using a brush. It is convenient if the storage container is a plastic bottle with a dispenser or just a narrow nozzle. This will allow you to carefully apply the acid in the right amount;
- After this, with a heated soldering iron, solder is applied to both surfaces treated with soldering acid. This is called tinning.
Two tinned parts are easily soldered together: an even film of solder allows you to make an even and uniform joint, which is reliable and durable.
After finishing soldering, you need to remove any remaining acid so that it does not further corrode the metal. To do this, use a powder of regular baking soda, which is then washed off with water.
Materials and tools for making acid
You need to know that the soldering acid you make yourself will have a slightly different composition than the purchased one. However, it will be simpler. To prepare such acid, you need to use some equipment:
- Glass container or jar for mixing and preparing the material.
- Zinc granules or cups from used batteries containing this element.
- Tap clean water.
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid, which is capable of dissolving unnecessary impurities and substances.
Making acid yourself
First you need to take a container or jar for mixing the acid. This is where the zinc or batteries and their remains are placed. Only after all of the above can hydrochloric acid be poured into the container. The main thing is to act with great caution, because if it comes into contact with the skin, you can get a serious burn. The acid in the container should not be more than 3/4 of the volume of the entire composition.
As a result, it turns out that the proportions should be like this. For 1 liter of hydrochloric acid, 412 grams of zinc are needed, but this can only be measured using special tools. Therefore, it is worth knowing that there will be some deviations in one direction or another.
When further preparing soldering acid, you must wait for the reaction of the chemicals to finish. Zinc and acid come into contact with each other, the metal gradually dissolves. During this process, active hydrogen evolution occurs, so many bubbles can be seen in the liquid.
The liquid gradually becomes clearer and cleaner. When all processes are completed, it is necessary to pour the liquid into a tightly closed container. All these materials can be easily purchased in stores specializing in the sale of chemicals and reagents. When using batteries, you can see that almost any of them will do.
If you need to make a material with weaker properties, then you should slightly reduce the aggressiveness. In this case, it is recommended to add a little water to make the solution more liquid and with weaker properties. However, you need to be careful, because the liquid can splash and get on the skin and mucous membranes of a person. In this case, you should choose the proportions yourself, adhering to the specifics of the required soldering.
Active flux from aspirin tablets
Just one tablet of aspirin, and you can tin the black wires without any problems. You can solder directly on the tablet, as shown in the video:
Or you can transfer the acid from the tablet to the place of soldering with a soldering iron tip. In both cases, it is important not to lean over the fumes and carry out work in a well-ventilated area or outside.
Important. For soldering, only regular, non-effervescent aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is suitable.
Advice. To escape from acrid smoke, place a fan nearby and direct the air flow away from you.
Other soldering features
At the learning stage, many beginners have a question: “what is solder and flux.” Solder is a common form of low-melting metal that is required for successful soldering of radio circuits, electronic components, and jewelry. Most often, solder is made from tin, but in its pure form such metal is not cheap, so it is used only for tin-plating and soldering of utensils, which are used for storing and preparing food. If it is necessary to solder wires and electrical circuits, the tin-lead solder option is used.
When performing soldering work, you may need the following tools and accessories:
- stand for soldering device;
- side cutters;
- pliers;
- tweezers;
- stationery knife;
- vice;
- desoldering pump or copper braid.
The soldering process itself includes several steps:
- Cleaning the selected area to a shine.
- Dipping the soldering iron tip into rosin for more effective cleaning.
- Firmly pressing the connected elements together.
- Then it requires applying a soldering iron with a small amount of solder at the end to the junction of such parts.
- Next, you need to run the soldering iron tip along the part or wire, doing this as quickly as possible to avoid burning out the rosin on the tip.
- The soldering area should be thoroughly heated so that the rosin, when melted, covers the entire surface of the part, and the solder fills the gap between the parts.
- Be sure to remove excess solder with a soldering iron or desoldering iron. It also wouldn't hurt to use braid.
If all operations are carried out exactly according to the established rules, the hardness of the solder will become maximum, and its distribution will be uniform.
If during the solder solidification stage the soldered parts move from place, most likely the soldering is not good enough. To avoid such a course of events, it is enough to learn how to avoid making many mistakes.
Alcohol, rosin and glycerin are the basis of liquid flux
You can also make high-quality liquid flux from rosin, which dissolves in alcohol. Before dissolving, it is best to mash the rosin in a mortar until it becomes a powder. In this case, the rosin will completely dissolve in alcohol.
Everything will take several hours, but you can speed up the process of dissolving the rosin if you heat the container with liquid flux to a temperature of 80 degrees. It is better to heat in a water bath, avoiding unnecessary overheating of the mixture, since alcohol is a flammable liquid.
The uniqueness of this flux is that it is absolutely neutral, and therefore does not require any rinsing.
If you don’t have ethyl alcohol on hand, you can replace it with glycerin. But it is not recommended to use a solvent to prepare liquid flux, since its use will release many harmful substances.
Instructions for use
- Immediately before soldering, it is necessary to clean the surface with a file or sandpaper, which will avoid all kinds of contamination.
- Acid should be applied to the adhesion site, for which you can use a brush. Next, you need to cover the structure to be soldered with solder based on tin or its alloy. If the substance does not apply evenly, you will have to repeat the acid treatment again.
- In the next step, carefully solder the surfaces. When working with a heated soldering iron, do not forget about safety rules and try not to clutter the work area with materials that ignite very quickly.
- After completing the procedure, the acid should be neutralized using an alkali, for example, a soda solution, and then rinse the adhesion site to get rid of any remaining acid. In rare cases, acetylsalicylic acid plays the role of a flux, although its use requires a more complex approach.
How to wash off acid after soldering?
According to the strength of their effect, acid fluxes can be divided into active and inactive. What are their features? Examples of active ones: zinc hydrochloride, orthophosphoric. Fluxes of this type are used when soldering copper, iron, nickel, carbon steel or aluminum. They remove oxide well, but, remaining on the surface of the metal, cause corrosion. After finishing work, they must be neutralized and washed off with a solution of soda ash or water and soap. In some cases, it is recommended to use alcohol or acetone.
Neutral fluxes, for example. oleic, used for soldering radio components and printed circuit boards. They are safe in terms of corrosion and do not require rinsing. If necessary, flux residues are removed with alcohol, acetone or water.
The best recipes for homemade fluxes for soldering
Flux is an organic or inorganic substance that is used in soldering metal products. The main purpose of the flux is to remove the oxide film from the metal surface, protect it from exposure to oxygen and ensure uniform spreading of the solder.
There are two main types of fluxes - acidic or, as they are often called, “active fluxes” and acid-free, passive fluxes. A prominent representative of acid-free flux is pine rosin. This is the simplest flux, which is intended for soldering copper products.
However, not only rosin can be used as a flux. Acids are often used for these purposes, as well as various mixtures, which generally improve the quality of soldering. We will talk about them in this article.
Physico-chemical properties and composition
Before making soldering acid, you should familiarize yourself with the composition of the material. This substance includes:
- Hydrochloric acid;
- Ammonium chloride;
- Zinc chloride;
- Deionized water;
- Wetting additive.
Soldering acid at home may have other components in its composition. The main thing is to achieve the required properties that this flux has. Firstly, there must be a high activity of the material. Rapid interaction with the elements makes the environment aggressive and destroys almost all harmful substances that interfere with normal soldering. This has the side effect that small metal parts may be damaged if they come into contact with the acid. Active solder fat also has similar properties.
The acid emits a specific odor and is harmful to health when a person inhales its vapors. Thus, a respirator should be used during work, and the room in which this all takes place should be well ventilated. It is necessary to prevent flux from getting on your hands, eyes, and other surfaces except the workpiece itself and the solder.
Flaws
- Too aggressive an environment does not allow working with thin parts that are highly exposed to this kind of flux;
- There is a possibility of injury from direct contact with the material, since concentrated acid can corrode skin as well as muscle tissue;
- During operation, the material emits fumes, which are also harmful, but this time the respiratory tract is affected;
- The acid emits an unpleasant odor, which strongly spreads in the surrounding area.
How to replace soldering acid at home?
Over the entire existence of this substance, experts have found several options that can act as a replacement. Many of them are easy to prepare at home, but may not fully correspond to the specified properties of the original substance.
One of the first options that can replace soldering acid is aspirin dissolved in water. To do this, take an aspirin tablet, which can be crushed beforehand so that it dissolves faster. Then it is poured into a container of water, where dissolution occurs. When there are no solid particles of the tablet left in the liquid, it can be used. This is done as when working with ordinary liquid fluxes. The resulting substance is harmless.
Aspirin tablet in water
The use of concentrated acetic or citric acid is also allowed. Their efficiency is somewhat lower. In no case should you dilute such options, since they are often sold already diluted. As a rule, they have a certain level of aggressiveness, but do not reach the same levels as the acid itself.
Use of concentrated hydrochloric acid. This material is the basis of the original flux, and is also used to prepare soldering acid at home. This option is the most dangerous for health, but allows you to cope with almost all types of contaminants and provides reliable protection. But the level of aggressiveness here increases greatly, so thin parts should not be soldered using this method. Most often it is used for iron parts.
Active solder fat serves as an alternative to acid, since, unlike other varieties, it is quite aggressive and is also not recommended for use on thin metal products. It is much more convenient than other options in terms of placing flux on the surface of the workpiece, but it also has negative side effects that are harmful to human health. It may not always be possible at home. But you should have it in reserve, since it is solder fat that provides some of the best soldering conditions among all available analogues.
When choosing what type of acid is needed for soldering, in addition to soldering acid, you should also consider phosphoric acid. This is a simpler and more gentle option. It can also be purchased in a store and it copes well with working conditions, as it easily removes oxides, grease deposits and other films from the surface.
At home, you can also prepare soldering acid yourself, which will replace the original. It will not have as rich a composition as store brands, but it will be able to cope with the procedures for which it is designed. Its preparation will take longer than the above options, but the quality of the resulting substance will be slightly higher. In addition, it can then be stored for a long time for later use.
Conclusion
There are many things that can be used instead of soldering acid. They all have their own properties, but are quite suitable for soldering. Some have limitations due to their aggressiveness, others have the advantage of their cost and availability, and still others have a high level of quality. Each shareholder selects the option that is more convenient for him, but practically none of them can become a complete analogue, since each element of the composition brings its own nuances.