Metal forging, along with casting, is the most ancient technology for processing materials. Moreover, humanity began producing products in this way long before the advent of iron and steel. The first blacksmiths worked about 5-6 thousand years ago. Over time, the technology only improved and was supplemented with new techniques. Today, no production can do without metal processing by forging.
What does forging technology include, what equipment and techniques are used in the oldest form of metalworking?
Metal forging concept
In simple terms, forging is the processing of metal heated to forging temperature. The principle of the technology is based on the physical properties of any material that has a melting point. But before this threshold is reached, the structure of the substance will become softer.
Each metal has its own temperature, upon reaching which it becomes softer, and, therefore, more pliable for processing by forging.
However, there is also a metalworking technology where the workpiece is not heated, but forged cold. This technique allows you to obtain products that are no less durable; without heating, the workpiece is pressed and bent. The table shows the temperature limits at which a particular metal can be forged.
Cold forging method
Most cold forging work is performed on equipment specially designed for this purpose. You can name a certain list of equipment that is used for cold metal processing. As a rule, such equipment shows its effectiveness when performing large volumes of work in the architectural design of buildings and structures.
Among the equipment used in the production of cold forging products are the following:
- torsion bar, it is used to twist the rod along its axis;
- wave, various wave-like parts are made on it.
In total, the fleet of cold forging equipment includes about a dozen units. Some are powered by the operator's muscular strength, some are powered by an electric drive. Some craftsmen are engaged in the independent production of such equipment.
Types of forging
There are main types of metal forging:
- Free.
- Machine.
- Stamping.
Free forging means that the workpieces are not limited to any shape. Or the material will be fixed on one side on the anvil. This technological technique also includes hand forging of metal, when the product is shaped using a sledgehammer or hammer. Open forging is used both for the production of individual products and simply to improve the quality of the material.
When forging the surface of the workpiece, the properties of the metal improve. Large crystals of the material are crushed, the structure becomes more fine-grained and homogeneous. In addition, during forging, the internal shells are welded, strengthening the body of the workpiece.
Machine forging is a more modern processing option. This technology is used in mass, heavy industry. In this case, mechanized hammers (weighing from 40 kilograms to 5 tons), forging machines or presses are used. The weight of blanks and final forgings can sometimes reach several tens of tons.
VIEW Induction heater on AliExpress →
Stamping. This technological technique made it possible to make mass production. When making products, the metal is limited by stamps and, when deformed, receives the desired shape.
Stamping is used in mass production where it is important to obtain a large number of products. Open forging is typically used in small-scale and one-off production.
Operations of cutting, cutting and trimming metal blanks
Felling operations: a.
cutting with a chisel; b. chopping with a chisel and undercutting; V. cutting flakes in a vice; d. longitudinal cutting; d. cutting (cutting). The workpiece is cut to divide it into elements. To cut metal, it must be heated to a dark red heat temperature, placed on an anvil and, using a special chisel, cut through approximately 75 percent of the thickness. After this, the product is turned over and chopped with a chisel, this time to the end.
If you work with hot thick metal with forging chisels when chopping, then do not forget to cool the tool from time to time, since prolonged contact with a hot metal workpiece may cause the chisel blade to drop. Then, in order to use the tool again, drops of water need to be removed from it by lightly tapping.
Chopping (not to be confused with chopping) only allows you to chop a metal product. This operation is very often used by blacksmith artists when forging. The cut parts are subsequently stretched, twisted, subjected to various forging techniques and ultimately take the form of flowers, leaves and curls. The cutting operation is especially popular for the production of svetzets, zhikovins, etc.
The workpiece is cut only on one side, the front side. First, light blows are performed so that only the groove is cut. The workpiece should be slightly heated, which will make it possible to slowly cut the product. When the workpiece is cut, the metal is heated to high temperatures and cut through with one sharp blow.
Chipping is used to remove a layer of metal along the outer contour. This action is also called pruning. It is often used in the process of forging complex decorative forms: quilts, overlays, etc.
The cutting process is similar to cutting, only in this case the metal is separated along the internal contour. When performing these techniques, semicircular, carbon, straight and other forging chisels are used.
https://moyakovka.ru/youtu.be/ezdpKqWJnq4
Equipment and tools
The centuries-long development of this type of metalworking has led to the emergence of a huge number of tools and devices.
But hot forging of metal retained the same technological line as thousands of years ago: heating, fastening, deformation, hardening. When making forged products by hand, they use almost the same sets of tools and equipment that craftsmen have used since the inception of this technology. The list is as follows.
- Blacksmith hearth → VIEW on AliExpress
- Anvil → VIEW on AliExpress
- Ticks.
- Hammer → VIEW on AliExpress
A forge or forge is used to heat the material to the desired temperature. There are many different types of this equipment.
- Stationary and portable.
- Closed and open hearths.
- Fuel or electric.
- Liquid, gas or solid fuel.
- With side air supply nozzles or central lance.
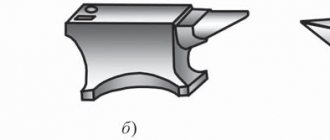
Anvils are massive metal tables where the workpiece is actually formed. They consist of a base, a horn and a casing with holes for bending. There are several varieties of this forging device, but a steel support with a weight of 30 kilograms or more is required.
In hand forging, the craftsman uses pliers to handle the workpiece during the work process.
Hammers, the main tool used in blacksmithing, can have different weights to work with workpieces of different sizes.
A little history + interesting facts
Interestingly, one of the most common surnames in the whole world comes from blacksmithing. In Russia it is Kuznetsov, in France Ferrand, and in Britain Smith. This shows how widespread this craft was and remains in this world.
It is generally accepted that the basis of the word “cunning” is a verb such as “forge.” The fact is that most tribes and peoples believed that blacksmithing was something obscure and shrouded in a terrible secret. The blacksmith (cunning) made forges, knitted fetters, and over time the word “cunning” became synonymous with wisdom, skills and abilities. After some time, it became synonymous with evil plans and intentions. At the same time, such common phrases as “forge your happiness” and “forge your destiny” began to appear, which are exclusively positive in nature.
With the large-scale unification of production and the use of such types of equipment as stamping, rolling, the use of control through computer software almost ousted blacksmithing from the industry, but, nevertheless, it remained and is now incredibly popular among designers, as well as specialists who are involved in design interior A modern blacksmith knows how to make products that will be used as fences, stairs, as well as in the role of architectural design of buildings, etc.
In the 21st century, this has led to the fact that the design of forged products is done in special 3D design programs, which are designed to develop parts for various purposes. Open forging is used for many types of metal. Using this operation, it is possible to make household items, as well as items that are of exceptional artistic value.
By the way, this method of metal processing is also used by jewelers. By the way, gold is considered the most malleable metal, since it has incredible ductility, fluidity, ductility and many other properties that make it possible to make incredibly beautiful and almost priceless products from it. You can look at photos and videos of forging metal, in particular gold. In practice, only two types of forging are most often used - cold and hot.
Blacksmithing techniques
Basic forging operations used in metal forging technology:
- Sedimentary.
- Landing.
- Drawing.
- Break-in.
- Rolling out.
- Firmware.
- Overclocking.
Sedimentary forging work involves reducing the height of the workpiece and increasing its cross-sectional area.
Upsetting is essentially a partial settling of the workpiece. It is used when some thickenings need to be made on the metal surface. This is achieved by reducing the length of the workpiece.
Broaching is another technological method of processing metal using the forging method. This operation involves lengthening the workpiece. This reduces the cross-sectional area.
Rolling on a machine
Rolling in blacksmithing involves giving the workpiece the shape of a cylinder. During the process of metal deformation, the workpiece rotates around its axis.
Rolling - processing of a ring blank. When it is necessary to increase its internal and external diameters, the metal is rolled out on a mandrel by reducing the wall thickness.
In blacksmithing, broaching is used to produce a through hole through the use of a punch.
Dividing is the operation of obtaining a wider workpiece. Essentially, the metal for forging is flattened on the surface of the anvil with a hammer, moving across the axis of the product.
There are also many other techniques by which the required product shapes are obtained.
Forging drawing technology
Metal extraction: a.
on the edge of the anvil; b. using the back of a sledgehammer; V. on the hem; g. on a pair of lining; d. with top tamper; e. using a smoothing iron; and. in mandrels. The metal drawing operation is used to increase the length of the product while simultaneously reducing the cross-sectional area.
The workpiece is drawn as follows. The heated metal is placed on an anvil, where it is stretched under the blows of a hammer or sledgehammer. Then they turn the product 90 degrees and hit the bulge from the first blow. After performing several more such cycles, the blacksmith gradually pulls out the metal.
The main condition for drawing is to maintain the square shape of the cross-section of the metal workpiece.
To speed up the drawing process, you can forge on the anvil horn. Then the product will be stretched between a pair of convexities, which accelerates the increase in the length of the product.
There is another way to stretch the workpiece - using rolling or spreading. As a rule, the rolling has a semicircular shape. The direction of the drawing will depend on how the rolling is located on the metal - across or along.
Extraction at the end is used to make svets, zhikovins, and nails.
Application areas of steel castings and forgings
Steel casting and forging are used to produce parts for the following industries:
- petrochemical plants (such as forged valves, forged fittings, flanges, etc.)
- power generation and waste recycling
- mining and processing of minerals
- agriculture and livestock
- water purification
- aeronautics
- automotive industry (pulleys and gears)
- materials processing
- brickworks
- asphalt plants
- storm drain parts
- plant rendering
- railways
Punching, bending and twisting
To make a hole in a metal workpiece, it must be punched. This manipulation is performed under high temperature conditions. A punch (punch) is mounted on the area in which the hole is planned, then blows are applied with such force that the punch penetrates 75 percent of the thickness of the workpiece.
Punching a hole in a product: 1. Pre-punching. 2. Turning the workpiece over. 3. Final punching.
The part of the workpiece where the hole will be made must be placed on the anvil clearly above its round hole. If it does not fit in size (very small), then use a square-shaped hole. After the first blows under the punch, bulging is observed in the lower layer of the workpiece. After this, the product is moved to the front side of the anvil, while the punch is not removed, and a small force is struck on the punch. At the convex place there should be a clear trace of the area in which you need to install the punch for the second time. The punch is removed, then the product is turned over and the punch, cooled with water, is installed exactly at an elevation above the hole obtained after the first blows. It is necessary to take into account that for this work it is necessary that the punch has a cone-shaped working part. The resulting hole is slightly smaller than the diameter of the punch. After this, a mandrel of the same diameter is mounted in the hole.
Bending the product at right angles: 1. On an anvil. 2. On a shaped mandrel. 3. On the bracket. 4. On a ledge. 5. On the fork. 6. On a plate with removable pins.
To ensure that the resulting hole in the workpiece has the shape of a square, the lower part of the lining is used to hold the square during impact. To form a hole with a large cross-section, an anvil horn is used: the product is cut through, spread with the largest mandrel, the heated one is placed on the anvil horn and forged with a handbrake.
When forming holes, a cleaver can be used, the blade of which will not be straight, but curved.
Forgings are bent to give the product a curved shape. Bending thick layers of metal implies curvature of the original shape and cross-sectional size in the bending area, whereas when bending thin workpieces this can be neglected. To eliminate shrinkage and distortion of the shape, you need to settle the work area before starting bending. The smaller the radius of curvature and the larger the bend angle, the more the workpiece will tighten. The shrinkage cannot be eliminated by straightening, but the original cross-sectional shape can be returned by ironing and straightening.
There are several types of forging bending:
Bending the product along the radius: 1. On the anvil horn.
2. In the device. 3. In the fork. 4. In a fork (with a hammer). 5.On the radius insert. 6. On a spiral with a raised central part. 7. On a mandrel. 8. On a wedge. Bending at right angles with no rounding radius; performed in a vice. The heated metal is bent on the anvil, clamped with a yew, and then struck at the end of the workpiece. In the area of the bend, there is a sedimentation of material (compaction), a supply of which will be needed to straighten the bend.- Bending with an angle. It is carried out on the edge of the anvil with a heated bend area. The metal is mounted in such a way that the bending edge expected on it corresponds to the front edge of the anvil, after which it is pressed from above with a sledgehammer. They hit the handbrake not on the back of the product, but closer to the rib.
The twisting operation is intended to rotate one piece of the workpiece relative to another around one axis.
There are two possible ways of twisting:
- A fragment of the product is twisted at an angle of up to 180 degrees. The operation is performed on the anvil horn on a shperak using a handbrake. If the workpieces are small in size, use pliers.
- A fragment of the workpiece is twisted several times 360 degrees. Relatively thin products are twisted by a pair of blacksmiths: they rotate the workpiece in opposite directions, grasping it at both ends with pliers. A wrench and a vice are used to tighten thick products. It is convenient to use a fork to fix wide forging strips.
During the twisting process, the metal must be heated to a bright red heat temperature, otherwise the operation will require much more effort from the master, and the product itself may become deformed.
Advantages and disadvantages of hot forging
The hot forging method does not involve the production of similar products. Since this labor-intensive work requires significant human resources, unique artistic compositions are not cheap.
Table 2. Advantages and disadvantages of hot forging
| Advantages of hot forging | Disadvantages of hot forging |
| Product exclusivity: there are no absolutely identical products | Low production speed |
| Wide range: it is limited only by the imagination of the blacksmith and the customer | High labor costs |
| It is possible to produce a product of any design complexity | Low accuracy when maintaining size |
| There are no strict requirements for the selection of source material | Impossibility of mass production |
| After hot forging, the metal is strengthened | High price |
| Hot-processed metal is slightly susceptible to corrosion and oxidation | |
| Hot forging products have a high prestige |
Hot forging technology may involve the use of equipment such as a machine, steam or hydraulic hammer. But the main work is still done by hand.