Types of disks
To work with wood, it is not enough to purchase a good electric tool with one cutting wheel. This widely demanded material comes in many varieties. And each of them has its own hardness and elasticity.
In addition, in the process of work, tasks of varying complexity arise. And solving them requires an individual approach. That is, the use of a specific attachment suitable for the highest quality processing. Therefore, the master’s arsenal must be equipped for all occasions.
The circular saw blade for wood is available in only two types. The monolithic structure consists entirely of either high-carbon steel or high-speed steel. An inexpensive product that can handle any wood. In addition, it can cut polymer alloys.
A good advantage of a cast disc is its ease of sharpening. Moreover, it can be done repeatedly and independently. Because of this, the tool has a very long service life.
Set of cast saw blades Source prom.st
The carbide structure is made of tool steel. But its teeth are made of very strong alloys, to which tungsten carbide is added. This solution allows you to saw not only the most capricious wood, but also process many metals.
In addition, the design with hard solders has a number of advantages compared to the monolithic one:
- The disc does not require tooth alignment.
- One sharpening of the cutters allows you to work out the time during which the monolithic analogue will be sharpened several times. Therefore, the service life of a carbide disc is several times longer.
- It cuts through any material with literally a perfect clean cut and takes less time.
But sharpening a carbide blade for a circular saw cannot be done at home. This requires special equipment. And the price for such an instrument is very high. True, experts say that the disc manages to pay for itself even before re-sharpening. And many craftsmen do not spend money on it, but immediately buy a new cutting wheel.
Disc with carbide cutters Source s-bol.com
In addition to the main two types of disks for circular saws, mention should be made of disk cutters. The tool was developed for metal processing, but many wood operations are performed with its help. For example, a milling cutter is used when you need to select a groove in a wooden product.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in redevelopment of country houses of any complexity
Wood sawing tools
The following saws are used for sawing: bow saws (wooden and yoke), hacksaws, award saws, universal saws, circular saws and jigsaws.
Wood bow saws
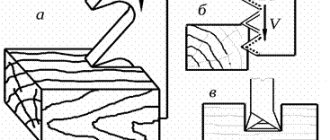
(Fig. 1.6,
a)
consist of a wooden machine (beam) and a blade with teeth. The wooden machine is equipped with two stands, a spacer, a screw and handles. The saw blade is tensioned using a bowstring made of string or wire.
Bow yoke saws
(Fig. 1.6,
b)
are recommended for cross-cutting thick boards and beams. The saw is a frame (arc) made of a metal pipe with a saw blade stretched in it.
Hacksaws
There are wide ones (Fig. 1.7,
a)
for sawing wide boards and slabs across the grain;
wide with a butt (Fig. 1.7, b)
for filing down tenons and eyes;
narrow (Fig. 1.7, c)
for sawing thin materials and cutting curved workpieces.
Award
(Fig. 1.7,
d)
is used for sawing narrow grooves for dowels on panels and boards.
Universal saw
(Fig. 1.7,
e
) is a hacksaw with replaceable blades for performing carpentry and various repair work on wood.
Depending on the type of component blade, hacksaw saws are used for transverse (Fig. 1.7, h
) and longitudinal (Fig. 1.7,
f)
sawing, figured cuts (Fig. 1.7, g), with a back for making tenon joints (Fig. 1.7 ,
And).
The base (main part) of the saw is the handle to which the saws are attached. This saw is currently the most widely used.
Circular saws and jigsaws
used for sawing curved parts.
The shape of the teeth of the saws considered for transverse, longitudinal and universal sawing is shown in Fig. 1.8.
Preparing hand saws for work
The preparation of saws for work includes the following operations: checking the quality of the tool, sharpening, planing and setting saw teeth.
Saw quality check
includes an assessment of their technical condition - the strength and integrity of the handles, the reliability of the blades and their fastening, the sharpness of the teeth and the quality of the setting. The effort spent on sawing largely depends on the quality of sharpening and the correct alignment of the saw teeth.
During the sawing process, the saw teeth become dull and must be sharpened to restore their cutting ability.
Hand saws are usually sharpened with triangular or diamond files.
The teeth of saws for cross-cutting wood have an oblique sharpening; they are sharpened at an angle of 60...70° to the saw blade (Fig. 1.9, a).
These saws have teeth that are sharpened one at a time and, when sharpening, the metal is removed from the beveled surface of the tooth. Having sharpened the teeth on one side, turn the saw towards you with the other side and, having secured it in a vice, sharpen the remaining teeth at the same angle.
The teeth of saws for longitudinal sawing are straight sharpened, so they are sharpened on one side at an angle of 90° to the saw blade (Fig. 1.9, b).
The teeth of rip saws, in which the angle between the front and rear edges of adjacent teeth is less than 60°, are sharpened with a diamond file.
The teeth of saws for universal sawing are sharpened with a triangular file using direct sharpening, removing metal simultaneously from the front and rear surfaces of the teeth (Fig. 1.9, c).
When sharpening teeth, for each working pass of the file, you need to remove a layer of metal of the same thickness. To do this, the file pressure must be uniform and only when moving forward. You need to move the file in the opposite direction freely, without pressure, tearing it off or without tearing it off the surface to be sharpened. The final finishing is done with a finely cut (velvet) file. After filing, the burrs from the side edges of the teeth are removed with a wet whetstone. For ease of sharpening, the saw blade is clamped in a wooden vice of various designs.
To prevent the protrusion of individual saw teeth and straighten their position along one line, they resort to jointing
a whetstone or a triangular file. If the deviations of the tops of the saw teeth from a straight line are significant, then all the teeth are planed with a file inserted into a wooden block (Fig. 1.10). The saw blade must be secured in a wooden vice. The saw teeth are planed with a file before sharpening or, as a rule, after setting.
During the sawing process, the saw blade rubs against the walls of the material being cut and is clamped in the cut. To avoid this, the teeth must be set apart.
Saw tooth alignment
consists in the fact that they are alternately bent in one direction (even teeth), then in the other (odd) direction. When setting, the tooth is bent not entirely in height, but halfway. When sawing hardwood, the teeth are set apart by 0.25...0.5 mm per side, and softwood - by 0.5...0.7 mm. The total tooth set should not be greater than the thickness of the blade.
When setting teeth, it is important to ensure that the teeth bend equally on each side. If this condition is not met, the cutting quality will decrease. The teeth are set manually using settings of various designs - from simple to universal (Fig. 1.11). The saw blade is tightly clamped in a vice, and then the teeth are bent alternately, in one direction or the other. You need to spread the saw teeth evenly with a simple set, without much effort, otherwise the tooth can be broken. In addition to the simple setting, a universal setting is used, which makes it possible to obtain the correct amount of saw tooth set. The amount of tooth set is checked with a template. You can move the teeth before and after sharpening, depending on their wear. If the saw is significantly distorted, it is better to first loosen and then sharpen the saw.
Important characteristics of the cutting wheel
Let's figure out how to choose a blade for a circular saw on wood, guided by the basic parameters of the tool. After all, it is from them that you can understand whether the nozzle is suitable for performing a certain task. And knowing even small nuances, you can significantly improve the quality of work.
Disc thickness
Determines how wide the cut will be. This parameter also indicates the strength of the cutting disc. The standard value is 3.2 mm. If you use a nozzle thinner than this indicator, then there is a high probability of it overheating and failure. And too large a size leads to increased consumption of processed material. As the masters say, “translation into shavings.”
Carbide disc with combined cutters Source ebayimg.com
External and internal diameter
The dimensions of the circular saw blade for wood determine how deep you can go into the material being processed. But when purchasing, you must take into account the internal diameter of the protective casing. Otherwise, it will be impossible to install a cutting wheel that is too large on the circular saw.
Mostly sizes range from 130 to 250 mm. But, if the casing allows, then you can find a disk with a larger outer diameter. However, these numbers do not affect the processing speed. The depth of penetration into the material is important. But the thicker the cut, the more the disc will heat up.
You also need to take into account the thickness of the power shaft on the circular. So that the internal hole of the cutting wheel allows it to fit tightly on the tool. The rods on the circular are installed with a diameter of 16 to 32 mm. And some models of discs have additional holes for secure fixation on the saw.
saw teeth
The number of teeth on the saw blade determines how clean the cut will be. Their number varies from 10 to 90. And the highest quality of cut can be obtained with the maximum number of cutters. Also in this case it will be easy to work in the transverse direction. And for longitudinal cuts it is better to use a disk with a small number of teeth.
Special machine for sharpening circular saws Source prom.st
How to set up hand saws
If the blades are processed incorrectly, the saw will clamp and jam in the cut, thereby making it more difficult to saw and reducing the quality of the work and the material being cut.
To prevent this from happening and to prevent the file from getting clamped, the teeth are thinned. The teeth are moved in different directions in a checkerboard pattern, and more than half their height should not be exceeded. Otherwise, that is, when fully bent over the entire height, the saw may crack and fail, since the cutting part becomes wider and the cleanliness of the sawing decreases, a lot of waste is generated. In addition, it is difficult to work with a highly set saw. With uneven extension, a lot of inconvenience also arises; teeth bent less than others will not be used, and the workers will quickly grind down.
To set the saw, the saw is clamped with a wooden vice near the base of the teeth. When using an iron vice, several boards are placed under both sides of the panel to protect it from deformation. The process is carried out using pliers or a screwdriver, but it is better to use specialized wiring having various designs. To ensure uniform spacing of the teeth, there are props that work as a support. After setting, the teeth are sharpened.
How to choose the right disc
The selection criteria depend on many important nuances. For example, in order to make a clean cut on wood, a circular saw blade must have certain parameters. But for the correct selection, you first need to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of the wood. And according to its structure, look for the required cutting wheel in your inventory.
First you need to comprehend the upcoming task. That is, what kind of cut needs to be made - longitudinal or transverse. Then the thickness of the wooden blank and its structure are assessed. After all, each type of wood will require its own disk rotation speed.
Optimal speed of sawing tool:
- soft wood - from 50 to 90 m/s;
- hard rocks - from 50 to 80 m/s;
- exotic type of tree - from 80 to 85 m/s;
- joinery wood and chipboard - from 60 to 80 m/s;
- MDF – from 30 to 60 m/s;
- laminate – from 40 to 60 m/s.
After this, you can search your inventory for a suitable cutting wheel. And tool marking helps a lot with this. The disk contains all the necessary information. And a reliable and consumer-respecting manufacturer will definitely apply it using a laser in the form of pictograms.
Laser pictograms on the saw blade Source hobbywood.ru
Devices for precise marking
Before processing, it is important to mark the workpiece; the correctness of the calculations determines what the created product will be like. It may seem from the outside that marking is simple, but it is not. Because if you make a mistake even by a fraction of a centimeter in the calculations during aviation modeling, you can sometimes reject the entire structure.
Devices for drawing and creating straight lines:
- Reismas;
- scriber and compass with sharp limbs;
- folding tape measure;
- metal calipers and ruler;
- iron triangle and carpenter's protractor (malka).
Judging by the dimensional set of accessories, the highest accuracy of marking lines for small parts is assumed. Based on this sketch, we will have to cut out full-fledged parts from wood. To do this, you need not only a high-quality hacksaw, but knowledge of such terms as: processing of transverse, longitudinal, oblique, inclined directions in sawing wood. For more precise sawing of small parts, a hacksaw is adapted, working in different directions and is considered a universal assistant. The hacksaw must always be in good condition, which requires sharp teeth, straightness, spread and a comfortable handle.
Briefly about the main thing
You can process wood on a circular saw with two types of discs. A simple and inexpensive monolithic one, as well as its analogue with carbide tips. The latter, although much more expensive, is much more effective. And passing it through any material gives a smoother and cleaner cut.
When purchasing a disk for your circular saw, you need to know the dimensions of the working shaft and protective casing. In order not to make a mistake with the choice of the outer and inner diameter of the cutting wheel. You should pay attention to the sharpening of the teeth and their configuration. If you often have to solve complex problems in your work, then these characteristics are very important.
Ratings 0
Features when sawing wood
Before sawing, you need to use the appropriate posture: keep your back straight, legs slightly apart, the tilt should be in the pelvis, resting on your left hand, taking into account a comfortable balance. Sawing is carried out along the intended strip, avoiding the unnecessary part of the workpiece, so as not to reduce the size of the part itself. This requires experience in holding a hacksaw at an angle and tilting and securing the product. During the process, the working hand should not strain and carry out linear movements along the front side of the part.
The beginning of sawing is called sawing. Several test movements are made on the intended strip, if necessary, the position of the saw is adjusted, and watch how the edges of the teeth are positioned. Make sure that the line is not touched; if everything is in order, begin immersing the hacksaw into the material to a depth of two mm, without pressing movements. The saw must choose the optimal cutting depth itself.
There are three types of sawing:
- Horizontal sawing is the process of cutting wood along its grain into beams.
- Vertical sawing is performed perpendicular to the growth of the fibers.
- Crosscut - used crosswise when cutting thin plywood along curved lines.