- compressive hardness;
- extensibility;
- tear resistance;
- bending resistance;
- shearing force.
The use of concrete that is resistant to mechanical stress and aggressive environments is the key to the durability and strength of buildings. Therefore, in construction, great importance is attached to testing concrete for strength.
Mechanical methods for studying the performance of concrete mixtures
Table of types of concrete.
The oldest and most popular method for determining the compressive strength of a material is called the standard specimen method. To conduct the study, control samples are made from the concrete mixture, which are cubes with a side length of 20 cm. For testing, the cubes must have a curing period of at least 28 days. Then the finished samples are placed under a press and compressed until they are completely destroyed. The load indicators at which the destruction occurred are recorded, and then with their help the strength of the monolith is calculated.
Non-destructive testing of concrete is carried out using special mechanical devices. In this case, methods are used that determine the properties of the monolith when exposed to certain tools. Instrument readings are taken into account during such manipulations as chipping, tearing, plastic deformation and some others.
Methods for testing concrete using Fizdel and Kashkarov hammers
The principle of operation of the testing mechanisms is based on the depth of penetration of the device into the thickness of the surface layer of a concrete monolith. As an example, consider the Fizdel hammer, which, when struck, leaves holes on the surface of the material. The diameters of the holes determine the strength characteristics of concrete.
The device of the Kashkarov hammer.
Then 10-12 medium-sized blows are carried out on the surface of the area selected for testing. Hammer marks should be at least 3 cm apart from each other.
After this, using a caliper and a special ruler, the diameters of the holes are measured. Each measurement is made with an accuracy of tenths of a millimeter, first in one direction of the hole, then in a strictly perpendicular direction. Based on the information obtained and data on the diameter of the imprints of laboratory samples, taken as a standard, a calibration curve is drawn up, which makes it possible to determine the compressive strength of concrete.
In addition, you can determine the strength characteristics of a monolith using a Kashkarov hammer. The operating principle of this tool, like the Fizdel hammer, is based on the properties of plastic deformation. Structurally, the Kashkarov hammer is a device into which, in addition to the working element, a control rod is also inserted. Due to this, the device leaves not a single, but a double print. One is located on the surface of the object under study, and the other is on the control rod. Analysis of the imprints and left hole diameters makes it possible to calculate the compressive strength of concrete.
Studying the properties of concrete using a sclerometer and pistols
Concrete strength ratio table.
Tools that are used to determine the strength characteristics of a concrete monolith based on the properties of elastic rebound are equipped with a rod striker, or striker. Examples of such instruments are Borovoy and TsNIISK pistols, KM sclerometer and Schmidt hammer.
Research determines the magnitude of the rebound force of the striker, which during testing is reflected on the scale of the mechanism. As a rule, the spring energy force should have a constant value during experiment.
The rod striker is released independently when the tool comes into contact with the surface. The KM sclerometer has a built-in firing pin that has a certain mass value. Using a spring with a specified stiffness, a strike is made on a metal striker pressed against the surface being tested.
Methods for monitoring the strength of concrete, based on the indicators of separation with spalling, make it possible to determine the characteristics of the monolith not on the surface, but in the body of the element. For research, areas without metal reinforcement are used.
Methods for establishing the strength of concrete.
Special anchors are installed into the thickness of the concrete, with the help of which the strength characteristics of the concrete are then examined in a non-destructive way.
To date, the described methods of non-destructive testing of concrete strength are considered the most accurate, since they use for calculations a dependence in which only 2 parameters can change: the size of the concrete mortar filler fractions and its type. At the same time, the disadvantages of non-destructive testing of concrete strength are its high labor intensity combined with the impossibility of using these methods with high reinforcement of the material. In addition, during testing, partial damage to the surface of the monolith under study occurs.
Where can I buy?
You can buy a Kashkarov hammer in one of the specialized stores that sell various measuring instruments. You can also order it in an online store of a similar nature. The cost of this device is from 2500 rubles. In addition to the tool, you will need to purchase standard rods, a set of ten pieces of which will cost you 2,000 rubles.
See the video below for more information about Kashkarov’s hammers.
Determining the quality of finished concrete products often involves measuring their strength. Unfortunately, unlike metals, concrete is not a homogeneous structure, and it is also quite fragile. Therefore, direct measurements of the mechanical characteristics of this material either require special laboratory studies or are characterized by a large error, reaching 70...75%. A reasonable compromise for non-destructive quality control of concrete is the use of a Kashkarov hammer.
How to choose a hammer?
A hammer can perform not just one function, but several at once:
- Driving in nails or other fasteners (dowels, slate nails).
- Removing mortar from walls and splitting bricks.
- Editing sheet metal.
- Working with tiles and parquet.
For instrumental work, hammers weighing from 50 to 300 grams are used. For metalwork work, samples weighing 400 - 500 grams are suitable. A tool weighing 600 - 800 grams is used for repair work. Sledgehammers weighing 4-16 kg are indispensable when carrying out dismantling work.
Before purchasing a hammer, you should check it thoroughly. A high-quality instrument should not leave any marks after hitting metal. The fastening of the components must be strong, without backlash.
Typically, hardwoods (birch, beech, oak, rowan, maple, yew) are used to make handles. The wood must be smooth, with a texture that allows you to comfortably hold the instrument in your hands. A high-quality wooden handle should not have cracks.
The reinforced plastic handle is more durable than the others, and does not allow the working part to loosen. A durable all-metal hammer should have a rubber-coated handle. This dampens vibrations from impacts and prevents accidental electric shock.
This is interesting: Priming walls for wallpaper: high-quality finishing
How much does a Schmidt hammer cost?
The cost of a hammer depends on:
- appointments;
- equipment and functionality;
- type;
- degree of innovation.
An electronic unit costs from 31,000 to 58,000 rubles. Its mechanical analogue is approximately 3 times cheaper (from 13,000 to 30,000 rubles).
The Schmidt hammer can be replaced with other tools that can perform the same functions. For example, it will be possible to test the strength by penetrating into the thickness of a concrete sample using Fizdel and Kashkarov hammers.
Popular categories:
Equipment
Construction is a rather labor-intensive process. To eliminate unnecessary costs and not waste time, you should take good care of the quality of materials. First of all, you need to think about how to check the brand of concrete mix.
The ordered solution does not always correspond to the characteristics specified in the document. If the added raw materials for making concrete do not meet the proper proportions, the quality of the solution automatically changes. To accurately recognize the brand, it is necessary to conduct a quality assessment.
Average price on the market
The most expensive are the original Proceq SA products: on average from 75-140 thousand rubles.
Domestic brands can be purchased at reasonable prices:
- OMSh-1 can be found even for 11 thousand, and on average it costs about 15 thousand;
- electronic OMSh-1E is already about 40 thousand;
- RGK: about 16 thousand;
- MSh series: from 20 thousand.
If you intend to buy an elite sclerometer from Proceq SA, you might want to consider purchasing an ultrasonic hardness tester, since its price will be even lower than most copies from this Swiss manufacturer. If you take products from regular brands, then, of course, they are much cheaper.
How to conduct research correctly?
Each Kashkarov hammer is sold complete with instructions for use, which clearly describe how to correctly use this measuring tool. To test the strength of concrete using a Kashkarov hammer, you need to select a section of a concrete object measuring 10x10 cm. It must be smooth, without grooves or bumps, and there must be no visible pores. The distance from the edge of the product should be more than 5 cm.
You need to take a Kashkarov hammer and insert a standard rod into the corresponding groove with the sharp end inward. A clean piece of paper and a piece of carbon paper should be placed on the selected area of concrete. Then you need to hit the workpiece with a hammer, as described above. After each blow, move the standard to a new area and replace the sheet of paper. The next blow should fall on a new place (at a distance from the previous one of more than 3 cm).
The next step is to measure the prints. If the difference in the obtained values is more than 12%, all studies should be repeated again. Based on the obtained indicators, the class of concrete is determined, and the smallest of the resulting indicators is selected.
Low air temperatures have virtually no effect on the results of the study. Therefore, this measuring instrument can be used at ambient temperatures down to -20 degrees. However, the temperature indicators of concrete and reference rods must be the same. This means that before testing carried out in the cold, the reference rods must be left outside for at least 12 hours.
Advantages and disadvantages
Kashkarov's hammer has both pros and cons. The advantages of using this tool include, first of all, the ease of measurement. Even a beginner in construction can cope with such research.
For testing, it is not necessary to destroy the sample, that is, the study can be carried out directly on the finished product. This is especially important if the research items are large. Another advantage is the cost of the device. Such a tool can be purchased for everyday use, for example, when building a monolithic house for yourself.
But Kashkarov’s hammer also has significant disadvantages. The error of the device ranges from 12 to 20 percent, which is quite a lot. Modern electric sclerometers provide more accurate results. The strength of concrete is determined only in the surface layers (1 cm deep). As is known, these layers are often subject to destruction due to carbonization. In addition, the device is practically insensitive to the strength of coarse aggregate and its grain composition.
Characteristics, types and purpose of the tool
Hammers vary in shape, weight and material. Summarized data on tool modifications are presented in the following table:
| Name | Dimensions | Average weight | Application |
| Hammer | The height of the hammer in mm depends on the weight of the hammer and ranges from 1830 mm to 3500 mm | From 0.5 kg to 9 kg, in large forges - from 40 to 100 kg, in steel and iron factories up to 50 tons | For striking when breaking stones, forging metals |
| Locksmith's hammer | Standard design | 300-500 g – for home and household use, more massive – 2 kg | Working with metal products, striking a chopping tool or hitting a core |
| Carpenter's hammer | Handle length – from 20-30 cm | 250-450 gr | For driving or removing nails in carpentry or carpentry |
| Mallet (wooden hammer) | 130×90×60 mm | 300 gr | Assembly, dismantling, molding of materials and structures |
| Sledgehammer | Volumetric tool | From 3 to 15 kg | Dismantling and installation work (breaking walls, driving posts and pipes into the ground) |
| Fizdel's Hammer | The impact part of the hammer ends with a steel ball Ø17.5 mm | 250 gr | Testing the strength of concrete |
| Kashkarov's hammer | 253×40×53 mm | 1.5 kg | Testing the compressive strength of concrete using the impact method |
| rock hammer | 290 mm | 600 gr | In rock climbing, mountaineering, speleology, for setting and removing rock pitons, processing the edges of rock ledges, punching bolt holes |
| Jackhammer | Average shank size Ø 24 mm, length 70 mm | From 3 to 30 kg | Cutting down openings and niches in walls, dismantling brick and concrete permanent structures, destroying frozen or heavy soil, removing old road surfaces |
| Roofing hammers | 300×120×50 mm | 0.6 - 0.75 kg | For roofing work, leveling and sealing seams |
Schmidt hammer: operating principle and instructions for use
To test the strength of concrete, the Schmidt hammer, invented in 1948 in Switzerland, is used as a non-destructive testing tool. Engineer E. Schmidt equipped his invention with the ability to accurately detect the mechanical strength of concrete:
- compressive hardness;
- extensibility;
- tear resistance;
- bending resistance;
- shearing force.
The use of concrete that is resistant to mechanical stress and aggressive environments is the key to the durability and strength of buildings. Therefore, in construction, great importance is attached to testing concrete for strength.
Methods for testing the strength of concrete
At the moment, there are two main methods for determining the strength of concrete: using destructive or non-destructive testing. Mechanical non-destructive testing methods are based on the relationship of concrete strength with other mechanical properties, such as shearing force, peel strength and compressive hardness. Depending on the type of property being assessed, the following non-destructive testing methods are often used:
- separation;
- plastic deformation;
- rib chip;
- elastic rebound.
The choice of testing method depends on the size and shape of the products, the purpose of the activities being carried out, the requirements for the accuracy of the results obtained and the degree of convenience of testing. In world practice, the most widely used device for determining strength characteristics is the Schmidt hammer. In our country it is often called a sclerometer, which translated from Greek means “hardness meter” .
The Schmidt hammer was developed in 1948 by Swiss engineer Ernst Schmidt. It was Schmidt's hammer that first made it possible to measure the strength of concrete structures at the construction site.
Peculiarities
Each type of device has its own characteristic features.
For ultrasonic models this is:
- ability to exchange data with a computer;
- convenient control and configuration of the device using buttons and an interface;
- switching off during a long break in use;
- memory for saving measurements;
- voicing the work process;
- automatic wave change;
- ability to search for defects and cracks.
Distinctive features of electronic models are:
- ability to record measurements;
- the ability to transfer indicators to a PC;
- measured data sorting function;
- changing the direction of impact.
The specificity of mechanical models is as follows:
- possibility of working at a temperature of – 40°;
- low cost;
- high error;
- heavy weight.
Design and principle of operation
The designs of most sclerometers consist of the following elements:
- impact type plunger, indenter;
- frame;
- sliders that are equipped with rods for direction;
- cone at the base;
- stop buttons;
- rods, which ensures the direction of the hammer’s functioning;
- caps;
- connector rings;
- back cover of the device;
- spring with compressive properties;
- protective structural elements;
- strikers with a certain weight;
- springs with locking properties;
- spring impact elements;
- a bushing that directs the functioning of the sclerometer;
- felt rings;
- scale indicators;
- screws that carry out the coupling process;
- control nuts;
- pins;
- safety springs.
The functioning of the sclerometer is based on a rebound, characterized by elasticity, which is formed when measuring the impact impulse that occurs in structures when they are loaded. The device of the meter is made in such a way that after impacting the concrete, the spring system gives the striker the opportunity to make a free rebound. A graduated scale mounted on the device calculates the desired indicator.
What does a sclerometer consist of?
The term "sclerometer" means "hardness meter". Structurally, the device consists of 22 elements. In addition to the indenter (impact plunger) and housing, the device includes:
- body cone;
- guide rods with slider;
- a button that performs the function of a corkscrew;
- striker with a given mass;
- guides the movement of the indenter; the striker rod;
- washer for fixing the striker;
- cap;
- back cover of the sclerometer;
- felt ring.
Some models are equipped with a fuse and a control nut, as well as 4 springs (compression, impact, safety, fixing). A coupling screw, a pin, a Schmidt scale, and a display are required.
Characteristics of modern models and selection tips
Any modern model of a strength meter for solid materials facilitates processes in all areas of construction work. Using a small device, you can easily carry out quality control even on brickwork without serious damage.
The main characteristics of all types of sclerometers include several parameters.
- Measurement error. The biggest error is with mechanical models. It is usually not indicated, but often reaches 20%. Mechanical models also have the highest frequency of breakdowns. For electronic equipment this figure is 5%, and the lowest for ultrasonic equipment: 1%.
- Working strength range. For mechanical devices it is 60 MPa, for electronic devices it is 100. For ultrasonic devices, the interval varies in time and speed.
- Comfort of use. A mechanical device is less convenient to use due to the lack of storage of results and large weight (1 kg).
- Price. In this indicator, the opposite is true: the most expensive is the ultrasonic device.
It is best to purchase the latest models from popular manufacturers of measuring instruments. The top companies producing quality products include the Interpribor company with devices of the Onyx series, the Condtrol company with products of the same name, as well as the companies Schmidt Hammer and RGK.
For a review of the IPS-MG4 sclerometer, see below.
Why and when is control exercised?
Let's consider this topic in more detail. Knowledge of the issue can be useful not only to specialists, but also to ordinary people who build on their own plots with their own hands.
Without controlling the quality of concrete used for construction, you cannot be sure that the dam is reliable
Of course, when pouring a concrete path near the house, there is no need to check the quality and strength. But, for example, if during the construction of a summer house you used a purchased concrete mixture, and then the house shrinks, or cracks appear along the foundation, one of the reasons may be poor-quality concrete.
Once you are sure of this, you can recover money for repairs from the supplier. To do this, you need to know what concrete testing is to determine strength and how it is carried out.
What are the guidelines for assessing strength?
This interstate standard is used to guide concrete quality control.
The quality of concrete is checked both by construction supervision authorities and by the manufacturers themselves (construction organizations). For this purpose, there is GOST - quality control of concrete is carried out in accordance with its requirements. Document number: 18105-2010. The full document is called “Concrete.
Rules for monitoring and assessing strength." It is interstate and operates on the territory of the entire commonwealth, including Ukraine, which recently left the CIS. Let us consider the requirements of this document in more detail, but without delving too deeply into the terms. It defines methods and schemes for laboratory testing of concrete.
When is control carried out?
Concrete is tested when it reaches design strength - that is, usually 28 days from the moment the mixture is prepared.
- But for prefabricated and prefabricated monolithic structures, tests are also carried out upon delivery or acceptance of products (called incoming concrete inspection).
- Indeed, often at the time of transfer the stone has not yet acquired the necessary characteristics. This is the so-called transfer strength.
- For monolithic buildings, control can also be carried out at the time of removing the formwork or loading the structure - this strength is called intermediate.
- Moreover, if, when checking at an earlier date, it is determined that the material has gained more than 90 percent of the design strength, then it is allowed to no longer carry out assessments. At the same time, the product or structure is considered to be of high quality.
- Also, the quality of concrete is determined during various examinations in order to determine the cause of damage or destruction of buildings and structures.
Sclerometer and its types
According to the principle of operation, measuring instruments are divided into mechanical and ultrasonic devices.
- The mechanical instrument has a cylindrical body with an internal impact mechanism consisting of a scale with an indicator arrow and repelling springs. Such a device is designed to determine the compressive strength of a concrete layer in the range from 5 to 50 MPa, and is widely used for examining concrete or reinforced concrete structures.
- Depending on the model, an electronic device may have an external or built-in electronic unit. The obtained measurements are shown on the display and remain in memory for a certain period. In addition, the instrument is equipped with a keyboard and connectors for connecting to a computer. Measurements are diagnosed in the range from 5 to 120 MPa with a methodological error of up to 5%, signals are supplied with an error of up to 0.2%. The results memory limit is designed to store up to 1000 versions over a 100-day period.
You can compare two types of sclerometers using photos posted on the Internet. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the Hilti electric jackhammer and Makita rotary hammer.
The operating principle of the mechanical device is elastic rebound. The impact force is normalized by the energy of the striker and is measured in conventional units on the instrument scale. The impact is carried out on a concrete or other hard surface, as a result of which the rebound height of the striker (H) is determined, which gives an indirect characteristic of the compressive strength of concrete.
The operating principle of the electronic tool is the shock-pulse method in accordance with GOST 22690-88. The signals arrive at the sensor, where they are subjected to statistical processing and pulse rejection. Varieties of concrete trowels are here.
The scope of application of the sclerometer covers the construction sector, where such an instrument monitors the condition of buildings and structures, tests the strength of concrete, mortars and other composite materials in erected structures and individual elements.
READ MORE: Lobelia description of varieties, growing seedlings from seeds, care features, application in garden landscape design
An inspection of an object in this direction is carried out approximately once a year.
You can familiarize yourself with the diagram of the sclerometer in the user manual, which is included with the instrument when you purchase it.
The price of the instrument varies greatly, so everyone can choose the most affordable device for themselves:
- Mechanical devices cost from 13,000 to 30,000 rubles.
- Electronic analogues - from 31,000 to 58,000 rubles.
The presence of a sclerometer makes it possible to determine not only the strength of concrete surfaces over a large area, but also narrow joints in brickwork. Mechanical and electronic devices carry out control without the slightest destruction. Read information about the universal grinding machine here.
Varieties
Based on their operating principle, strength meters for concrete structures are divided into several subtypes.
- Sclerometer with mechanical action. It is equipped with a cylindrical body with an impact mechanism located inside. Moreover, the latter is equipped with an indicator scale with an arrow, as well as a repelling spring. This type of Schmidt hammer has found its application in determining the strength of concrete structures ranging from 5 to 50 MPa. This type of meter is used when working with concrete and reinforced concrete objects.
- Strength meter with ultrasonic action. Its design has a built-in or external unit. The readings can be seen on a special display, which has a memory property and stores data. The Schmidt hammer has the ability to connect to a computer, as it is additionally equipped with connectors. This type of sclerometer works with strength indicators from 5 to 120 MPa. The meter's memory stores up to 1000 versions for 100 days.
The strength of the impact energy has a direct impact on the strength of concrete and reinforced concrete surfaces, so they can be of several types.
- MSh-20. This tool is characterized by the lowest impact force - 196 J. It is able to accurately and accurately determine the strength of cement and brick mortar.
- The RT hammer operates with a value of 200–500 J. The meter is usually used to measure the strength of fresh concrete in screeds made from a mixture of sand and cement. The sclerometer has a pendulum type and can take vertical and horizontal measurements.
- MSh-75 (L) works with impacts of 735 J. The main direction in the use of the Schmidt hammer is to establish the strength of concrete, which is characterized by a thickness of no more than 10 cm, as well as brick.
- MSh-225 (N) is the most powerful type of sclerometer, which operates with an impact force of 2207 J. The instrument is capable of determining the strength of a structure that has a thickness of 7 to 10 cm or more. The device has a measurement range from 10 to 70 MPa. The case is equipped with a table that has 3 graphics.
Operating principle
All tools of this type (including the famous Kashkarov hammer) use the results of plastic deformation of concrete under the influence of impact loads. Due to the spherical shape of the ball, these deformations are localized in a small zone, and therefore they can be considered homogeneous. The diameter of the imprint left by the ball will determine the strength of the concrete.
The Fizdel hammer test must be carried out on areas whose strength determines the strength of the entire structure. The following requirements apply to the selected areas:
- The surface must be flat and smooth, thoroughly cleaned of adhering particles.
- The prepared surface is treated with water until the layer of hardened lime milk is removed.
- The minimum test surface area is 400 cm2; this is enough to repeat the test at least 8...10 times.
- The area selected for testing should not be adjacent to the ends of concrete elements, corners or sharp edges. There should be no pores in the material.
- The distances between the axes of adjacent prints cannot be less than 35...40 mm (for reinforced concrete - 40...45 mm).
The effectiveness of the method depends on the homogeneity of the concrete: in the presence of coarse aggregate – crushed stone with fractions of 30 mm or more – the accuracy of the result will be low.
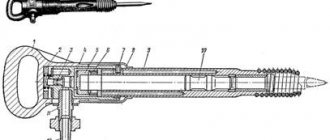
Device and principle of operation
The Kashkarov hammer is a tool for indirectly determining the strength of concrete without destroying or damaging the structure. The assessment is made using the plastic deformation method - based on the size of the print obtained on a reference plate. The technology for obtaining the result complies with the technical requirements of the main regulatory documents - GOST 22690-88, GOST 28570-90, GOST 18105-2010 and GOST 10180-2012.
The compactness of the instrument and the simplicity of the method (with relatively high accuracy and reproducibility of results) predetermined the widespread use of a hammer of Kashkarov's design in comparison with devices of a similar purpose (meaning the Schmidt hammer, Fizdel hammer, etc.).
The Kashkarov hammer consists of the following parts:
- Steel body.
- Rubberized handle.
- Impact hemispherical head (it can be manufactured in the shape of a truncated cone), which has a threaded part.
- Springs with goujon.
- Glass.
- Hardened ball.
- A pointed rod made of steel with a tensile strength of at least 415 MPa, having strictly defined dimensions. Sets of such rods (at least 40) with different mechanical characteristics are usually offered, which expands the scope of application of the device.
- Replaceable metal plate.
The advantage of the design is the independence of the obtained result from the test conditions.
What it is?
The Kashkarov hammer is a measuring device that is capable of determining an indicator indicating the compressive strength of concrete through plastic deformation. Despite the fact that this device gives rather inaccurate indicators, it is often used on construction sites where monolithic work is carried out, as well as in reinforced concrete factories.
The design of the Kashkarov hammer is regulated in GOST 22690-88. It consists of:
- metal body, which guarantees the durability of the instrument;
- handle (metal frame);
- heads (working part of the hammer);
- springs that dampen the impact force from the hammer;
- glasses where the reference rod and ball are placed;
- a reference rod, with the help of which the research is carried out;
- a steel ball that hits the rod;
- rubberized lining that prevents the tool from slipping in the hand.
This design of the hammer makes it possible to almost completely eliminate the influence of the impact force on the concrete sample. In this case, the imprint of the impact remains immediately on both the tested concrete and the reference rod.
Standard bars are made from hot-rolled steel billets from which reinforcement is produced. VstZsp and VstZps are used, which comply with GOST 380. The samples have temporary tensile strength. The rods are tested at the manufacturer's factory.