Photo source pressfoto/freepik
Professions related to wood processing have been valued since ancient times. Which is not surprising, because previously it was the main building material. Nowadays, of course, it has been replaced by much more economical, practical and durable raw materials (reinforced concrete, steel, brick and stone). However, wood still has many uses. It is valued for its environmental friendliness, ease of processing, and aesthetic qualities.
Therefore, carpentry specialists will not disappear anywhere and are unlikely to remain without work in the coming years.
Excursion into history
Wood was one of the first natural materials that people began to use in their everyday lives due to its pliability and accessibility. There is archaeological evidence that the carpenter profession already existed in Ancient Egypt. Initially, the best craftsmen carried out orders from rich and influential people; later their products became publicly available.
The word “joiner” came into the Russian language around the 18th century from Polish, in which stolarz is a derivational tracing from the German tishler (tish means table, and -ler is a suffix indicating the character). Then the craftsmen worked only with furniture, but over time the list of products expanded significantly.
Where do carpenters work?
Carpenter working
on the construction and repair of residential buildings, baths, saunas, beam bridges, installs fences and scaffolding, arches and wooden supports for communication lines, lays floors. Carpentry can rightfully be considered an art.
Interesting materials:
Where is it convenient to read books? Where is coal mined by open pit mining? Where is the registration number? Where is the passport number? Where is the expiration date for protein? Where is the driving experience indicated? Where is the date of issue of a driver's license indicated? Where is the estimated service life of the vessel indicated? Where is the series indicated in the international passport? Where did Sergei Bodrov Jr. die?
Description of the profession
So, who is a carpenter today? It is believed that a modern representative of this profession has a higher level of skill than a carpenter, who produces mainly building materials or large (usually simple) structures from solid wood.
A carpenter is engaged in more delicate work; he makes a wide variety of wood products, including in combination with other materials:
- cabinet furniture;
- doors;
- window frames;
- plinths and cornices;
- hangers;
- parquet;
- stairs;
- various carved decorations (figurines, picture frames, children's toys).
Most often, carpenters work in furniture factories and workshops, but it also happens that industrial enterprises in the aircraft and shipbuilding industries need their services to produce some parts or models for testing in a wind tunnel. Typically, craftsmen specialize in individual profiles: the manufacture of furniture, musical instruments, ship parts, doors and windows. Cabinetmakers work with rare types of wood and restore antiques.
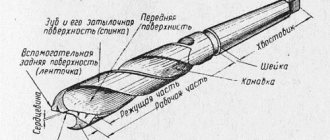
In his work, the master uses techniques such as planing, sawing, carving, turning, and gluing. To do this, he uses a number of familiar hand tools: an axe, a plane, a chisel, a saw, a jigsaw, a jointer, and a grinder. There are also more rare ones, for example, thicknesser, fillet, gruntubel or yarunok.
The best colleges for studying
As an example, there are several colleges and technical schools that graduate qualified carpenters from their walls:
- College of Industrial Technologies "Krasnoderevets" (St. Petersburg). Furniture makers, parquet floor workers, glaziers, and construction carpenters are trained here. There are profiles on woodworking technologies and the production of art products. You can enroll after 9, 11, and for some specialties even after the 8th grade of school. Secondary college cooperates with many educational institutions in the North of Russia.
- Educational complex of urban planning "Capital" (Moscow). Woodworkers are trained in the Zyablikovo department. After 9th grade you can get a diploma in 2 years and 10 months. Among the college’s social partners are JSC Mospromstroy, LLC Ecopromdesign, State Budgetary Institution “Zhilishchnik” of different districts of the city, the group.
- Tyumen Forestry Technical College provides enterprises and institutions of the region with carpenters, joiners, parquet floor workers and window makers. The services of graduates are used by Tyumen Plywood LLC, PC Furniture Group LLC, and the Intedi furniture factory.
- Okhtinsky College (St. Petersburg) is one of the oldest professional institutions in Russia. It runs training programs for woodworkers and wood product assemblers.
- The Pskov College of Industrial Technologies and Services in the construction department provides professional knowledge and skills to carpenters and joiners without obtaining a general secondary education. This allows you to reduce the training period to 1 year and 10 months. At the multifunctional center for applied qualifications, you can additionally master the profession of a parquet floorer in 144 academic hours.
In secondary schools, students receive a general secondary education, as well as a good theoretical basis for working with different types of wood (including exotic ones). Some people prefer to go directly to production as an assistant foreman and gain the necessary practical skills right on the job. This path makes it possible to quickly enter the profession, but reputable enterprises will not hire an employee without a technical school or college diploma.
Responsibilities at work
A carpenter's job responsibilities include:
- selection of the necessary wood raw materials, taking into account its condition and type of wood;
- processing of selected raw materials using hand and power tools;
- cooking glue yourself or choosing a suitable one from factory mixtures;
- production of small solid products or individual parts with subsequent assembly (for example, furniture);
- polishing, grinding parts, tarring them, painting or varnishing;
- installation of finished products (including door and window frames of any complexity, doors and windows);
- installation of built-in furniture;
- performing roofing work, covering wooden elements with roofing felt, felt or other materials;
- assembly of fences, parquets, plank floors, stairs, railings, etc.
The responsibilities of a specialist are prescribed in the job description, based on the specifics of production. For each qualification category (there are 6 in total) specific functionality is designated. The higher the rank, the more complex and responsible work can be entrusted to a master. Thus, only carpenters of categories 4–6 can work on shaped products.
In general, when hiring a candidate, they require the following professional knowledge and skills:
- knowledge of different types of wood, their basic properties and scope of application;
- methods for processing and marking them, manufacturing all kinds of carpentry structures and products;
- experience in the use, adjustment and sharpening of hand and electric tools, woodworking machines;
- the ability to read drawings, sketches or outlines, and, if necessary, create them independently;
- skill in selecting and installing suitable fastening hardware;
- finishing walls and ceilings with cladding materials on a base frame;
- ability to repair wooden products.
The labor market now requires carpenters both for the mass production of standard wood products (windows, parquet, stairs, fences) and for the creation of unique things from valuable wood (carved door panels, picture frames). High-quality cabinet makers often work to order, decorating the homes of the rich and famous.
Job tips
It is not difficult to get a job as a carpenter, since professionals are in demand in many industries: wood processing, timber chemicals, construction, ship repair, etc. You can choose a large enterprise or a small private workshop that produces custom carpentry.
During the interview, you need to find out the working conditions and scope of responsibilities in order to correlate experience and qualifications with the tasks to be solved in production. When choosing a company, you should focus on the level of wages, working conditions, as well as the social package offered.
Who is it suitable for?
Mostly men work as carpenters, although there are no legal barriers for women. Everyone has certain health limitations: functional disorders of the musculoskeletal system, primarily the arms and back, as well as problems with vision, respiratory tract, and a tendency to allergies to dust or chemicals.
In order to cope well with his professional responsibilities, a carpenter will need a set of personal qualities, which include:
- endurance and good physical health;
- responsibility and patience;
- accuracy and scrupulousness;
- developed eye and coordination of movements;
- artistic taste and creativity;
- understanding of proportions and overall composition.
Who can be a carpenter
When thinking about choosing a future profession or retraining, it is worth considering that not every person can become a good carpenter. Professionalism and the high level of manufactured products directly depend on how a person’s temperament and personal qualities relate to the characteristics of the labor process.
What does a future carpenter need:
- Love the tree.
- Have good health (vision, joint-muscular sensitivity, endurance).
- Be able to distribute your attention well.
- Have a quick visual-motor reaction.
- Possess the ability to concentrate for a long time, as well as be able to flexibly distribute it.
- Be sure to have good spatial imagination.
- Have developed visual-figurative thinking, attentiveness, accuracy.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of the profession: demand in industry and everyday life, good earnings. In addition, there is the possibility of earning additional income from part-time jobs based on advertisements or recommendations (the basic carpentry tools that will be required to complete orders are relatively inexpensive).
Disadvantages: constant noise, vibration, possibility of industrial injury: most often the hands suffer when tools are used carelessly and the eyes (damaged by splinters or shavings) when sawing, grinding and during other production operations. The fumes from the varnishes and paints used also have a bad effect on the respiratory system and skin. To avoid these troubles, carpenters need to strictly follow safety rules, work in special clothing (suit or robe), use safety glasses, earplugs, arm guards, and gloves.
Negative sides
The negative side of the profession is high risks to life and health, and possible injuries. When working with tools and machines, you can get cuts and wounds from flying chips. From time to time, carpenters have to inhale the smell of varnishes, glue, and paints, which can provoke the development of pulmonary diseases and allergies. Some employees' hearing is impaired due to the constant noise in the workshop from working tools.
Diseases of the joints and spine are possible, because You constantly have to lift heavy objects (logs, boards, cabinets, wall panels, etc.).
How to build a career
A carpenter can gradually increase his qualifications by gaining experience and receiving additional training. With a certificate of assignment to the 6th category, you can become a foreman. For engineering and higher management positions (for example, foreman or shop manager), you need a higher education diploma in construction or management.
Author: Alexey Kuznetsov
If you still have even the slightest doubt that the carpenter profession is right for you, then we strongly recommend taking a career guidance test from Profgid . It costs mere pennies, and at the same time allows you to avoid mistakes that can go in the wrong direction and cripple your whole life. Find out more >>
Professional fees
After describing who a carpenter is and what his responsibilities are, you can understand what disadvantages are typical for this profession. First of all, this is physical fatigue that occurs as a result of constant active work.
There are also some diseases that are most often diagnosed in carpenters:
- Damage to the respiratory tract (lungs, nasal cavity).
- Injury to the musculoskeletal system (sacrum, spine).
- High risk of injury to extremities (fingers, palms, toes and feet).
- Carpenters and machine operators are characterized by gradual hearing loss.
At the moment, a carpenter is a profession with an average level of demand. When entering an enterprise, an employee can hope for career growth, increase in rank and promotion to foreman.
Having a higher education, a carpenter can apply for the positions of a foreman or foreman. If desired, he is able to retrain and become a carpenter or parquet worker.