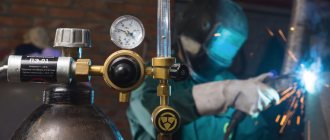
To ensure that the process of joining parts into a single whole is not difficult and everything works out the first time, before practical work you need to understand the theory of how semi-automatic welding is carried out in a carbon dioxide environment for beginners. Let's consider the main aspects and essence of this method.
Where is carbon dioxide welding used?
The assurance that semi-automatic welding machines for welding in a carbon dioxide environment are used exclusively for repairing car bodies is incorrect. Carbon dioxide welding is also used in the following industries:
- Production of steel structures with a large number of welds per 1 linear meter.
- Repair and production of forged structures: gratings, railings, gates, fences, etc.
It is possible to use welding using CO2 in other areas of production, where special attention is paid to low heating of the surface and deformation of the part during processing.
Characteristics of carbon dioxide welding
Carbon dioxide has no taste or smell, and is colorless. In moderate quantities, it does not pose a danger to human health and life, and is not explosive. Its density is 1.98 kg/m3, which means that it is much heavier than air (with a density of 1.2 kg/m3).
It goes on sale in iron cylinders of 10, 20 or 40 liters in liquid and under pressure. Before the welding process, it is necessary to place the cylinder in a vertical position for some time so that all the moisture that is there is glassed. After this, the gas is supplied to the welding zone. An installed reducer with a regulator controls the pressure and gas supply.
Important: before purchasing a cylinder, it is important to clarify the possibility of refueling.
Welding in carbon dioxide can be performed by several types of welding equipment:
- A rectifier is a semi-automatic welding machine, inside which the current is converted from alternating to direct. They are used for all types of semi-automatic arc welding using different electrodes and for joining various metals, except aluminum.
2. The inverter is the power source for the welding arc. This is a device that can convert electricity from a 220V network into direct current to create and hold an arc. You can learn more about the operating principle and advantages of the inverter here.
Carbon dioxide welding technique
The implementation of welding work and the technology of semi-automatic welding in a carbon dioxide environment is quite simple; in fact, the master is required to withstand the required wire extension and move the machine’s torch at the same speed.
The result is a uniform seam without beads, ensuring sufficient penetration of the steel and mechanical strength of the resulting joint.
When performing work, the master is required to comply with the following recommendations:
Before starting welding, make sure that the shielding gas is escaping from the torch. The working pressure of carbon dioxide during semi-automatic welding is 0.02 kPa. But this indicator is not absolute; the presence of a draft or wind slightly increases the consumption of material. Accordingly, the pressure to create a normal seam will increase.
The burner angle should be between 65-75°. The seam must be drawn from right to left, this way the welded edges are better visible.
What is the carbon dioxide pressure during welding?
GOST for semi-automatic welding in carbon dioxide is regulated by guideline document 26-17-051-85. According to the document, a standard cylinder filled with CO² is enough to provide 15-20 hours of continuous operation. To increase productivity, be sure to use a dehumidifier.
The supply of carbon dioxide can be changed upward in the presence of drafts, wind and other negative factors. The quality of the resulting seam plays a decisive role when choosing a suitable operating mode.
The essence of welding in a carbon dioxide environment is that CO² protects the surface being processed from overheating. As a rule, the quality of the weld directly depends on the consumption of carbon dioxide during semi-automatic welding. At the same time, the master is required to ensure optimal costs between the use of gas and the consumption of welding wire.
Carbon dioxide consumption for semi-automatic welding machine
Although carbon dioxide consumption rates depend on many factors, on average, the following consumable costs are provided for a semi-automatic device:
- Wire feed speed – depends on the width of the consumable material, ranges from 35-250 mm/sec.
Calculation of carbon dioxide consumption during semi-automatic welding can be done independently, knowing the following parameters:
- The costs of preparatory work account for about 10% of the total CO² consumption.
Also, when calculating, the thickness of the wire and the metal being processed is taken into account.
About 25 kg of carbon dioxide is poured into the cylinder. As a result of the chemical reaction, about 509 liters of gas are produced from each kilogram. Accordingly, one standard cylinder is more than enough for continuous operation for 12-15 hours.
It is possible to do without the use of shielding gas. Instead of CO², cored wire is used. When heated, the powder-coated wire releases gas, which protects the treated surface from overheating.
The set of equipment for semi-automatic welding in carbon dioxide includes:
- Rectifier - can be transformer or inverter type. The first is optimal for thick wire, the second ensures a uniform voltage supply and a stable welding arc.
Feeding mechanism – has restrictions on the thickness of the wire. When choosing, you should take into account that not every flux can be used when performing welding work.
All equipment together ensures optimal operating conditions and creates conditions for the formation of a high-quality weld.
Technical requirements
Steel pressure vessels with a volume of 0.4–50 l are used almost forever . Domestic GOST 949-73 applies to containers for transportation of intermediate storage and technological distribution to consumers.
Solid-drawn seamless cylinders of small and medium volume made of structural steel 45D and alloyed 40KhGSA are designed for a working pressure of 15 and 20 MPa for vessels of 50–20 l and 15 MPa for smaller ones, which can be produced with a flat bottom.
Distinctive marking is a yellow enamel inscription “carbon dioxide”, “CO2”, “carbon dioxide” on a black field . The main physical parameters and standard sizes are presented in the table:
Vessels of smaller volumes are made of steel 45D, operating pressure 15 MPa
| Ø, mm | 12 l | 10 l | 8 l | 5 l | 4 l | 2 l | ||||||
| L, mm | M, kg | L, mm | M, kg | L, mm | M, kg | L, mm | M, kg | L, mm | M, kg | Ø, L, mm | M, kg | |
| 140 | 1020 | 17,6 | 865 | 13,0 | 710 | 12,4 | 475 | 8,5 | 400 | 7,3 | 108/330 | 3,7 |
- oxygen shut-off valve with right-hand thread, brass;
- rubber safety rings for the cylindrical part;
- rectangular support shoe for stability;
- safety cap made of steel or molded from non-metals.
Cylinders in use undergo periodic re-certification after 5 years , including technical inspection and testing with excess pressure exceeding the working pressure by 50%. Information with the date of inspection is applied with impact stamps to the cleaned neck, framed by a yellow stripe around the perimeter.
This is a “carbon dioxide cylinder passport” with a complete list of information:
- date of issue, recertification;
- Cylinder number assigned by the manufacturer;
- filling capacity;
- process hydraulic pressure;
- steel grade and physical quantities of weight and dimensions.
Tell me how to cook semi-automatically
I bought myself a device like this (picture below). I purchased a 12L cylinder.. Now the questions are: what pressure should be in a full cylinder? (the picture shows a full cylinder) what pressure should be at the outlet when welding? what length of wire should stick out from the burner?
Otherwise, sparks fly in different directions; if you bring it closer, it seems to be a little better, but it turns out that I’m almost touching the tip. If you move further, the wire goes jerkily (in the sense that the spark burns out again and then burns out again) I tried to increase the feed speed, the same effect only with a larger amplitude. In general, don’t scold me too much, I’m just learning.
With flux it worked almost immediately, but with gas it didn’t work. I switched the terminals in places.
We have the same problem, so I decided to redo the control unit, is your voltage not too low?
alan62 wrote: what pressure should be in a full tank? (the picture shows a full tank)
depends on temperature.
alan62 wrote: what pressure should be at the outlet when welding?
depends on the diameter of the throttle washer at the output of the gearbox.
alan62 wrote: what length of wire should stick out from the torch?
Zifrius wrote: We have the same problem, so I decided to redo the control unit, is your voltage not too low?
Yann: -I encountered a similar problem, low voltage in the network. I made a step-up transformer. An increase of 20 volts solved the problem.
The voltage is normal. Interesting answer about temperature. And if so, in the picture with the cylinder on the pressure gauge it shows the pressure when the cylinder has just been filled. Temperature -5. I would just like to know how to at least navigate when refueling. Otherwise, if there is a lot of gas, then everything sparkles and splashes around, if there is not enough, then you boil 3 cm, and it feels like half a coil of wire has been devoured. How to navigate? Approximately what the consumption should be (well, of course, it depends on the welder), but still. And if everything depends on the temperature, then if it suddenly rises above zero, then why not approach the cylinder? will he kill? I specifically posted a photo with a full cylinder and an open valve.
And what is a throttle washer? Should I at least understand how hard it should blow on the arc?, if that’s how it is in Russian.
alan62 wrote: I would just like to know how to at least navigate when refueling.
You need to focus on weight. In a 12-liter (if you really have a 12-liter) cylinder you can fill approximately 7 kg of liquid carbon dioxide.
alan62 wrote: Don't go near the cylinder? will he kill?
I definitely don’t recommend putting it on the stove. The throttle washer is located between the gearbox housing and the outlet fitting. gas consumption - 8-12 liters per minute.
Maybe you should invite an experienced welder for a consultation. It’s not so much about knowing how to feel these things. I had to service a welding shop for the production of Lada steering wheels. I can do manual welding, and automatic welding was easy for me. But then I saw how the newcomers were poking. But we quickly got used to it, since the pros were nearby. It was easier for me; I could practice my skills and solve technical problems on the decommissioned one. Many years have passed, but I remember the brands. TDM 400 and 303. Not bad cars, but not all were of high quality. Even in welding they differed from me. The pros immediately got involved and selected the cars. Young people understand worse
Application: gas treatment
Long-term and intermediate storage of cylinders is allowed on ramps equipped with roofs and protective partitions that prevent the ingress of precipitation, in cold and heated rooms with natural ventilation.
Liquid carbon dioxide supplied for welding work is purchased in the highest and first grades . Refilling cylinders with carbon dioxide for food producers is expensive, but desirable: The gas humidity is zero.
The use of second grade gas is allowed if drying is possible: an unregulated amount of liquid vapor is added to 1% of the aqueous sediment. A gas dryer extracts water vapor from a gas flow.
This is a sealed container filled with hygroscopic materials. Low pressure dryers are installed after the reducer, high pressure dryers take gas from a cylinder in front of the reducer. Desiccants are aluminum gel, silica gel, and copper sulfate .
Adiabatic cooling of a gas provokes a sharp volumetric expansion. Gas consumption in the range of 15–20 l/min leads to freezing of moisture vapor, which can lead to clogging of the gearbox. A high-volume gas intake requires the installation of a 24/36 V coil-type gas heater. The thermoelement neutralizes the freezing of water vapor and is designed to pass large volumes.
Active gas protection of welds during semi-automatic arc welding with a consumable wire electrode is carried out with carbon dioxide in pure form or mixed with argon.
The use of cylinders implies a limited daily consumption by welding stations . A 40-liter cylinder with an internal pressure of 6 MPa holds 25 kg of liquefied substance. In gaseous form, after evaporation, the liquid is transformed into 12.5 thousand liters of gas.
The most productive gases for semi-automatic welding: how do professionals approach this issue?
Today there are many modes and types of welding.
Some types require portable (inverter) power supplies, while others can only be used in a workshop environment under the supervision of several specialists. To get a good, even and durable seam, you need to follow all the rules, know what gases will be optimal for this device and what rules you need to follow when working with metals.
Purchase: selection and rejection criteria
Purchasing high-pressure (HP) equipment for long-term use, new or used, is not difficult. Difficulties will arise when refilling carbon dioxide cylinders if the buyer does not take into account the restrictions on operation and refilling:
- Refilling cylinders with carbon dioxide is difficult if the filling station equipment is designed for a larger displacement - fire extinguisher refillers will help out;
- Filling small-capacity containers in a garage is possible using a donor cylinder with a high-pressure hose, subject to safety conditions;
- If the certification period is missed, the HP vessel is subject to inspection and certification testing;
Peculiarities
The semi-automatic welding algorithm is a kind of modification of manual electric arc welding. To fully appreciate the advantages and disadvantages, you need to consider how exactly semi-automatic welding is carried out.
Before you begin the welding process, you need to understand a few points:
- You need to connect the burner to the positive terminal, and the workpiece to the negative terminal.
- A special wire is used for each type of metal.
- The strength of the current and the speed at which it feeds the wire are directly proportional. The stronger the current, the higher the feed rate should be and vice versa.
- The current collecting tip is a consumable item that will be changed frequently. Its diameter should correspond to the diameter of the wire itself.
- Basically, the quality of the finished seam depends on the operating parameters of the falling wire mechanism.
- In order for the wire feed to be continuous, the hose that feeds it must be extremely rigid.
- If the thickness of the metal being welded is less than 1 mm, then it is better to do spot welding, then the workpiece will not overheat and will not burn out.
- In the case when the voltage in the network is 190 volts and not 220, that is, less than the standard, it is better to use a wire of small diameter. For example, instead of 0.8, take 0.6, then the machine will cope with it much easier and the seam will be of high quality.
- If welding with a semi-automatic device occurs without gas, then the positive terminal must be connected directly to the workpiece and a special wire must be used for welding.
Gearbox
Stabilization, reduction of gas protection supply pressure, optimal consumption of carbon dioxide during semi-automatic welding, and blocking of the supply of carbon dioxide when welding is stopped are carried out by the gearbox.
Single-chamber and two-chamber (two-stage) pressure regulators with a sequential arrangement of pressure reduction cavities are adjusted by turning the manual regulator for changing the CO2 supply flow.
The inlet pressure gauge records the pressure of carbon dioxide in the cylinder. The second is in the regulation chamber, the carbon anhydride distribution network . Not limited to the function of a change recorder, the reducer works as an outlet pressure stabilizer.
The consumption of carbon dioxide in the cylinder should not affect what pressure of carbon dioxide should be when welding with a semi-automatic machine. The reducer membrane takes the position of allowing gas into the cavity of the chamber to reduce the operating pressure during the initial setting. Changing the voltage settings of the control spring activates the opposite control spring.
The open cross-sectional area of the intake valve gradually changes upward, but the consumption of carbon dioxide during semi-automatic welding remains the same. The constancy or change in the output pressure is adjusted according to the current reading of the pressure gauge using an adjusting screw.
Manipulations of the ball valve included in the package are used to clarify the amount of gas flow . The flow washer with nozzle adjusts the outlet according to the pressure value in the working chamber.
The pneumatic reducer is protected by a built-in safety valve. A pressure surge will cause the membrane to rupture. Loss of tightness at the inlet fitting with an increase in gas flow leads to preventive locking of the system.
Pneumatic reducers are classified by the number of pressure equalization stages (chambers) . A two-stage reducer with a consistent reduction in pressure in an unheated room in winter is indispensable.
Separation of pneumatic regulators according to conditions of use:
- network – work in a stationary network of a carbon dioxide station;
- ramp – servicing multi-post areas.
Interchangeability of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Structurally they are similar, and their replaceability is partial . The oxygen reducer is designed for a pressure 2.5 times higher, and the operating requirements are more stringent. Carbon dioxide is chemically neutral and does not damage the membrane. But carbon dioxide on an oxygen cylinder will not last long precisely because of the destruction of the membrane.
But using it for other purposes would be a mistake. When welding with carbon dioxide, the oxygen reducer freezes . The expansion coefficient of carbon dioxide leads to a decrease in the temperature at the reducing valve to –60 0 C. Crystallization of moisture will lead to failure of the device.
UR 6-6
Among the variety of gearboxes, the compact universal pointer UR 6-6 with a calibrated jet is distinguished. Suitable for regulating the supply of argon, other gases and mixtures with a maximum oxygen content of up to 23% on gas cylinder equipment of 20–50 l . The impact-resistant body is made of brass. It is recommended to connect an electric heater.
- a cleaning filter is built into the inlet valve, preventing backflow into the cylinder;
- inlet pressure – up to 20 MPa;
- throughput – up to 1.8 m 3 /hour. (30 l/min.);
- working pressure – 0.35 MPa;
- operating pressure unevenness limit – 4%
- weight – 0.7 kg;
- considered the most economical model.
With rotameter
The convenience of a flow meter while maintaining the functionality of a conventional regulator in displaying carbon dioxide consumption during semi-automatic welding in the current mode. The rotametric regulator is equipped with a calibrated throttle valve at the output. The accuracy of control and gas flow readings is guaranteed .
The pressure gauge indicates the units of flow. The device is configured and further adjustments are not recommended. Two-rotameter gearboxes are designed to protect the seam of chemically active metals on both sides.
Source
| Ø, mm | L, mm | M, kg | Ø, mm | L, mm | M, kg | Ø, mm | L, mm | M, kg |
| 15 | 219 | |||||||
| 1685/1660 | 71,3/62,5 | 219 | 1370/1350 | 58,5/51,5 | 219 | 740 | 32,3 | |
| 20 | 1755/1650 | 93,0/62,5 | 1430/1350 | 76,5/51,5 | 770 | 42,0 |
What can you cook?
A semi-automatic machine can weld metal of any thickness, however, thick products need to be heated red-hot with a blowtorch. An inverter power supply is excellent for these purposes.
Welding in argon is completely different, because the principle of operation of a semi-automatic machine is to melt steel wire and fill the seams with it. To prevent the oxidation process from occurring, the procedure is carried out under the influence of carbon dioxide. Argon is used to protect active metals from oxidation.
An atmosphere of inert gases will prevent oxygen from reacting with the surface.
Varieties
Let's consider the types of gases that are used in semi-automatic welding
Acetylene is a colorless gas that is lighter than air. It has a special smell. One of the widespread gases that are used in this area, as it has the highest combustion temperature and has increased polarity. Often used due to high temperatures when cutting metal structures.
Hydrogen is also a colorless, odorless gas that is classified as explosive. Upon contact with oxygen, the air forms an explosive mixture. For safety reasons, hydrogen cylinders should not be under pressure greater than 15 mPa.
Coke oven gas is colorless, but has a specific odor. It is a waste product recovered from the coke extraction process that is used in welding. It is derived from coal. Gas can be transported using pipelines.
Natural gases such as methane, butane and propane do not have special requirements for storage and transportation. Gas production most often occurs right at the source.
Adjustment
The tension of the main spring is adjusted using an adjusting screw, depending on the initial gas pressure in the cylinder. The control spring lowers with the diaphragm, opening an opening for carbon dioxide to pass under reduced pressure to the shut-off valve. From there, the gas flow moves through the hose to the burner. The membrane of the carbon dioxide reducer is made of oil-resistant rubber and ensures its precise positioning relative to the outlet. As the gas pressure in the cylinder decreases over time, the upper control spring can drop, changing the flow area of the inlet valve. The carbon dioxide reducer also allows manual control of the gas flow; to do this, simply unscrew/screw in the adjusting screw, depending on the current readings of the pressure gauges.
The constant pressure in the reducer chamber is ensured due to the fact that when the gas pressure coming from the cylinder decreases, the membrane moves upward, compressing the return (upper) spring, and when the pressure increases, it moves down. The outlet pressure remains stable due to a corresponding change in the flow area of the shut-off valve.
To ensure the resistance of the membrane against sudden excess of gas pressure (which can cause the membrane to rupture), carbon dioxide reducers are equipped with a safety valve. It is triggered when the inlet fitting for some reason loses its seal and begins to let an increased volume of carbon dioxide from the cylinder.
Consumption at work
A typical 40-liter cylinder contains 24 kg of carbon dioxide. When evaporated, 12,000 dm is formed from it. cube If you take into account the data that was displayed, you can find out how long the cylinder will last with continuous use.
If you use wire 1 mm thick and a current of 100 A, then 40 liters of gas will last for about 24 hours. It follows from this that a cylinder with a volume of 10 liters can provide 6 hours of continuous operation. According to reference books, 1 kg of molten metal contains 1100 grams of carbon dioxide and 1350 grams of welding wire. Using this data, you can determine the proportion of carbon dioxide and wire. For 1200 grams of wire, approximately 1 kg of carbon dioxide in liquid form is consumed.
Based on statistics, we can say that in most cases these data correspond to reality.
| Specific gas consumption (carbon dioxide or a mixture of Argon and carbon dioxide) during welding | |||
| Wire diameter, mm | Current range, A | Gas consumption | |
| m 3 /s *10 4 | l/min | ||
| 0,8 | 60-120 | 8-9 | |
| 1,0 | 60-160 | 1,33-1,5 | 8-9 |
| 1,2 | 100-250 | 1,5-2,0 | 9-12 |
| 1,4 | 120-320 | 2,0-2,5 | 12-15 |
| 1,6 | 240-260 | 2,3-2,5 | 14-15 |
| 1,6 | 260-380 | 2,5-3,0 | 15-18 |
| 2,0 | 240-280 | 2,5-3,0 | 15-18 |
| 2,0 | 280-450 | 3,0 – 3,33 | 18-20 |
Design versions
Sizes and characteristics of devices must comply with the requirements of GOST 13861-89, ISO 2503-83 and GOST 12.2.052-81. Classification of carbon dioxide reducers can be made according to the following parameters:
- According to the number of working chambers. The predominant number of such devices are of the single-chamber type, however, to improve the stability of operation in conditions of low outside temperatures, double-chamber gearboxes are also produced. The working chambers in such devices are located sequentially.
- According to working conditions. There are ramp, network and balloon reducers. Ramp ones are intended for operation in multi-post areas, and network ones are powered by a stationary network laid from the carbon dioxide station of the enterprise. For the operation of individual posts, cylinder carbon dioxide reducers are designed, which are designed for lower specific gas consumption and a limited range of operating pressures.
- According to the principle of opening/closing the inlet valve, reducers for a carbon dioxide cylinder can be direct or reverse acting. The operating principle of the second type of gearbox is discussed above, and in direct-acting gearboxes all changes in flow and pressure occur in the reverse order. Such gearboxes are less convenient to use and therefore are used much less frequently.
Read also: Service life of PVC wire
Gas mixtures
Read more about mixtures - they have a certain number of advantages over clean eyes, namely:
- low metal spattering;
- good penetration depth;
- low degree of deformation;
- reduced wire consumption;
- fast welding speed;
- high efficiency in terms of efficiency.
What types of mixtures are there?
- Gas mixture NP-1: consists of 85% helium , 13.5% argon , 1.5% carbon dioxide . Provides an even, smooth seam, without an oxide film. It interacts well with thin surfaces because it does not deform them.
- Gas mixture NP-2: consists of 55% helium , 43% argon , 2% carbon dioxide . Provides low seam level and fast welding speed. You can cook materials of any thickness in any mode (including automatic).
- Gas mixture NP-3: consists of 38% helium , 60% argon , 2% carbon dioxide . Provides arc stability, low degree of deformation and metal spattering. Suitable for welding surfaces thicker than 9 mm.
Ultimately, the choice of mixture will depend only on the specific operating mode. If welding occurs under automatic conditions, then it is better to choose a mixture of NP-2 or pure Argon. If welding is done manually, you will have to choose between NP-1 and NP-3. Then everything depends on the thickness of the metal that will be welded.
For industrial enterprises and large batches of welding, our own mixture is often developed that satisfies the specific conditions of the product. Such mixtures on the market are often much cheaper than usual ones, but you can purchase them only at your own peril and risk, because if it was suitable for one batch, it may not be suitable for your product, and the manufacturer needs to put the leftovers somewhere.
How to cook with carbon dioxide
How to cook with carbon dioxide for beginners
Welding in a carbon dioxide environment has its pros and cons. Among the advantages, it is necessary to highlight the narrow zone of thermal influence on the metal, which in turn makes it possible to weld even the thinnest workpieces.
In addition, the efficiency of welding work increases significantly: arc combustion improves, and the seam is of very good quality. One should not discount the fact that carbon dioxide is the most accessible of all types of gases for welding.
As for the disadvantages of welding in a carbon dioxide environment, they are mainly associated with metal spattering. Also, in order for a weld using carbon dioxide to be of high quality and beautiful, it is very important to carefully prepare the surface of the metals before welding.
What is the difference between an oxygen reducer and a carbon dioxide reducer?
The designs of carbon dioxide reducers are very similar to oxygen ones, and differ mainly in the methods of connection to the valves, and - sometimes - in the absence of a second pressure gauge. Therefore, the question often arises: are oxygen and carbon dioxide reducers interchangeable?
Much higher performance requirements are placed on the oxygen reducer. They are due to the fact that, unlike CO2, oxygen is not liquefied, and therefore is in the cylinder under much higher pressure (up to 200 atm versus 70...80 atm for liquefied carbon dioxide). Therefore, when oxygen enters the carbon dioxide reducer, the sealing membranes will gradually destroy. Therefore, the carbon dioxide reducer is not used to supply oxygen (reverse replacement is acceptable).
The gearboxes also differ in the possibilities of connection options to the cylinder. The carbon dioxide reducer can be connected using a clamp rather than a union nut, since CO2 does not have fire or explosion properties in case of leaks.
To improve the purity of the gas entering the reducer, cleaning filters are often included in the inlet valve design. The presence of a filter reduces the risk of gas venting back into the cylinder, where it can form a surface cushion over the liquefied gas.
How to cook with carbon dioxide for beginners
As mentioned above, the quality of the weld seam when welding with carbon dioxide largely depends on the degree of preparation of the materials. Also, it is equally important to pay attention to the correct settings of the inverter semi-automatic device and gas consumption.
You should know that for welding each metal, depending on its thickness, its own welding current parameters and a certain wire diameter are selected. It is also important to consider the speed of wire feed into the welding zone.
You can adjust the welding wire feed speed on a semi-automatic machine using gears and a mechanism. Semi-automatic welding in a carbon dioxide environment is carried out as follows:
- The semi-automatic torch is located in the welding zone, so that the tip is located at the place where the seam is formed. By pressing the “Start” button, you must simultaneously move the torch, touching the wire to the metal being welded.
- At the same time, the welding arc will be initialized and the semi-automatic welding process will begin.
- During this process, it is necessary to move the welding torch tip evenly along the seam, constantly monitoring its inclination and position.
It is impossible to make sudden movements with a gas torch during semi-automatic welding, as this will lead to a deterioration in the quality of the weld. In addition, do not forget about the main disadvantage of using semi-automatic devices with gas: the protective gas can be blown away by the wind.
In order not to spoil the workpiece, it is important to practice semi-automatic welding with carbon dioxide on an unnecessary piece of metal in advance. This is the only way to select the correct gas flow rate and select the desired welding wire feed speed.
Color coding
Essentially, a reducer is a pressure regulator for a welding mixture. It is a mandatory part of the equipment for semi-automatic welding machines that use the principle of welding in a protected gas environment. At least two gearboxes (each connected to its own cylinder) are used in a gas welding and cutting installation.
Of course, the best solution would be to choose only a reducer specifically designed for it for a cylinder with a certain gas. There is a strict color coding system:
- blue color with black inscription - oxygen;
- white with red text - acetylene;
- black with blue inscription - technical argon;
- black with white lettering - raw argon;
- black with yellow inscription - carbon dioxide (CO2).
Depending on whether you use gas welding, argon arc welding or carbon dioxide welding, choose the appropriate gearbox.
At the market or in a store, this can be easily done by color - the color of the welding gear matches the color of the cylinder for which it is intended. Blue is for oxygen, black is for argon (also suitable for carbon dioxide), and so on.
A couple of tips on choosing a semi-automatic welding machine
Before choosing a semi-automatic welding machine, read a few important tips:
- The greater the power of the semi-automatic machine, the thicker the metal it can weld;
- Inverter semi-automatic machines are much simpler and more efficient in operation;
- It is preferable to choose a semi-automatic machine whose design will include removable holders;
- It would be good if the instructions for the semi-automatic machine were in Russian, clear and informative to use.
Semi-automatic welding with carbon dioxide differs significantly from manual arc welding. To obtain a high-quality weld, you need to take into account many nuances: gas consumption, wire feed speed, filler material diameter and much more.
Types of capacity of carbon dioxide containers
To obtain carbon dioxide of a high level of quality, you need to work with a manufacturing company that also supplies containers and carries out inspections. Cylinders are delivered to the site and connected to the operating units.
| Cylinder capacity, l | Gas quantity, kg | Diameter, cm | Height, cm |
| 40 | 24 | 21,9 | 140 |
| 20 | 12 | 21,9 | 85 |
| 10 | 6 | 14 | 86,5 |
This is the most common container. The choice depends on the purpose of use and other factors.
Features of semi-automatic welding using carbon dioxide
Welding using carbon dioxide is somewhat reminiscent of gas welding. It is possible to make a connection with or without protection. The principle of operation of such welding is the injection of carbon dioxide at the junction of two parts of the material being welded. The welding arc heats parts of the material to maximum temperatures; the substance breaks down into parts such as O2 and CO. The result is a weld that is resistant to corrosion, oxidation and rust.
Design and principle of operation of a carbon dioxide reducer
The carbon dioxide reducer supplies gas at the required pressure, as well as shuts off the CO2 supply valve from the cylinder when welding stops. The design of the unit includes:
- Inlet valve.
- Sealing elements.
- Chamber with a regulating membrane.
- Release valve.
- Upper spring.
- Control spring.
- Connection fitting.
- Frame.
- Two pressure gauges that control the carbon dioxide pressure at the inlet and outlet.
- Shut-off valve.
A conventional single-chamber carbon dioxide reducer works as follows. Gas under pressure (which is controlled by a pressure gauge) from the cylinder enters the inlet fitting. Having passed into the chamber, the CO2 flow overcomes the resistance of the spring and presses it down, as a result of which the gas enters the cavity of the chamber. Since its cross-sectional area is significantly larger than the flow area of the fitting, the gas pressure in the chamber decreases. This change is recorded by a second pressure gauge.
Carbon dioxide arc welding
Semi-automatic carbon dioxide welding is used in industry and private workshops to join small parts and workpieces. This method gained its popularity due to a number of advantages:
- Welding of the thinnest workpieces;
- High performance;
- Minimum costs. (Carbon dioxide is quite cheap);
- Welding of metals and alloys with various characteristics;
- Availability of different modes for welding;
- More stable electric arc;
- Reducing the risk of weld oxidation due to reactions with the external environment;
- Improved seam quality;
- Semi-automatic welding is considered one of the safest for human life and health: both the worker and the consumer;
- Refilling used gas cylinders.
Carbon dioxide supply options
The product is pumped into cylinders. It arrives on site in a fully ready-to-use condition. There are three delivery options:
- In the form of liquefied gas. The delivery pressure should be 50 kg/cm2. In storage areas, as well as directly during operation, the temperature level should not exceed +31 degrees.
- Liquid. During transportation and storage, specially designed, tested and sealed thermoses are used.
- Dry ice. For production, it is necessary to comply with requirements for both pressure and temperature.
Special black tanks are used to store the substance. They are marked with yellow inscriptions, special markings that give a complete picture of the characteristics of the goods.