A chain is a flexible long product made of links connected in series and movably. This ingenious invention of mankind in modern realities has not lost its former popularity and is widely used on ships, in ports, logging, cargo transportation, manufacturing, mining, agriculture, everyday life, interiors and landscape design.
Chains are distinguished by purpose, design, material, link size, strength and many other characteristics, which determine their scope of application. Among the huge variety of link structures, four main groups can be distinguished.
General purpose circuits
This group includes steel round link chains of normal strength with a caliber from 2 to 16 mm with a welded connection of the links. They are manufactured in accordance with DIN 763, DIN 5685 Form C (long link) and DIN 766, DIN 5685 Form A (short link) from low-carbon steel class 2. They are used for braces, suspensions and other fastening systems not subject to dynamic loads and not related to lifting loads. In the household they are used for tying animals, raising well water and making swings. Chain branches consisting of long links have better mobility, but are inferior to their counterparts with short links in strength.
Comparison of short and long link general purpose chain
Preparing a fuel mixture for a chain saw.
Since the majority of chain saws available to consumers are equipped with two-stroke engines that do not provide separate lubrication of rubbing parts, it is very important to prepare the correct fuel mixture during break-in. It is prepared from gasoline and two-stroke engine oil in a certain proportion recommended by the chainsaw manufacturer
What gasoline should I use for the fuel mixture?
The basis is gasoline with an octane rating of at least 90. For Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan and other CIS countries, the optimal fuel option is AI-92. Avoid using questionable fuels, as well as using any additives that increase the octane number. Over time, additives lose their properties, and gasoline becomes of low quality.
Using fuel with a low octane number when running in and operating a chainsaw causes uneven engine operation and knocking. At the same time, there is an increase in engine temperature and an increase in the load on the main bearings. Imaginary savings most often lead to failure of the cylinder-piston group, requiring significant funds to restore it.
New chainsaw owners often have a question about what kind of gasoline to pour into the tool tank: leaded or unleaded? Leaded fuel is used to start an engine without a catalyst. If your saw has a catalyst (green gas tank cap), then use unleaded fuel.
What oil should I use in the fuel mixture, and in what proportions?
Two-stroke engine oil is used both for break-in and for continuous operation of the chainsaw. If you don’t want to take risks and experiment, then purchase the lubricant recommended by the tool manufacturers. As a rule, large companies produce fuel and lubricants for them to order. This allows the manufacturer of chain saws and other gas-powered tools to guarantee proper starting and trouble-free operation of their products.
Since branded oils for chainsaws Husqvarna, Stihl, Partner, Oregon, Jonsered are bottled from the same barrel, you can break in the tool with any of the following
In this case, it is very important to take into account the recommendations both in the instructions for oils and the recommendations of chain saw manufacturers. When using branded fuels and lubricants, when preparing the fuel mixture, follow the operating instructions for the gas-powered tool
| Recommended proportions of fuels and lubricants when preparing fuel | |||
| Break-in chainsaw | Proportion | Gasoline, (liters) | Oil, (liters) |
| Husqvarna up to 1.5 kW | 1:40 | 1 | 0,025 |
| Husqvarna over 1.5 kW | 1:50 | 1 | 0,020 |
| Stihl up to 1.5 kW | 1:40 | 1 | 0,025 |
| Stihl over 1.5 kW | 1:50 | 1 | 0,020 |
| Partner | 1:40 | 1 | 0,025 |
| Partner | 1:33 | 1 | 0,030 |
If branded oils are not available, you can break in a new chainsaw using third-party lubricants of the JASOFB or ISOEGB class. According to the instructions, the ratio of components is taken at the rate of 1:33. At the same time, the tool manufacturer does not recommend using four-stroke motor oils or two-stroke motor oils for water-cooled outboard engines, labeled as TCW.
The fuel mixture for a chainsaw to be run in should be prepared in a clean container intended for storing fuel and lubricants.
- Pour half the required gasoline into the container;
- Add required amount of oil;
- Gently mix the ingredients;
- Pour in the remaining gasoline and stir.
Load and traction chains of normal strength
These are products with quality classes 2, 2.5, 3.5, 5, 7, 8, with a minimum breaking load voltage of 240 to 800 N/mm². They are used for the production of chain slings and are used as part of various lifting and transport machines and mechanisms. With their help, large and heavy loads are secured in water and land transport. They are used primarily with blocks and winches for tying, suspending, lifting and holding loads; traction - for moving loads. Manufactured according to GOST 2319 or TU (manufacturer’s internal standards).
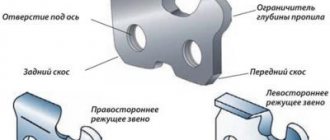
How are saw chains classified?
The quality and speed of cutting depends on the type of saw chain, location and total number of its constituent links. Manufacturers produce chipper and chisel products, differing in the shape of the cutting tooth.
Chains of the first type are installed on professional and household chainsaws. It got its name from the shape of the cutting element. The word chipper translated from English means “chopping into chips.” Indeed, sickle-shaped cutters, rounded at the top, allow you to cut at high speed. However, such chains are less efficient in operation, since they have an increased contact area between the cutting edge and the wood. They are convenient to sharpen, since a precise angle is not required.
Chisel products (chisel in translation means “chisel”) are more often installed on professional equipment. A sharper angle of attack of the working tooth allows you to cut more aggressively into the wood, which increases the productivity of the saw, but reduces the cutting speed. When sharpening them, it is necessary to clearly indicate the correct angle.
Saw parts for chainsaws are also classified by purpose. For cutting down trees and bucking trunks, a transverse chain is used, the sharpening angle of the cutting edge of which ranges from 5 to 15 ̊. To cut along the fibers, you need longitudinal chains, which must be sharpened at an angle of 25 to 30 ̊. The harder the wood, the sharper it is sharpened with a file or machine.
Heavy Duty Lifting Chains
This group includes high-strength hardened chains of class T(8) with a tensile strength at a breaking load of 800 N/mm² and higher. They are made from a round steel bar with a cross-sectional diameter from 4 to 20 mm from high-alloy steel. The place where the rings meet is welded by electric welding and treated to remove burrs. Finished products are high temperature hardened to improve load capacity, fatigue strength, resistance to abrasive materials and excessive friction. The calibration of each link guarantees high accuracy of shapes and sizes and allows them to be used for work on the sprockets of lifting and traction devices. Technical requirements for them are established by GOST 30188-97 and GOST 25996 (for mining equipment).
Standards defining the dimensions of drive roller chains
To standardize the sizes of chains in different regions and countries, their own Standards have been developed, which regulate the parameters and characteristics of not only drive chains, but also other types, as well as sprockets for them. The lack of a single global Standard, as well as the import of equipment and machinery, imposes a number of difficulties in selecting chains by size.
The most well-known standards: GOST (GOST 13568-97 - Russian standard for drive chains, also used in the CIS countries), ISO, DIN (ISO 606, DIN 8187, DIN 8188 - standard used in European countries), ANSI (ANSI B29. 1M is the standard used in the USA). All standards describe the types, parameters and sizes of chains, features of choosing chain pitches and their markings, steel grades, as well as many other issues. The main issue remains the size range of chains and their compliance in different Standards (chain analogues).
Since the first standards for roller chains were created in the inch system, a number of chain sizes correspond to fractions of an inch, and only then it is converted to the international metric system and indicated in millimeters.
Decorative chains
This group of products amazes with the variety of shapes, sizes, colors and materials used, which suggests many options for their application. Thanks to various coatings, they perfectly imitate non-ferrous and precious metals, which allows you to realize any creative idea in interior design and landscape design. Decorative chains are often used by designers of costume jewelry, clothing and haberdashery. Plastic chains with links in bright signal colors are used for zoning public spaces, parking lots, and sports fields.
Most common sizes
When choosing a bike, 3 main quantities are taken into account, the values of which indicate the differences between bicycle chains.
- Distance between pins (step).
There is no need to measure the indicator yourself, because according to GOST, on all modern two-wheeled vehicles the standard pitch is 12.7 mm (1/2”).
- Chain width.
The standard is determined by measuring between the internal planes of the plates. The most common width sizes (mm):
- one speed - 8.7-11;
- 7 speed cassettes - 7.3;
- 11 stars in the cassette - 5.5.
The higher the number of gears, the smaller the distance between the sprockets and the width of the bicycle chain.
- Length.
To complete a bicycle transmission, chains of 110-118 links are most often made. For a 12-speed cassette, the figure increases to 126 links. The value is related to the type of bicycle. For example, regular mountain models will require 106-108 links; for new niners - 112. The working length can be determined independently.
For Double or Triple system:
- open the lock (squeeze one link with your hands towards the other, rocking from side to side);
- without extending the chain through the switches, put it on the largest sprocket at the front and rear;
- connect in a vicious circle, adding 1-1.5 links.
This measurement is relevant if the bike has 2 or 3 sprockets.
If a single chainring system is installed (one star at the front and 9-11 at the rear), the chain length is increased by 2 links.
Classification of welded round link chains
Depending on the ratio of pitch to gauge, chains are divided into:
- short link (type A)
- long-link (type B)
When choosing a chain for a particular application, consumers often ask the question: - “What is the difference between a short-link and a long-link chain, other than the obvious size of the links?”
The short link design (P/d < 3.5) makes the chain easier to handle and less likely to tangle when placed in a storage container, but is not as flexible as a long link chain. Its main advantage is in terms of strength: with the same caliber, a chain with a short link can withstand greater loads than with a long link. It is more difficult to damage when tightening at sharp angles. Short links fit more tightly to the gripping hooks, so there is less risk of them coming off.
The design of long links (P/d ≥ 3.5) has a large degree of freedom in all directions and is better suited for fastening, extending, and shortening. It is easy to make a loop out of it by threading a link into a link. But its main advantage over the short-link one is its lower weight and price, since there are fewer rings per meter.
Conclusion:
The type of chain must be selected depending on the tasks assigned to it. If mobility and weight are less important criteria than strength, then you should opt for a short link. In lifting mechanisms with blocks and drums, only short-link chains are used to operate in order to prevent the occurrence of a large bending moment.
Important:
When purchasing, make sure that the internal dimensions of the link are sufficient to thread a hook or other connecting elements (clips, rings, carabiners, eyelets, etc.) through it.
According to the accuracy of execution, round link chains are divided into:
- calibrated (version 1)
- uncalibrated (version 2)
Recommendations for extending service life
The approximate service life of a branded tire is equal to the total service life of 3 high-quality saw chains; the drive sprocket varies depending on its condition. Experts recommend using a set of several circuits.
The main factors for early tire failure:
- excessive chain tension or discrepancy between its pitch and the characteristics of the drive sprocket crown, which initiates the rapid development of the groove and shanks;
- applying significant force when sawing hard or frozen wood;
- the tire heats up and wears out intensively due to lack of lubricant supply, due to a malfunction or incorrect adjustment of the standard oil pump;
- saving money on the use of low-quality chain oil or oil surrogates such as waste.
Forced consumption of the saw set resource occurs when soil or sand gets into it, or when a new chain operates on a worn drive sprocket.
Additionally: Chainsaw MAKITA EA3202S40B, owner reviews
How do calibrated chains differ from uncalibrated ones?
The calibrated chain is made of round calibrated steel and has high precision within a given tight tolerance for pitch, section diameter, link width, external and internal length. The maximum deviation from the regulated dimensions is ±3%. Calibrated chains after heat treatment are necessarily subjected to stretching by a calibration load to obtain the specified maximum deviations of the pitch and length of the segment.
Uncalibrated chains have a normalized maximum deviation of ±10%, therefore they are designed to work on smooth drums or in static fastening systems.
Where are calibrated chains used?
The calibrated chain is used as a flexible lifting and traction element for chain conveyors, elevators, winches, hoists and other mechanisms that have toothed drums or sprocket chain blocks. It operates as part of bucket conveyors, lifting equipment, traction and lifting mechanisms with manual and mechanical drive. Sprockets or drums are typically designed and manufactured to ensure compatibility with the specified chain size and calibration for optimal engagement.
Note:
Both types of chains can be used as cargo chains.
Design and elements of the drive roller chain
A distinctive feature of the roller chain design , which makes it a separate type of drive chain, is the presence of rollers that reduce friction between the chain and the sprocket . This made it possible to increase the efficiency of this type of drive chains.
The design of the drive roller chain is based on a basic chain consisting of two types of sequentially alternating links: internal and external. The dimensions of the links along the length are selected to ensure uniform pitch of the drive chain. The connection is made by a connecting or transition link.
The main elements of a roller chain are plates (inner and outer for the inner and outer links, respectively), a roller or pin connecting the links, a bushing and a roller, which allow the chain to slide.
Thanks to its design, the roller chain has greater wear resistance under high loads and is also more resistant to contamination. The disadvantage of the design is the greater weight due to the additional element - the roller.
How to choose a chain that will not bind or slip on sprockets?
It's not enough to get the gauge and pitch right, it's important that the chain is calibrated to tight tolerances, otherwise it will "bounce" under load. When the link pitch has deviations from tolerances of more than 3%, this is difficult to determine visually, but is easily confirmed during practical tests. The problem of slipping or binding usually occurs after the chain has gone through a few revolutions under load.
How to check chain calibration?
If you are selecting a calibrated chain for your anchor winch and are unsure about the quality of the calibration, there is an easy way to check that it meets the tolerance limits and your winch drum.
To do this, you need to buy a meter-long piece of chain branch and measure the length of 11 links. Why exactly 11 links? – because this is the generally accepted standard length. Use a ruler to determine the distance from the inside of the first link to the inside of the last link. When doing this, make sure that the chain is tensioned to ensure an accurate measurement.
Important!
The maximum pitch deviation for a calibrated chain should not exceed ±3% of the regulated value!
Table 1. Normal measurement results of a calibrated short link chain DIN 766
| Caliber, mm | Pitch, mm | Length 11 links, mm |
| 6 | 18,5 | 203,5 |
| 7 | 22 | 242 |
| 8 | 24 | 264 |
| 10 | 28 | 308 |
| 12 | 36 | 396 |
| 13 | 36 | 396 |
Advice:
For European-made anchor winches, choose calibrated DIN 766 short-link chains, as they are fully compatible with the drums installed on them.
Varieties and main differences
A chain with a guide bar is replaceable equipment, which means, for example, when deciding which chain for a budget-class Stihl chainsaw is better, you can also consider carved elements of a different class. In other words, owners of budget gasoline chainsaws can choose a durable saw kit for their tool that is more wear-resistant.
When trying to figure out which chains are best for a chainsaw, you can rely on reviews from owners of different power units. You can do it differently by turning to specialists for professional advice. It is possible to make the right choice, focusing on the rating and characteristics of the replacement equipment. To select the ideal components that do not reduce the performance of the tool and cause its malfunctions, take into account a number of criteria, according to which the carved element differs:
- the quality of the material from which the chain is made;
- chain length;
- chain pitch;
- thickness of the replacement headset;
- groove features;
- features of the links (there are two types in total).
In a number of characteristics, branded and budget chains differ significantly. Nevertheless, some operators of fairly powerful budget gasoline saws manage to combine the unit with a perfect saw set produced by the companies Oregon, Husqvarna, Shtil. If you believe unofficial data, recently the Hammer and Power Sharp models have taken leading positions in consumer demand ratings for such products.
The higher the price range, the greater the likelihood that a branded chain will compensate for the technical imperfections of the tool by improving work results even when performing complex sawing work, due to an increased repair life, and due to the stability of a number of operational characteristics.
Evaluation of the strength of round link chains
In the product characteristics, manufacturers indicate three types of load. Maximum operating loads are based on routine testing and should never exceed the operating load ratings suggested by the chain manufacturer, individual specifications, or testing agency for the size and grade of chain being considered.
Working load (carrying capacity) is the maximum load to which a product can be subjected during operation. It is the breaking load divided by the safety factor. This coefficient varies from 3 to 8 depending on the purpose of the chain and the manufacturer. It is usually equal to 4, in which case the working load is a quarter of the breaking load.
The proof load is the reference tensile test load with which the specimen was loaded at the factory during the testing procedure. Typically, it is twice the maximum working load, which is half the breaking load. This is a very important test to prove that each link has been welded to perfection.
The breaking load is the tensile strength that is 4 times the working load limit. The standards require a certain level of breaking load for each size, gauge and grade of chain. For some manufacturers it may exceed the minimum standard, which is reflected in the test certificate.
Example of circuit calculation:
When choosing a welded round link chain for the lifting mechanism, a simple calculation is performed based on the given load and safety factor.
For example:
For a manually driven hoist, it is necessary to select the size of the calibrated chain. Estimated maximum working load: S = 12 kN (1200 kgf).
In accordance with Gostekhnadzor standards, we accept a safety factor of 4.5:1.
We calculate the breaking load using the formula P = 4.5 x 12 kN = 54 kN (5400 kgf)
.
According to Table 2 (source: GOST 2319-81), we select a short-link calibrated chain of size 13x36 mm, for which the tensile strength is 66 kN (6600 kgf).
Table 2. Dimensions and loads on load and traction chains, type A, version 1
| Caliber, d mm | Pitch, p mm | Width, b mm | Prev. deviation section length l=11p | Load, kN | ||||
| nominal | pre-deviation | nominal | pre-deviation | nominal | pre-deviation | trial | destructive | |
| 5 | ±0,4 | 18,5 | ±0,5 | 17 | ±0,5 | +1,5 -0,5 | 5,0 | 10,0 |
| 6 | 18,5 (19) | 20 (21) | ±0,6 | 7,0 | 14,0 | |||
| 7 | 22 | 23 | ±0,7 | 9,0 | 18,0 | |||
| 8 | 23 (24) | ±0,6 | 26 (27) | ±0,8 | 13,0 | 26,0 | ||
| 9 | ±0,5 | 27 | 32 | ±0,9 | +2,5 -0,8 | 16,0 | 32,0 | |
| 9,5 | 27 | 31 | ±1,0 | 17,0 | 34,0 | |||
| 10 | 28 | 34 | ±1,1 | 20,0 | 40,0 | |||
| 11 | 31 | ±1,0 | 36 | ±1,3 | 23,0 | 46,0 | ||
| 13 | 36 | 44 (43) | ±1,6 | +3,8 -1,3 | 33,0 | 66,0 | ||
| 16 | ±0,8 | 45 (44 | 53 (54) | ±1,8 | 51,0 | 102,0 | ||
| 18 | 50 | 60 | ±2,0 | 63,0 | 126,0 | |||
| 20 | 56 | ±1,5 | 67 | ±2,3 | +5,5 -1,8 | 80,0 | 160,0 | |
| 23 | ±1,0 | 64 | 77 | ±2,6 | 100,0 | 200,0 | ||
| 26 | 73 | ±2,0 | 87 | — | — | 126,0 | 252,0 | |
| 28 | 78 | — | 94 | — | — | 150,0 | 300,0 | |
| 30 | 84 | — | 101 | — | — | 170,0 | 340,0 | |
| 33 | ±1,5 | 92 | — | 112 | — | — | 200,0 | 400,0 |
| 36 | 101 | — | 122 | — | — | 250,0 | 500,0 | |
| 39 | 109 | — | 132 | — | — | 280,0 | 560,0 | |
| 42 | 118 | — | 142 | — | — | 340,0 | 680,0 | |
Thickness of link components (tails)
The main part of the load falls on this element of the chainsaw. To measure the thickness of the connecting elements of the chain included in the tire, use a caliper.
Let's list the standard indicators:
- 1.1-1.3 mm - more often found in products for infrequent home use and gentle operation. This tail thickness is suitable for light loads.
- 1.5mm is the most common option found in household saws, but is not suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- 1.6-2.0 mm is an option for complex work. This width of tails is found in professional saws, the elements of which are made of special steel.
What is the chain quality class?
Quality class is a characteristic that allows you to evaluate the strength of a chain. It depends on the mechanical characteristics of the finished product, and not on the ultimate strength of the alloy used for its manufacture. The quality class is usually designated by numbers from 2 to 12. Some standards, for example, GOST 29996-97, establish a letter designation of the class - B, C, D.
Chains of normal strength (load, traction and general purpose), depending on the mechanical properties, have the corresponding quality class - 2; 2.5; 3; 3.5; 5; 7, and high-strength (load-lifting) classes 8, 10, 12 (T8, T10, T12).
Table 3. Strength indicators for chains of different quality classes
| Quality class | 2 | 2,5 | 3,5 | 5 | B | 7 | 8 (C) | 10 (D) |
| Tension at test load, N/mm | 75-120 | 120 | 240 | 315 | 500 | 600 | 640 | 800 |
| Stress at breaking load, N/mm | 150-240 | 240 | 360 | 500 | 630 | 750 | 800 | 1000 |
With the same nominal diameter of the links, the load capacity of a chain of quality class 8 is 50% higher than the load capacity of chains of quality class 5, and class 10 is 25% higher than that of products of quality class 8. Accordingly, the load capacity of class 12 is 25% higher than that of class 10.
The use of high-strength chains in lifting and rigging operations reduces the weight of chain slings. With equal load capacity, the weight of a chain of quality class 8 is 30% of the weight of class 3. The higher the quality class, the higher the surface hardness of the bows and the higher the wear resistance and susceptibility to damage from sharp edges.
Correspondence between engine power and the distance between the cutting teeth of the chainsaw chain
Based on data obtained experimentally, it is recommended to select a chainsaw by considering the ratio of drive power and the distance between the cutting edges. It is known that the higher the pitch, the more force must be applied to rotate the drive sprocket and the greater must be the maximum torque developed by a gasoline engine.
To select the correct tool configuration, it is necessary to use the minimum power data for each of the three typical chain pitches.
Critical power indicators of gasoline engines rotating the drive:
Chain pitch value.
- step 0.325” – power of at least 1.8 hp. (1.47 kW);
- 3/8” pitch – power of at least 3 hp. (2.21 kW);
- pitch 0.404” – power of at least 4.5 hp. (3.31 kW).
If the power of the driving motor is less than the specified values, then during the cutting process the following phenomena are possible: jamming of the chain in the tree, a decrease in the rotation speed of the drive, leading to overheating of the motor, increased cutting time and increased operating costs for fuel.
The use of powerful motors with a small pitch chain is not advisable, as this will also increase the time for dissolution and increase fuel costs. However, this combination is allowed if there is a need to perform precise work with wood.
The indicated minimum values of the drive characteristics indicate the ability of the equipment to operate reliably, but do not indicate the time of its continuous use in a professional environment. Rather, these values are given as recommendations for occasional work or for operating conditions where the tool is used for long periods of time. For long-term use of the equipment, which involves professional mode, the following technical data are required:
- step 0.325” – power 2.5 hp (1.84 kW);
- 3/8” pitch – 4 hp power. (2.94 kW);
- pitch 0.404” – power 6 hp. (4.41 kW).
And if, for example, it will be used occasionally or for summer cottage work, then such a choice is inappropriate.
What chains are used on car tires?
To ensure vehicle stability when driving on ice, loose soils and snowy winter roads, snow chains are used. These are ready-made chain products that fit onto car wheels and allow you to easily overcome even the most impassable areas. For their manufacture, high-strength hardened galvanized steel is used, which guarantees special resistance to abrasion, reliability and durability.
The range of snow chains covers almost all possible wheel sizes. A special chain tread pattern such as “ladder”, “diamond” or “honeycomb” provides optimal traction and comfortable movement.
Preparatory work
In the package version of making a knife from a chain, the product is suitable for various mechanisms: a motorcycle, a car, a bicycle or a chainsaw. Having decided on the manufacturing method, you need to prepare the tools and materials:
- an anvil, two hammers - large and small;
- oven or forge;
- vices, angle grinders with discs for various purposes;
- tetraboric acid (borax);
- Hydraulic Press;
- grinding machine;
- welding machine, steel chain;
- high carbon steel plate;
- motor oil and a container of water;
- drill, wooden block, epoxy glue;
- masking tape, sandpaper of different grains;
- Handle impregnation made from natural oils.
Knife from a chain. Tools and materials are professional in nature. From the very beginning it was stated that this was a job for experienced craftsmen. Beginners should not try this material. You need to start experimenting with simple preparations.
Instructions for making a knife from a chain
A distinctive feature of the batch forging process is the work with several metal plates. Having everything you need, you need to start the initial forging of the blade:
- Using a cutting wheel on an angle grinder, cut the chain into several pieces of equal length. Having folded them into a single form, using welding, we “grab” them to obtain a solid workpiece.
- A rod is welded to the resulting rectangle for ease of holding. Having warmed up the oven, place the workpiece in it and heat it to 1100-1200 °C.
- Once the metal has reached a bright red hue, remove it and sprinkle it generously with borax. This will allow you to more reliably fasten the pieces of the chain together and get rid of voids in the links. Place in the oven for further heating.
- We take it out again, sprinkle it with borax and quickly move to the press. With its help, we gradually compress the workpiece from all sides. We monitor the temperature; when the part has cooled down, go back into the oven. The process performed by the press will help get rid of voids in the workpiece and forge weld it into a monolith.
- After making sure that the welding is sufficient, use a large hammer to flatten the workpiece into one plate. Cool the product in air, cut off the rod using an angle grinder. And with the same tool we halve the plate.
- Between the resulting halves we lay carbon steel, sprinkling the layers with brown. We carefully “grab” it with welding and return the rod to its place. Place in the oven and heat until bright red. Having taken out the plates, we forge them with a large hammer. The plates must be welded together using the forging method.
Knives from a chainsaw chain.
How to choose chains for wheels?
On finished chain treads, manufacturers indicate the tire size and the type of vehicle for which they are intended. For those who plan to make wheel chains with their own hands, we recommend using the following gauge and link pitch:
- for passenger cars: 3.5x12 mm
- crossovers, SUVs, commercial vehicles: 4.5x16 mm
- trucks, buses and special equipment: 7x24 mm
Chain consumption depends on the wheel diameter, tread width and tire profile height, as well as the selected pattern. For example, to “shoe” two wheels of a passenger car into lugs with a “ladder” pattern, it will take approximately 15 meters.
How to choose an anti-theft chain for a bicycle or motorcycle?
One of the most reliable ways to protect an unattended motorcycle or bicycle from theft is a chain bike lock. It's easy to make yourself. To do this, you will need a length of chain and a padlock (with a key or combination). Don't look for an old chain in the garage or buy it at a hardware store. For an anti-theft chain lock, you need not a household chain, but a high-strength hardened chain.
The anti-theft chain is made of thermally hardened steel and has an increased strength class of T-8. It is difficult to cut and almost impossible to cut even with a powerful bolt cutter. And not every thief carries hydraulic shears or a grinder in his pocket. The chain links are firmly welded, so they cannot be bent with wrenches. WITH
Even experienced hijackers will have to tinker with such a chain, and this will give you time or the attacker will look for another, less protected candidate for theft.
Saw chain lubrication system
The reliability and efficiency of the latter directly depends on the quality of lubrication of the chain and chain saw bar. In order to ensure normal operation of the tool, manufacturers supply it with an oil pump, which supplies oil to the cutting system through special holes. The chain itself is responsible for the uniform distribution of oil - its shanks, passing through the sprocket, capture the lubricant, which, as a result of the movement of the headset, spreads over it and the saw bar. Often, to increase the efficiency of lubrication, special channels are made in the drive links using a milling cutter or drill, and additional recesses are made in the connecting links.
The chain saw's lubrication system works to reduce the destructive effect of friction and, of course, heating. This significantly increases the service life of both the chain set and the tool as a whole. Therefore, the user must control the lubrication process. If, when the chain accelerates, there is no oil trace on the cutting line, this means that the saw is overheating, and the chain itself can quickly become dull, or even burst.
In order to increase the lubrication effect, global manufacturers produce saw oils on an organic basis. They cost a little more, but provide a quarter of the consumption, and when released into the environment, they self-decompose within a few hours.
Connection types
To facilitate installation and dismantling of the chain, connecting locks are used. The part is made up of two folding plates. A metal rod (pin) is pressed into one of the sides. Manufacturers produce models with different types of connections. For example, SRAM Power Link and KMS produce bikes with a connecting lock. Shimano and Campagnolo make chains without a connecting link. Locks for single-speed and multi-speed chains are distinguished by the locking method. Thus, in multi-speed rivets are “built-in” into the structure and do not protrude above the side plates. Modern inventors are trying to install seals on connections that resemble a motorcycle device.
How does a digital caliper work?
There are three modifications of calipers, they are divided according to the method of taking dimensions.
- The simplest vernier models can be used for home needs. Integer values are taken from the bar, the fractions are determined by the vernier - these are the basic rules for how to use a vernier caliper.
- The mechanical measuring principle is used in dial models. Through a gear transmission, fractions of a millimeter are transferred from the rod scale to the dial, and whole values are taken from the rod.
- The most convenient and accurate is the digital option, where all results are obtained from the display screen. The electronic part itself can be customized, making it even more convenient to use.
To understand how to use it, you need to understand how a digital caliper works. The work is based on a digital capacitive vernier: inside the device there is a capacitive matrix, several plates, the main ones being the stator and the slider. When taking calculations, they are displayed on the display, the stator is located on a mechanical ruler, and the rotor is located under the display itself.
How to use a caliper?
Before use, you should always check the caliper visually and evaluate its mechanical condition. If the moving parts are skewed, there are nicks or obvious scratches with rusty areas, this device cannot be used. The readings will be inaccurate. Before measuring anything with a caliper, you need to look at the location of the parts: the ends of the rod with the ruler must coincide after aligning the jaws. The scale itself must remain clean, all numbers on it must be clearly visible.
How to use a caliper and how to check the accuracy of the device?
The question of how to use a caliper is relevant for every home craftsman, because this measuring device helps out in almost any situation. With its help, you can determine the main dimensions of all parts and select the one you need based on the measurements taken. Proper care of the device will ensure longevity and accuracy in operation.
What does a caliper look like?
Universal and irreplaceable, tested by more than one generation of home craftsmen, the metric device looks a little like a hammer crossed with a ruler. Before choosing a caliper, you should know the following: there are several modifications, but they all consist of the same set of design features.
- A rod or measuring ruler with a marking scale on it. The standard length is 150 mm, which also determines the maximum measurement value. For measurements with larger values, there are special calipers with a longer measuring ruler.
- The moving part of the caliper is the measuring frame. It moves along the measuring ruler. Due to the spring inside, the frame is pressed tightly against the rod, and a special screw fixes it in the desired position. On the frame itself there is a vernier scale; tenths and hundredths of a millimeter are determined on it.
- The fixed jaws of the caliper are rigidly fixed to the rod. This part is intended for determining external dimensions; its working surface is located inside.
- Movable jaws are located on the other side of the rod and are designed to measure the internal size. The working surface is located outside.
- A retractable bar is rigidly connected to the moving frame, with the help of which the depth is determined.