Methods of protection against metal corrosion are relevant. Because metal is one of the most popular materials used in the automotive industry. And although it has been successfully replaced in some areas, the main problem associated with the use of metal products is corrosion. Types and methods of protecting metal corrosion differ from each other.
Corrosion, destruction of metal as a result of electrochemical action. This is the dissolution of an electrolyte or chemical action in a moisture-containing or airy environment, as a result of which metals combine with chemical elements located in an airy or aqueous environment. Rust is the corrosion of iron and its alloys; the corrosion of other metals comes down to oxidation, the formation of oxides. Chemical corrosion occurs as a result of exposure to dry gases and liquids that react chemically with the metal.
Types of metal corrosion:
- processes are chemical and electrochemical
-by the nature of destruction, uniform and not uniform
- by type of corrosive environment: gas, liquid, atmospheric, soil
Chemical corrosion
Based on the reaction between metal and an aggressive environment. The result of this corrosion is the formation of scale on the metal, or in the case of copper, a green coating. This type of corrosion spreads evenly over the entire surface of the metal. Chemical corrosion does not affect metal as strongly as electrochemical corrosion.
Electrochemical corrosion
This is a process in which metals and alloys lose some of their electrons, they pass into an electrolytic solution formed on the surface of the metal in the form of ions, and the electrons replacing the metal atoms pass into the metal with a negative charge, a galvanic reaction is formed, resulting in the destruction of the metal . Metals used in construction are usually subject to electrochemical corrosion due to the presence of moisture on the surface of the metal, this is caused by a constant change in temperature, resulting in the formation of condensation.
Atmospheric corrosion
Atmospheric corrosion of metal is similar to the occurrence of electrochemical corrosion, due to the presence of air humidity. When humidity rises above 70 percent, intense loss of steel occurs. The corrosion process is also affected by the presence of aggressive elements in the environment such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide,
uniform across the surface , but it does not pose a great danger if it does not reach critical levels of metal damage. Uneven is the most dangerous because it can form separate areas of damage to the metal, which will lead to a significant weakening of the elements of the metal structure.
It is impossible to completely avoid corrosion processes, but it is possible to reduce the impact of these processes.
There are several types of corrosion control measures.
Types and causes of corrosion on metal products
When taking measures to protect metal products from corrosion, you need to know what exactly it is. The following types of corrosion exist:
- Liquid. Forms on metal surfaces in contact with a damp environment. As for seawater, the oxidation process occurs much faster in it due to the increased concentration of salt in the liquid.
- Soil. This type is typical for metal structures that interact with the ground for a long time. When exposed to chemical elements contained in groundwater, soil or various leaks, irreversible chemical processes are triggered.
- Atmospheric. The main cause of oxidation is the interaction of the metal with water vapor and oxygen contained in the air. If the air is saturated with contaminants of chemically active substances, then rust appears faster.
The manifestation of corrosion on metal structures can be expressed as:
- the formation of a continuous layer of rust or individual areas of surfaces;
- the appearance of deep cracks;
- small affected areas directed towards the inside of the product;
- oxidation of one of the alloy components;
- deep distribution throughout the entire volume;
- several signs at once.
One of two reasons for the development of such a process may be:
- Chemical interaction - when a metal begins to deteriorate due to a chemical reaction with active components.
- Electrochemical nature, due to the fact that upon contact with electrolytic solutions, electric currents are generated, under the influence of which electrons are replaced in the metal. This leads to destruction of the crystal lattice and the formation of rust.
Methods of protection against metal corrosion
Methods of protection against metal corrosion are divided into technological, active and passive.
Active methods
Methods of protection against corrosion of metals involve constant exposure to the metal, these include methods of changing the corrosive environment. This is a decrease in soil acidity, a decrease in chlorine content in water. Protective protection also belongs to the active method; it consists of binding the metal to a contact material that is more susceptible to oxidation, it is called a protector and is essentially a lightning rod. Takes over electrolysis processes that affect metal rusting.
Technological techniques
This is when, during the production of metal, chromium, titanium, manganese, and nickel are added to the steel alloy, which help to obtain steel with anti-corrosion properties. For example, when chromium is added, a high-density oxide film is formed on the metal surface.
Passive methods
The metal is insulated using various coatings that prevent the formation of corrosion. Cathodic and anodic coatings are used.
Anodic coating
When applying anodic coating, a metal is coated with another metal with a large negative potential. This is usually zinc or cadmium. Currently, it is common to protect metal by applying a layer of zinc.
Cathodic coating
produced by metals with a more positive potential. When cathodic coating of metal, mechanical protection of the metal is observed. Tin-copper is used as a cathode coating. nickel. To coat metal, the hot method, spraying, metallization, galvanization are used. With the hot method, steel is placed in molten metal, which is coated with a thin layer. The hot method is used for tinning, coating metal with tin, and galvanizing.
Oxidation
Chemical methods of coating the metal are also used, this is oxidation, an oxide film is formed that protects the metal from corrosion, this process is also called steel bluing. You can also treat steel with anodization, which is the electrolysis of aluminum. Also through phosphating and nitriding.
Application of enamels and primers
The most accessible method of protecting metal is the use of special enamels and primers.
They provide barrier protection from the effects of harmful environmental factors; it consists of mechanical protection of the surface. Damage to the coating occurs when microcracks form, resulting in under-film corrosion. To prevent this, passivation of the metal surface is carried out using special paint and varnish coatings.
The composition includes special chemical agents. Such paint and varnish coatings include primers and enamels containing phosphoric acid and other inhibitory elements that slow down the corrosion process. More effective paint and varnish materials are those that provide protective protection. This is achieved by adding metals that create donor electron pairs to paint coatings, these include zinc, magnesium and aluminum.
To protect metal structures that are operated in an industrial atmosphere, special enamels are being developed that form moisture-protecting urethane coatings. To protect against constant contact with an aqueous environment, enamels are produced that can be applied to zinc, copper and other surfaces.
Currently, a wide range of anti-corrosion enamels are available on the market. One of the innovations is the coating of metal with fluoroplastic; it is chemically inert to almost all aggressive environments. Enamels based on it are applied with a brush, air or airless spray, to a cleaned metal surface. When using a particular material, it is necessary to take into account factors such as the type of metal, the conditions of its operation, production capabilities and the feasibility of use.
Corrosion treatment agents are used depending on the type of metal, the operating environment, and the loads acting on it. For each area of operation of the structure, standards are provided. The optimal method is metal processing in a factory. That is, the application of transport primer.
Before he gets to the construction site. The application of anti-corrosion materials provides only 20 percent of metal protection; the main factor influencing the quality protection of metal is its pre-treatment from dirt. rust, as well as any other substances that will interfere with the painting of the surface.
Features of tread protection
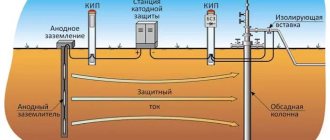
Taking into account the physicochemical features of such protection of metal structures, we can conclude that the use of a protector is inappropriate if the structure is operated in acidic environments. Protective protection is recommended for use if the structure is located in a neutral environment (soil, water, air, etc.).
To protect an iron pipeline, it makes sense to use cadmium, chromium, zinc, magnesium (more active metals) as a protector. But even when using them, there are a number of nuances.
For example, pure magnesium has a high rusting rate, pure zinc dissolves unevenly due to its coarse-grained structure, and aluminum quickly becomes covered with an oxide film. To prevent negative phenomena, alloying components are introduced into the pure substance that will serve as a protector. In fact, the protector is not pure metal, but its alloy with other substances.
Magnesium protection
Magnesium alloys are most often used as protection. The alloying components of the composition are aluminum (maximum 7%), zinc (up to 5%), copper, lead and nickel are also introduced, but their total share does not exceed a hundredth of the composition. As a protector, such compounds can be used in environments with an acidity index of no higher than 10.5.
Even as part of an alloy, magnesium quickly dissolves, and then poorly soluble compounds appear on its top layer. Magnesium alloys have a significant drawback - after application, they can provoke cracking of metal products and contribute to the occurrence of increased hydrogen embrittlement.
Zinc protection
An alternative to magnesium alloy for protecting structures located in salt water are zinc compounds. The alloying components for zinc are cadmium (maximum 0.15%), aluminum (less than 0.5%) and small amounts of iron, lead and copper (total up to 0.005%). Such a protector will be ideal against the influence of sea water, but in neutral environments, zinc alloy protectors will quickly become covered with oxides and hydroxides, nullifying the entire anti-corrosion complex.
Zinc alloys act as protectors against corrosion, providing maximum explosion and fire safety. It is advisable to treat pipelines for flammable and explosive substances, such as gas, with these compounds. Such compositions receive another “point” for their environmental safety - no pollutants are formed during anodic dissolution. Therefore, zinc compositions are often used for corrosion protection of oil pipelines, as well as for oil tankers and ships.
Aluminum compounds are usually used to protect against exposure to running salt water. Zinc (up to 8%), magnesium (up to 5%) and indium with silicon, thallium and cadmium with a small proportion (up to 0.02%) are also introduced into the alloy. Additives prevent the formation of oxides on aluminum. Aluminum alloys are also suitable in environments where magnesium protection is used.
Metal corrosion treatment
Mechanical cleaning of the surface using brushes, scrapers, as well as using power tools with various attachments
Sandblasting is the most effective method for cleaning surfaces, but it has a number of disadvantages, such as low productivity, the creation of dust, which disrupts working conditions at the construction site.
Hydrojet cleaning increases productivity, and the use of abrasive materials improves cleaning quality.
Chemical cleaning . It involves the use of special materials that are divided into washable and indelible.
Rinse-off chemical cleaning methods
Washable materials include a 5% solution of hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, but when using these materials it is necessary to use a substance that slows down the chemical process, the so-called inhibitor. If you do not slow down the chemical reaction, in addition to rust, the metal itself will be destroyed. You can use a 15-30% solution of orthophosphoric acid; as a result of its use, rust turns into a solid structure, which is protection against subsequent corrosion. A mixture of 50 g of lactic acid per 100 ml of petroleum jelly helps well. Acid converts rust into salt, and petroleum jelly dissolves it.
Leave-in chemical cleaning methods
Consider the use of soil converters; rust is converted into soil and does not require further rinsing. If it is not possible to completely get rid of rust, it is necessary to pre-paint the metal using a primer with special anti-corrosion properties. Final surface treatment is carried out using varnishes, paints, and enamels with special properties.
Advantages and disadvantages of tread protection
The advantages of this method are:
- simplicity, autonomy and efficiency due to the absence of a current source and the use of magnesium, aluminum or zinc alloys;
- the possibility of forming single or group installations;
- the possibility of using tread protection both for designed objects and for structures already in operation;
- organization of protection in almost any conditions where it is impossible or impractical to construct current sources;
- if used correctly, the system can operate for a long time without any maintenance;
- safety and possibility of use in explosive objects (due to low voltages).
But this type of rust protection has its drawbacks:
- Limited application of the method in poorly conductive environments.
- Irreversible loss of tread.
- Possibility of contamination of adjacent areas.
Stages of anti-corrosion work
- Preparation of necessary materials.
- Applying a primer to ensure better adhesion of the enamels.
- Application of enamels with protective coating
- Drying the coating or heat treatment.
The most effective method of applying paint and varnish coatings is considered to be the airless spraying method. Since it allows for painting with the highest quality. Existing metal irregularities.
A less effective way is to paint with a brush. It is not advisable to apply paint coatings with a roller.
Basic galvanizing methods
Zinc coating is the best method for protecting iron surfaces from corrosion.
Galvanizing is performed in the following ways:
- Hot galvanizing. Immersion of iron sheets, sections or shaped metal products into molten zinc, the temperature of which is 460-480 degrees. This technology allows you to protect metal from corrosion for a long time, but it is difficult and unsafe to implement. Other disadvantages include: limitation of processing by the size of the baths, the possibility of deformation of thin structures and sheets when heated, damage to the protective layer during welding.
- Cold galvanizing. It is considered the optimal way to protect metal with zinc. It is performed by painting metal surfaces with powdered primer with 96-98% zinc content. The coating is applied with a roller or brush directly at the installation site of the structure (i.e., for anti-corrosion protection, there is no need to transport the product). Cold galvanizing makes it possible to protect iron from rust for 30-50 years; under a layer of zinc primer, the metal corrodes three times slower compared to other processing methods. Other advantages of this technology include cost-effectiveness (compared to hot-dip galvanizing). Disadvantages: difficulty in covering uneven surfaces and internal cavities.
- Gas-thermal method. Application of molten zinc to a metal surface in a gas stream. This technology is suitable for large-sized metal structures that do not fit in a bath of zinc solution. The coating lasts for 25-30 years. The disadvantages of the technology are the unevenness of the resulting coating, which is complemented by the application of paint and varnish.
- Thermal diffusion method. Melting zinc atoms into iron at high temperatures (over 2600 degrees). At this temperature, zinc goes into a gaseous state, after which diffusion of zinc molecules with the metal occurs. Advantages of the method: high class of anti-corrosion protection, preservation of the product configuration, the ability to adjust the thickness of the zinc coating, no need to clean up waste. Disadvantages: heterogeneity of the thickness of the protective film, low productivity and harmfulness of the technological process.
- Galvanic method. Electrolytic galvanizing method, which allows you to apply a thin (5-40 microns) layer of zinc to a degreased metal surface. It consists of placing metal and zinc plates in an electrolytic solution and connecting an electric current. Zinc dissolves in the electrolyte and settles on the iron in the form of a protective layer. It is distinguished by the uniformity and smoothness of the coating layer, including hardware of complex configurations and porous surfaces. Disadvantages: high cost, the need to clean the waste before discharging it into the sewer.
The choice of galvanizing technology depends on the requirements for the technical characteristics of the coating, operating conditions of metal products or structures. If you have questions about how zinc protects metal from corrosion and which galvanizing method is suitable for a particular type of rolled metal, you can get advice from a specialist from our company.
Quality control of work performed
The methods used to protect against metal corrosion are subject to quality control. Performed to verify previously performed production controls. Defect prevention. Development of measures to eliminate detected defects. Quality control of anti-corrosion work begins with checking the documentation. Documentation on the anti-corrosion protection facility, the materials used, and product quality certificates must be provided. Upon completion of the quality control of the work, a report is drawn up containing information about the location of the work, the state of the work performed, the materials of their grade and consumption used. Information about the organization that performed the work, and the signatures of the persons who carried out the work. The commission conducting quality control checks the following parameters:
— type of anti-corrosion coating, there should be no areas that have not been treated.
— the thickness of the coating layer is checked by measuring in various places where poor quality processing is presumably possible.
— the adhesion of the paint and varnish material to the metal surface is controlled.
Violations detected during quality control of work.
After completing the work, rusting occurs on the surface of the treated metal, this is due to the fact that the temperature regime was not observed or the moisture was not completely removed. It is also possible that the metal is not sufficiently cleaned of oxides, which leads to subsequent corrosion. Insufficiently removed various contaminants, oil, soap, salts, all this will lead to damage to the paintwork and further rusting of the metal. The presence of dust on the surface being treated reduces adhesion. Which leads to peeling of the paintwork. Failure to maintain the time allowed for the metal to remain untreated leads to its rusting; interlayer holding must also be observed; the solvent does not have time to dissolve and it leaks through other layers. Which leads to disruption of the coating in the form of bubbling. All these violations identified during quality control must be corrected immediately.